Antarafacial (Woodward-Hoffmann symbol a) and suprafacial (s) are two topological concepts in organic chemistry describing the relationship between two simultaneous chemical bond making and/or bond breaking processes in or around a reaction center.[1] The reaction center can be a p- or spn-orbital (Woodward-Hoffmann symbol ω), a conjugated system (π) or even a sigma bond (σ).
- The relationship is antarafacial when opposite faces of the π system or isolated orbital are involved in the process (think anti). For a σ bond, it corresponds to involvement of one "interior" lobe and one "exterior" lobe of the bond.
- The relationship is suprafacial when the same face of the π system or isolated orbital are involved in the process (think syn). For a σ bond, it corresponds to involvement of two "interior" lobes or two "exterior" lobes of the bond.
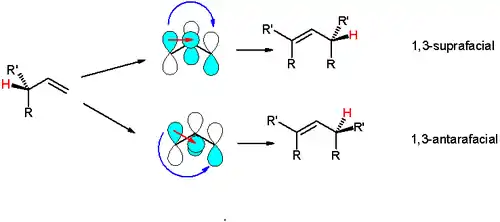
The components of all pericyclic reactions, including sigmatropic reactions and cycloadditions, and electrocyclizations, can be classified as either suprafacial or antarafacial, and this determines the stereochemistry. In particular, antarafacial topology corresponds to inversion of configuration for the carbon atom of a [1, n]-sigmatropic rearrangement, and conrotation for electrocyclic ring closure, while suprafacial corresponds to retention and disrotation.
An example is the [1,3]-hydride shift, in which the interacting frontier orbitals are the allyl free radical and the hydrogen 1s orbitals. The suprafacial shift is symmetry-forbidden because orbitals with opposite algebraic signs overlap. The symmetry allowed antarafacial shift would require a strained transition state and is also unlikely. In contrast a symmetry allowed and suprafacial [1,5]-hydride shift is a common event.[2]
References