 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
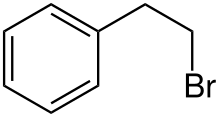
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2-Bromoethyl)benzene | |
| Other names
Phenethyl bromide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.846 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H9Br | |
| Molar mass | 185.064 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.355 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −56 °C (−69 °F; 217 K) |
| Boiling point | 221 °C (430 °F; 494 K) |
| Insoluble in water | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 89 °C (192 °F; 362 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2-Phenylethyl bromide is an organobromide with the formula C6H5CH2CH2Br. It is a colorless liquid, although older samples appear yellow. Analogous to the preparation of most 1-bromoalkanes, it is prepared by free-radical addition of hydrogen bromide to styrene. These conditions lead to anti-Markovnikov addition, giving the 1-bromo derivatives.[1]
Upon reaction with hydrazine, phenelzine is produced.
References
- ↑ Dagani, M. J.; Barda, H. J.; Benya, T. J.; Sanders, D. C. "Bromine Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_405. ISBN 978-3527306732.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.