 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
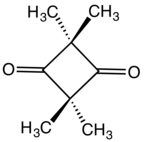
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2,4,4-Tetramethylcyclobutane-1,3-dione | |
| Other names
Tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanedione, Tetramethylcyclobuta-1,3-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.063 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 140.182 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless or white solid |
| Melting point | 112–115 °C (234–239 °F; 385–388 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2,2,4,4-Tetramethylcyclobutanedione is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)4C4O2. The compound is a diketone of cyclobutane, bearing four methyl groups. It is a white solid that is used as a precursor to diverse industrial products.
Synthesis and reactions
2,2,4,4-Tetramethylcyclobutanedione is the head-to-tail dimer of dimethylketene. It arises spontaneously when dimethylketene is produced by dehydrohalogenation of isobutyryl chloride with triethylamine.[1]
The 2,2,4,4-tetramethylcyclobutanedione isomerizes to the lactone called dimethylketene dimer (4-isopropylidene-3,3-dimethyl-2-oxetanone).[2] Dimethylketene dimer is a precursor to various alkyl ketene dimers, which are used in papermaking.
Hydrogenation of 2,2,4,4-tetramethylcyclobutanedione gives 2,2,4,4-tetramethylcyclobutanediol, which is of interest in polymer chemistry.
References
- ↑ R. Huisgen, P. Otto (1968), "The mechanism of dimerization of dimethylketene", J. Am. Chem. Soc., vol. 90, no. 19, pp. 5342–5343, doi:10.1021/ja01021a090
- ↑ R.H. Hasek; R.D. Clark; G.L. Mayberry (1968). "Dimethylketene β-Lactone Dimer". Organic Syntheses. 48: 72. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.048.0072.