 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Truqap |
| Other names | AZD-5363 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Truqap |
| MedlinePlus | a623056 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Threonine kinase inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.066 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
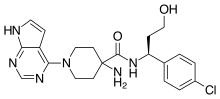
| Formula | C21H25ClN6O2 |
| Molar mass | 428.92 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Capivasertib, sold under the brand name Truqap, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of breast cancer.[1][2] It is taken by mouth.[1]
The most common adverse reactions include diarrhea, cutaneous adverse reactions, increased random glucose, decreased lymphocytes, decreased hemoglobin, increased fasting glucose, nausea, fatigue, decreased leukocytes, increased triglycerides, decreased neutrophils, increased creatinine, vomiting, and stomatitis.[3]
In November 2023, capivasertib was approved in the United States for people with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer when used in combination with fulvestrant.[3][4][5] The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[6]
Medical uses
Capivasertib, used in combination with fulvestrant (Faslodex), is indicated for adults with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer with one or more PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-alterations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, following progression on at least one endocrine-based regimen in the metastatic setting or recurrence on or within twelve months of completing adjuvant therapy.[1][3]
History
Efficacy was evaluated in CAPItello-291 (NCT04305496), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial in 708 participants with locally advanced or metastatic HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, of which 289 participants had tumors with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-alterations.[3] All participants were required to have progression on aromatase inhibitor-based treatment.[3] Participants could have received up to two prior lines of endocrine therapy and up to one line of chemotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic disease.[3]
Society and culture
Legal status
Capivasertib was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2023.[3] The FDA granted the application for capivasertib fast track designation.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Truqap- capivasertib tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 16 November 2023. Archived from the original on 20 November 2023. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ↑ Turner NC, Oliveira M, Howell SJ, Dalenc F, Cortes J, Gomez Moreno HL, et al. (June 2023). "Capivasertib in Hormone Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer". New England Journal of Medicine. 388 (22): 2058–2070. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2214131. PMID 37256976. S2CID 259002400.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "FDA approves capivasertib with fulvestrant for breast cancer". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 16 November 2023. Archived from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Oncology (Cancer) / Hematologic Malignancies Approval Notifications". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 16 November 2023. Archived from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- ↑ "Truqap (capivasertib) plus Faslodex approved in the US for patients with advanced HR-positive breast cancer". AstraZeneca (Press release). 17 November 2023. Archived from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- 1 2 New Drug Therapy Approvals 2023 (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Report). January 2024. Archived from the original on 10 January 2024. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
External links
- Clinical trial number NCT04305496 for "Capivasertib+Fulvestrant vs Placebo+Fulvestrant as Treatment for Locally Advanced (Inoperable) or Metastatic HR+/HER2- Breast Cancer (CAPItello-291)" at ClinicalTrials.gov