 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
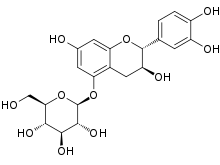
(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,7-dihydroxydihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-5-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Other names
Catechin 5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside C5G[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24O11 | |
| Molar mass | 452.412 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Catechin 5-O-glucoside is a flavanol glucoside. It can be found in rhubarb and in the bark of Rhaphiolepis umbellata.[2] It can also be formed from (+)-catechin by plant-cultured cells of Eucalyptus perriniana.[3]
References
- ↑ Catechin glucosides: occurrence, synthesis, and stability. Raab T, Barron D, Vera FA, Crespy V, Oliveira M and Williamson G, J Agric Food Chem., 2010 Feb 24, 58(4), pages 2138-2149, doi:10.1021/jf9034095
- ↑ Flavanol glucosides from rhubarb and Rhaphiolepis umbellata. Gen-Ichiro Nonaka, Emiko Ezakia, Katsuya Hayashia and Itsuo Nishioka, Phytochemistry, Volume 22, Issue 7, 1983, Pages 1659–1661, doi:10.1016/0031-9422(83)80105-8
- ↑ Biotransformation of (+)-catechin by plant-cultured cells of Eucalyptus perriniana. Shuichi Otani, Yoko Kondo, Yoshihisa Asada, Tsutomu Furuya, Hatsuyuki, Hamada, Nobuyoshi Nakajima, Kohji Ishihara and Hiroki Hamada, Plant Biotechnology, 2004, 21(5), pages 407–409 (article Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.