| Adelophryne patamona | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Eleutherodactylidae |
| Genus: | Adelophryne |
| Species: | A. patamona |
| Binomial name | |
| Adelophryne patamona MacCulloch, Lathrop, Kok, Minter, Khan, and Barrio-Amorós, 2008[2] | |
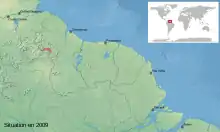 | |
Adelophryne patamona is a species of frog in the family Eleutherodactylidae. It is endemic to the Pacaraima Mountains of southwestern Guyana,[3][4] although it is likely to also occur in the adjacent Roraima state of Brazil.[1][3] It is most closely related to A. gutturosa.[5]
Description
Adult males measure 17–18 mm (0.67–0.71 in) (based on just two individuals) and adult females 21–23 mm (0.83–0.91 in) in snout–vent length. It is the largest species of its genus. The snout is rounded. The tympanum is small and covered by a fold posterodorsally. The skin of the dorsum, venter, and limbs is smooth but has scattered small tubercles. The flanks and rear of the thighs are areolate. The front toes are flattened, unwebbed, and have small pointed discs at their tips. The back toes are also flattened, unwebbed, and have small narrow discs at their tips. Colouration is variable; the colour of the dorsum, flanks, and dorsal surfaces of limbs is medium brown, and there are black markings. Some specimens are darker and have more pale blue spots and more conspicuous tubercles on dorsum.[2]
The male advertisement call is a group of three soft, unpulsed, whistle-like notes. The first two are short and third one is long, all produced in rapid succession.[2]
Habitat and conservation
Adelophryne patamona is known from medium-cover forests at elevations of 678–1,414 m (2,224–4,639 ft) above sea level (the highest of all Adelophryne species[2]). Specimens have been found amidst leaf litter, among rootlets near the base of trees, and in ground holes covered by leaves. Males call in the afternoon and night, mostly from concealed sites.[1][2]
This species is common in its native range. Human population is sparse in the area. However, gold mining the area could be a threat to its habitat.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2018). "Adelophryne patamona". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T158609A120109053. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T158609A120109053.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 MacCulloch, R.D.; A. Lathrop; P.J.R. Kok; L.R. Minter; S.Z. Khan & C.L. Barrio-Amorós (2008). "A new species of Adelophryne (Anura: Eleutherodactylidae) from Guyana, with additional data on A. gutturosa". Zootaxa. 1884: 36–50.
- 1 2 Frost, Darrel R. (2021). "Adelophryne patamona MacCulloch, Lathrop, Kok, Minter, Khan, and Barrio-Amoros, 2008". Amphibian Species of the World: An Online Reference. Version 6.1. American Museum of Natural History. doi:10.5531/db.vz.0001. Retrieved 7 March 2021.
- ↑ Cole, C.J.; C.R. Townsend; R.P. Reynolds; R.D. MacCulloch & A. Lathrop. "Amphibians and reptiles of Guyana, South America: Illustrated keys, annotated species accounts, and a biogeographic synopsis". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 125: 317–620. doi:10.2988/0006-324x-125.4.317.
- ↑ Fouquet, Antoine; Loebmann, Daniel; Castroviejo-Fisher, Santiago; Padial, José M.; Orrico, Victor G.D.; Lyra, Mariana L.; Roberto, Igor Joventino; Kok, Philippe J.R.; Haddad, Célio F.B. & Rodrigues, Miguel T. (2012). "From Amazonia to the Atlantic forest: Molecular phylogeny of Phyzelaphryninae frogs reveals unexpected diversity and a striking biogeographic pattern emphasizing conservation challenges". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 65 (2): 547–561. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2012.07.012. PMID 22842094.
