| Mark Life Company Prussian Life Company Life Guard Regiment 1st Infantry Regiment | |
|---|---|
| 1. Preußisches Infanterieregiment | |
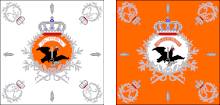 Regimental and Company colours of the 1st Prussian Infantry Regiment | |
| Active | 1615 – 1806 |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Line Infantry |
| Size | Regiment of three battalions |
| Part of | Brandenburg Inspectorate |
| Depot | Berlin, Neumark |
| Motto(s) | Fidem Patriamque Servabo (I Serve My God And My Country) |
| Engagements | |
| Insignia | |
| Prussian national colours | .svg.png.webp) |
The 1st Prussian Infantry Regiment (von Kunheim) (German: 1. Preußisches Infanterieregiment) was a line infantry regiment of the Old Prussian Army which had initially formed part of the Prussian Life Guard, but later transferred to the line. After notably serving in the War of the Austrian Succession and Seven Years' War, the regiment was demolished following the Battle of Auerstadt. A small part of the regiment went on to help form the famed 8th (1st Brandenburg) Life Infantry Regiment, which in turn would serve notably till its disbandment after World War I.[1]
Background
On 21 July 1615, Captain Wilhelm von Kalckumb raised the Mark Life Company (Märkische Leib-Kompagnie) in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. On 1 June 1641, the Prussian Life Company (Preussische Leib-Kompagnie) was raised, and in 1657 these companies merged with four newly raised companies to form the Life Guard Regiment (Leib-Garde Regiment). That year, the first regimental chef was assigned, Oberst Georg Bernhard, Freiherr von Pöllnitz. By 1688 the regiment was expanded to thirty companies, but in 1702 five of these companies were transferred to the 18th Infantry Regiment.[2][3]

In 1701, the regiment was absorbed into the new Prussian Army. In 1707, the regiment was further reduced by ten companies, (bringing it down to fifteen companies), when those were transferred to the 5th Infantry Regiment (Füsilier-Garde Regiment). In 1713, the regiment lost its Guard status and was henceforth known by the regimental Chef (see list below), thus becoming 1st Infantry Regiment (1. Infanterieregiment). Simultaneously its size was again reduced with four companies going to the new 23rd Infantry Regiment (von Kamecke) and one company to the 24th Infantry Regiment (von Schwendy). At this point the regimental fielded eleven companies.[2]
During the reign of King Frederick the Great, the regiment had a very high reputation as said at the Battle of Hochkirch:[2]
It's true, I always considered the [1st] Winterfeld Regiment was brave but today it has surpassed all my expectations. I shall never forget it.
— Frederick the Great of Prussia
From 1768, the regiment was ranked after the Guard (6th Grenadier Guards and 15th Foot Guards), regardless of the seniority of the Chef.[2]
The regiment's numeric successor, the 1st Infantry Regiment (1st East Prussian) would later be raised to the status of Grenadiers and serve with distinction until its disbanded in 1919. That regiment's successor, the 1st (East Prussian) Infantry Regiment would then serve in the Reichswehr and Wehrmacht until its final disbandment in 1945.
Austrian Succession

In 1741, the regiment fought at the Siege of Breig (7 April & 11 April–3 May), the 2nd Battalion being present at the Battle of Mollwitz (10 April) and the Siege of Neisse (19–31 October). In 1742, the regiment was present at the Battle of Glatz (9 January), the 1st Battalion at the Battle of Göding (10 March) and the Siege of Brünn (31 March–3 April), and again as a regiment at the Battle of Austerlitz (10 April).[2]
In 1744, the regiment was present at the Battle of Kloster Maria Schein (28 August), the Siege of Prague (2–18 September) and the Battle of Patschkau (21 December). In 1745, the regiment fought further at the Battle of Konstadt (20 April) and at the famed Battle of Hohenfriedberg (4 June). At Hohenfriedberg the regiment defeated three full Austrian infantry regiments, capturing many flags, while Oberst Ewald Wedig von Massow and 17 officers and 631 men were killed. There 5 men of the regiment received the Pour le Mérite, Prussia's highest military honour. The regiment had been reduced to 18 officers, 48 Non-commissioned officers, 22 musicians, and 378 men. Finally, they were present at the Siege of Neustadt (4–12 September) and the Battle of Hennersdorf (23 November).[2]
Seven Years War
Following the outbreak of hostilities over the control of Silesia once again, the Third Silesian War broke out. It would become part of the larger Seven Years' War, which had a profound impact on the future of the world as a whole. In 1756, the regiment joined in the blockade of the Royal Saxon Army in Pirna while the main Prussian field army was engaged against the Austrians at the Battle of Lobositz (1 October). On 6 May 1757, the regiment lost two thirds of its strength (22 officers and 1,168 men) during the failed Siege of Prague. At the end of August, the regiment was part of the small Prussian army hastily assembled at Dresden to oppose the Franco-Imperial Army invading Saxony. The regiment then fought at the Battle of Rossbach (5 November), the Battle of Leuthen (5 December) and finally the Siege of Breslau (7-20 December).[2]

In 1758, the regiment guarded King Frederick's headquarters during the Invasion of Moravia and fought at the Battle of Jenwitz (10-11 October). In 1760, the regiment was present at the Siege of Dresden (13-22 July), the Battle of Liegnitz (15 August) and finally the Battle of Torgau (3 November).[2]
In 1761, the regiment was present at the Siege of Bunzelwitz Lager (20 August-25 September). In 1762, it fought at the Battle of Burkersdorf and the Battle of Leutmannsdorf (both on 21 July), the Siege of Schweidnitz (4 August-10 October), and finally the Battle of Reichenbach (16 August).[2]
During the Seven Years' War, the grenadier battalions from the 1st and 2nd Infantry Regiments were combined to form a field grenadier battalion.[4]
Reorganisations
From 1768, regardless of the regimental chief, the regiment would be ranked hereafter following the Royal Guard.[5] During the French Revolutionary Wars, the regiment was not mobilised and subsequently not included in the Duke of Brunswick's Army, instead remaining on garrison in Brandenburg.
In 1770 the peacetime organisation of a Prussian infantry regiment was set with two battalions totalling 1,392 soldiers, plus the regimental staff. A battalion was formed with one grenadier and four musketeer companies. The strength therefore stood as the following:[6]
- Overall
- 25 Officers
- 59 Non-commissioned officers
- 1 Drum Major
- 3 Fifers
- 18 Drummers
- 126 Grenadiers
- 570 Musketeers
- 802 Total
- Grenadier Company
- 1 Captain
- 1 First Lieutenant
- 2 Second Lieutenants
- 10 NCOs
- 3 Drummers
- 2 Fifers
- 126 Grenadiers
- 1 Physician
- 145 Total
- 4 Musketeer Companies (each of)
- 1 Captain
- 1 First Lieutenant
- 2 Second Lieutenants
- 10 NCOs
- 3 Drummers
- 114 Musketeers
- 1 Physician
- 132 Total
In 1787, the Prussian Army reorganised its infantry regiments such that they had two musketeer battalions and one grenadier battalion. Each battalion had four companies. Each company was divided into four platoons (Züge). The use of the four platoons remained in the fusilier companies until 1806, but it was to remain in the musketeers only until 1798. At that time there began a gradual change. Each company had ten "Schützen" or riflemen who were issued rifled carbines "Büchsen". These men were the designated company sharpshooters and provided the battalion's skirmishers.[7]
Therefore, by 1798 each company was organised as follows:[8] One Captain, one First Lieutenant, two Second Lieutenants, twelve NCOs, three Drummers, four Artillerists (manning the company's 3-pounder field gun), ten Schützen and 140 Grenadiers or Musketeers, providing a total of 173.
The Order-in-Cabinet of 23 May 1787 directed that each regiment was to have ten flags; with six in the regimental armory. Each battalion had an Avancir-Fahne and a Retirir Fahne. The grenadier battalions were not to carry a flag because they were formed from companies of different regiments.[8]
In addition, an invalid company with 40 to 60 men was organised in each regiment, led by the commander of the depot battalion. The uniform of the invalid companies consisted of a blue coat with cuffs and collars of the regimental colour. The vest and breeches were blue and the buttons bore of the regimental number.[8]
In peacetime 20 men per company were to be furloughed, but in fact the musketeer companies usually shrank to about 80 men and the grenadiers to 90 men. For annual maneuvers they were brought up to 120 and 150 men respectively. In 1796 the depot battalions were raised to four companies each and added to the regiments and their 3rd Battalion. They now consisted of:[9] twelve Officers, twenty-six NCOs, one Drum Major, eight Drummers, eight Surgeons and 480 x Soldiers, for a total of 535.
Napoleonic Wars

1st–3rd Battalions
When the Prussian Army was mobilised for war on 9 October 1806, it was split between three major groups: the Advance Guard under General Frederick Louis, Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen, the Field Army commanded by King Frederick Wilhelm III and General Charles William Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, and Generalmajor Anton Wilhelm von L'Estocq's East Prussian Corps. When mobilised, the regiment was therefore split, the regiment was assigned to the Field Army, and made part of the Karl August, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach's separate corps, based in the reserve. Sometime later the corps joined the main force and was redesignated as the Corps of Battle. Along with the Grenadier Battalion, the regiment formed part of the Field Army and was present at the disastrous Battle of Auerstadt. During the battle, the regiment along with the 30th Infantry Regiment formed part of the 1st Brigade, Infantry Division of the Advance Guard.[10] The regiment along with the remainder of the army and grenadier battalion was decimated and fell back into Brandenburg. The regiment then, albeit significantly reduced, fought at Weissensee, Greussen, Nordhausen, Ellingen and finally at the Battle of Ratekau where it surrendered and was subsequently disbanded. The 3rd Battalion was reformed from the depot at the same time as the mobilisation and remained in Berlin till November when it joined the rest of the regiment at the Battle of Lübeck. It escaped to Stettin where it also surrendered following that siege.[11][5][12]
Grenadiers
By the time of 1806, the grenadier battalions of the 1st and 13th infantry regiments formed the Prinz August von Preußen Grenadier Battalion.[13][14] This unit formed part of the 2nd Brigade in the 1st Division of the Reserve within the Field Army.[10] This battalion was decimated following the Battle of Auerstadt, and its personnel flocked back into Brandenburg.[11][5][12]
Later elements
Following the disaster of the Saxon campaign, the 9th (later 8th (1st Brandenburg)) Life Infantry Regiment was formed merging elements from several units, including cantonists of the 1st Infantry Regiment.[15]
Regimental Notes
Depot
During the regiment's history, its depot and headquarters garrison was Berlin in Neumark, while the grenadiers were in Strausberg, Brandenburg. The majority of recruits came from the districts of Storkow and Zauche, partly from Teltow and Beeskow, and some from the cities of Storkow, Teltow, Märkisch Buchholz, Zossen, and Beelitz.[5]
Colours
Prussian Infantry regiments before 1806 had two official types of 'regimental colours', the Life Flag, which consisted of a white field and silver decorations. The orange medallion had a black eagle and a white scroll bearing the gold motto "Pro Gloria et Patria", "For Glory and Fatherland". The company flag consisted of an orange field and silver decorations. The white medallion had a black eagle surmounted by an orange scroll with the same model as above in gold.[2]
The regiment had a total of ten flags, five per battalion. These flags were grouped in the middle of the battalion, two flags in the first rank, one in the second, and two in the third rank. A Feldwebel was posted on either side of flags in the first and third ranks. The standards were carried by a Gefreiter. The regimental sappers were posted on the right wing of their battalion aligned on the first rank and the drummers formed on the right and left flanks of the second and third ranks.[7]
Uniform
Musketeer Uniforms
By the time of the Seven Years' War, the regimental uniform consisted of the following: Black tricorne laced white with white pom-poms, red stock, Prussian blue coat with two white pointed braid loops under the lapel and one button at the rear waist. The horizontal pockets had three buttons and two white pointed braid loops. White lace and white metal buttons. Red collar and straight cuffs with white pointed braid loops and white metal buttons. Red lapels with six white metal buttons and six white pointed white braid loops [2:2:2]. Blue shoulder straps, red turnbacks, and white waistcoat and breeches.[2][16]
Grenadiers had a separate cap design, with a white plate, white headband, blue back, white pompom, and white piping.[17]
Non-commissioned Officers Uniform
Black tricorne edged silver and black & white pom-poms. Prussian blue coat with red collars. Smooth white silk and silver braid was 23mm wide. Red lapels edged with silver lace. Silver edging to the Prussian cuffs and cuff flaps. White metal buttons [2:2:2].[2]
Drummers Uniform
The drummer lace was based upon the coat of arms of Caspar Otto von Glasenap who was its Chef from 1723 to 1742. Prussian blue coat richly decorated in white and red braid. The wings had four vertical and one base lace. The sleeves had nine bars of lace. White linen lace with red woolen zig-zag patter either 29mm or 50mm wide.[2]
Officers Uniform
Black tricorne edged with silver. Prussian clue collarless coat had 2 x silver embroidered buttonholes under the lapels and one both sides of the rear waist. Metallic embroidery of silver braid thread and white silk on red cloth was 29mm wide. The metallic buttonhole lace of silver braid and white silk on blue cloth was 34mm by 83mm. Red lapels edged with lace. Cuffs and cuff flaps edged with silver embroidery, and silver buttons.[2][16]
Uniform Gallery
.tiff.jpg.webp) Officer of musketeers in uniform the 1st Infantry by 1745. The rather elaborate spontoon was not used in combat (the officers' sword can be seen), and was therefore typically brilliantly engraved.
Officer of musketeers in uniform the 1st Infantry by 1745. The rather elaborate spontoon was not used in combat (the officers' sword can be seen), and was therefore typically brilliantly engraved..jpg.webp) The grenadier company of the 1st Infantry advances towards Austrian lines. The height different between the grenadiers and the musketeers can be somewhat seen, though the smoke does obscure them.
The grenadier company of the 1st Infantry advances towards Austrian lines. The height different between the grenadiers and the musketeers can be somewhat seen, though the smoke does obscure them.
Regimental Chefs
The chefs held the position of commanding officers of the regiment, which for several periods was known by their names. Below is a list of the chefs:[2][3]
- 1655–1657, Pierre de la Cave
- 1657–1677, Georg Berhard, Freiherr von Pöllnitz
- 1677–1684, Adolf von Gotze
- 1684–1691, Hans Adam von Schöning
- 1691–1698, Heino Heinrch, Graf von Flemming
- 1698–1702, Johannes Albrecht, Graf von Barfus
- 1702–1723, Alexander Hermann, Graf von Wartenslebe
- 1723–1742, Kaspar Otto von Glasenapp
- 1742–1754, Johann Christoph Friedrich, Graf von Hacke
- 1754–1756, Vacant
- 1756–1757, Hans Karl von Winterfeldt (killed at the Battle of Moys 7 September 1757)
- 1758–1760, Johann Sigismund von Lattorf
- 1760–1768, Karl Christoph von Zeuner
- 1768–1776, Erich Julius von Kosenbahr
- 1776–1778, Christian Friedrich von Bandemer
- 1778–1778, Ludwig Gottlob von Kalckreuth
- 1778–1792, Hans Ehrentreich von Bornstedt (Alt-Bornstedt from 1786)
- 1792–1806, Johann Ernst, Graf von Kunheim (Graf von 1798)
Footnotes
- ↑ "Regimenter". www.preussenweb.de. Retrieved 2021-07-27.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Summerfield, pp. 53–58
- 1 2 Haythornthwaite, pp. 19–20
- ↑ Haythornthwaite, p. 39
- 1 2 3 4 "Regimenter". www.preussenweb.de. Retrieved 2021-08-06.
- ↑ Nafziger, pp. 23–24
- 1 2 Nafziger, p. 24
- 1 2 3 Nafziger, p. 25
- ↑ Nafziger, p. 26
- 1 2 Nafziger, George. "Prussian Army Order of Battle at Auerstadt: 14 October 1806" (PDF). United States Army Combined Arms Center. Nafziger Orders of Battle Collection. Retrieved 6 August 2021.
- 1 2 Nafziger, p. 53
- 1 2 Smith, Napoleonic Wars Data Book, p. 226
- ↑ Nafziger, p. 29
- ↑ Hofschröer, p. 5
- ↑ Nafziger, p. 81
- 1 2 Smith, Uniforms of the Napoleonic Wars, p. 197
- ↑ Haythornthwaite, p. 38
References
- Summerfield, Stephen (2018). Prussian Musketeer Regiments of the War of the Austrian Succession and Seven Years War: Uniforms, Organisation and EQuipment. Huntingdon, United Kingdom: Ken Trotman. ISBN 978-1907417382. OCLC 855706053.
- Haythornthwaite, Philip (1991). Frederick the Great's Army. Vol. II: Infantry. Botley, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1855321601. OCLC 869307607.
- Nafziger, George F. (1996). The Prussian Army during the Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815). Vol. I: The Infantry. Chester, Ohio, United States of America: Self Publication. ISBN 978-1858183077.
- Smith, Digby (2006). An illustrated encyclopedia of uniforms of the Napoleonic wars : an expert, in-depth reference to the officers and soldiers of the revolutionary and Napoleonic period, 1792-1815. London Lanham, Md: Lorenz North American agent/distributor, National Book Network. ISBN 978-0-7548-1571-6. OCLC 60320422.
- Hofschröer, Peter (1984). Prussian Line Infantry 1792–1815. Fulham, London, United Kingdom: Osprey Military Publishings. ISBN 978-1780965253. OCLC 869308076.
- Smith, Digby (1998). The Greenhill Napoleonic wars data book. London Mechanicsburg, PA: Greenhill Books Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-1-85367-276-7. OCLC 37616149.