
The Bornrieth Moor (German: Bornriethmoor) is the remains of a raised bog in the German district of Celle and belongs to the Südheide Nature Park. It has an area of 115 hectares (280 acres). The bog, which has had most of its peat extracted, was reflooded and placed under nature conservation protection in 1988. The moor was also designated as a Special Area of Conservation. The responsible nature conservation authority is the district of Celle. The area is out-of-bounds to the public. Several cranes have turned up here again and are breeding. The otherwise rare bog myrtle (Myrica gale) is common here. Much of the moor is covered by the common reed ('Phragmites'). Bog asphodel (Narthecium ossifragum), cottongrass (Eriophorum) and sundews (Drosera) may also be found here.
History
Salt boiling
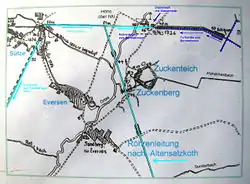
Between 1673 and 1678, boiling houses were built on the edge of the moor for the Sülze Saltworks, because the bogs in the vicinity of Sülze had been exhausted. Two salt houses were constructed here, each with two salt pans and a graduation tower, 200 m long and 7 m high. A boring mill was also built to manufacture water pipes from tree trunks. Peat was delivered by boat along canals excavated for the purpose. The brine was transported in wooden pipes from Sülze. As early as 1719 the first discussions were held about moving the boiling sites again because Bornrieth Moor had been exhausted. In 1723 the new pipeline to the Scheuer Bruch was ready and in 1725 brine was boiled in the newly established village of Altensalzkoth.
Dummy airfield
In the Second World War a dummy airfield was laid out on the moor. This was intended to simulate the nearby airfield at Faßberg and divert attention away from it.

