| Abu (Abu Volcano Group) | |
|---|---|
| 阿武火山群 | |
 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 641 m (2,103 ft)[1] |
| Listing | List of volcanoes in Japan |
| Coordinates | 34°30′N 131°36′E / 34.500°N 131.600°E[1] |
| Geography | |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | 800,000 years[1] |
| Mountain type | Monogenetic volcanic field |
| Last eruption | 6850 BCE[1] |
Abu (阿武火山群, Abu Kazan-gun) is the name of a group of shield volcanoes located on the coast of Japan on the southwest end of the island of Honshū. It is primarily based in the city of Hagi, Yamaguchi Prefecture.
The group dates from 800,000 years ago and was active into the Holocene era. The last eruption occurred around 9000 years ago.
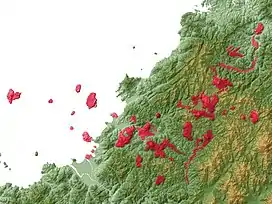
The group of volcanoes consists of basalt and dacitic lava flows, small shield volcanoes, cinder cones, and lava domes. Altogether, there are about 40 volcanoes, with the highest peak being Irao-yama.
Volcanic activity in the region is related to subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate.
The erupted magmas of Abu are mainly alkaline basalt and calc-alkaline andesite - dacite in composition.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Abu". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 2007-04-26.
- ↑ "Abu". www.volcanodiscovery.com. Retrieved 2019-07-07.
External links
- Abu Volcanoes - Japan Meteorological Agency (in Japanese)
- "Abu Volcanoes: National catalogue of the active volcanoes in Japan" (PDF). - Japan Meteorological Agency
- Abu - Smithsonian Institution: Global Volcanism Program
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.