| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
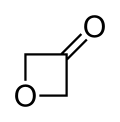
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxetan-3-one | |||
| Other names
1,3-Epoxy-2-propanone 1,3-Epoxypropanone 1,3-Epoxy-2-propan-2-one | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.190.619 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 72.06 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.124 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 53 °C (127 °F; 326 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
3-Oxetanone, also called oxetan-3-one or 1,3-epoxy-2-propanone, is a chemical compound with formula C3H4O2. It is the ketone of oxetane, and an isomer of β-propiolactone.
3-Oxetanone is a liquid at room temperature, that boils at 140 °C. It is a specialty chemical,[1][2] used for research in the synthesis of other oxetanes of pharmacological interest.[3][4] Oxetan-3-one also has been the object of theoretical studies.[5][6]
See also
- Malonic anhydride or oxetane-2,4-dione
- 1,2-dioxetanedione
References
- ↑ Synthonix Corp., 3-Oxetanone Archived 2009-12-16 at the Wayback Machine product sheet. Accessed on 2009-07-10.
- ↑ SpiroChem AG, Oxetan-3-one Archived 2012-03-26 at the Wayback Machine Product Sheet - 2011-07-07
- ↑ Wuitschik, G.; Rogers-Evans, M.; Müller, K.; Fischer, H.; Wagner, B.; Schuler, F.; Polonchuk, L.; Carreira, E. M., Oxetanes as promising modules in drug discovery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, volume 45, issue 46, pp. 7736-7739. doi:10.1002/anie.200602343
- ↑ Wuitschik, G.; Rogers-Evans, M.; Buckl, A.; Bernasconi, M.; Marki, M.; Godel, T.; Fischer, H.; Wagner, B.; Parrilla, I.; Schuler, F.; Schneider, J.; Alker, A.; Schweizer, W. B.; Muller, K.; Carreira, E. M., Spirocyclic oxetanes: Synthesis and properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, volume 47, issue 24, pp. 4512-4515. doi:10.1002/anie.200800450
- ↑ George M. Breuer, Roger S. Lewis, and Edward K. C. Lee (1975), Unimolecular Decomposition Rates of Cyclobutanone, 3-Oxetanone, and Perfluorocyclobutanone. An RRKM Calculation of Internally Converted Hot Molecules Journal of Physical Chemistry, volume 79, issue 19. doi:10.1021/j100586a001
- ↑ P. C. Martino, P. B. Shevlin and S. D. Worley (1979), The electronics structures of small strained rings. An investigation of the interaction between the oxygen and the π orbitals in 3-methyleneoxetane and 3-oxetanone. Chemical Physics Letters, Volume 68, Issue 1, pp. 237–241. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(79)80109-8
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.