| Lemon-scented boronia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Boronia citriodora on Needle Rock | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Rutaceae |
| Genus: | Boronia |
| Species: | B. citriodora |
| Binomial name | |
| Boronia citriodora | |
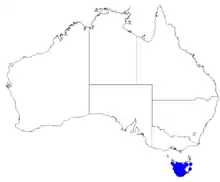 | |
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium | |
Boronia citriodora, commonly known as lemon-scented boronia,[2] lemon plant or lemon thyme,[3][4] is a woody shrub that is endemic to Tasmania. It has pinnate leaves and white to pink flowers that are arranged singly or in groups of up to seven, in the leaf axils or on the ends of the branches.

Description
Boronia citriodora is a woody shrub that is sometimes prostrate, otherwise erect and growing to a height of 3 m (9.8 ft). It has pinnate leaves that are 7–25 mm (0.28–0.98 in) long and 7–30 mm (0.28–1.2 in) wide in outline with between three and nine leaflets, on a petiole 1.5–6 mm (0.059–0.24 in) long. The end leaflet is narrow elliptic to narrow lance-shaped, 3.5–15 mm (0.14–0.59 in) long and 0.5–4 mm (0.020–0.16 in) wide. The side leaflets are similar but longer. The flowers are white to pink and are arranged singly or in groups of up to seven in leaf axils or on the ends of branches on a stalk 1–8 mm (0.039–0.31 in) long. The four sepals are triangular, 0.5–2.5 mm (0.02–0.1 in) long and wide. The four petals are 3.5–8.5 mm (0.1–0.3 in) long and the eight stamens have a few short hairs. Flowering occurs from November to February and the mature fruit are smooth, 3–4 mm (0.12–0.16 in) long and 1.5–2 mm (0.059–0.079 in) wide.[5][4]
Taxonomy and naming
Boronia citriodora was first formally described in 1855 by Joseph Dalton Hooker from an unpublished description by Ronald Campbell Gunn and the description was published in The botany of the Antarctic voyage of H.M. Discovery ships Erebus and Terror.[6][7] The name is derived from the characteristic lemon scent of the foliage. Hooker noted that the plant has a "strong and delicious smell of lemons" and that the species was called the 'lemon-plant' by early Tasmanian colonists.[5][7]
In 2003, Marco Duretto described three subspecies:[5]
- Boronia citriodora subsp. citriodora that has smooth sepals and leaves less than 15 mm (0.59 in) long;
- Boronia citriodora subsp. orientalis that has hairy sepals;
- Boronia citriodora subsp. paulwilsonii that has smooth sepals and at least some leaves more than 15 mm (0.59 in) long.
Distribution and habitat
Lemon-scented boronia grows in heath, woodland and near rainforest, often in rocky places.[5]
- Subspecies citriodora only grows on the Central Highlands of Tasmania, at altitudes above 900 m (3,000 ft) with disjunct populations further south, including on Mount Field.[8]
- Subspecies orientalis is only known from Ben Lomond and Mount Barrow;
- Subspecies paulwilsonii is only known from the south-west of Tasmania, south from Macquarie Harbour and west from Mount Shea.[5][9]
Use in horticulture
Boronia citriodora is cultivated as an ornamental plant for use in gardens. It tolerates sun, shade, wind, heavy frost; and dry, sandy or waterlogged soils.[10]
References
- ↑ "Boronia citriodora". Australian Plant Census. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ↑ Co, Schimmel &; Leipzig, Schimmel & Co. Aktiengesellschaft, Miltitz bei (1926). Annual Report on Essential Oils, Aromatic Chemicals and Related Materials. Schimmel & Company. Retrieved 5 May 2017.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Boronia citriodora". Atlas of Living Australia. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- 1 2 "Boronia citriodora". Understorey Network Incorporated. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Duretto, Marco F. (2003). "Notes on Boronia (Rutaceae) in eastern and northern Australia" (PDF). Muelleria. 17: 79–83. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- ↑ "Boronia citriodora". APNI. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- 1 2 Hooker, Joseph D. (1860). The botany of the Antarctic voyage of H.M. discovery ships Erebus and Terror in the Years 1839-1843 :under the command of Captain Sir James Clark Ross. London: Lovell Reeve. p. 68. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- ↑ UTas.edu.au: Boronia citriodora
- ↑ "Boronia citriodora". University of Tasmania. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- ↑ "Boronia citriodora". Plant This. Retrieved 27 February 2019.