 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 18-MT; 18-Methylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one; 13β-Ethyl-17β-hydroxy-18-norandrost-4-en-3-one |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
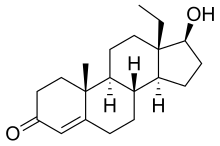
| Formula | C20H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.458 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
18-Methyltestosterone (18-MT) is an androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) which was never marketed.[1][2][3] Along with 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone) and 17α-ethynyltestosterone (ethisterone), it is a parent structure of a number of progestogens and AAS. These include the progestogens levonorgestrel (17α-ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone) and its derivatives (e.g., desogestrel, gestodene, norgestimate, gestrinone) as well as AAS such as norboletone (17α-ethyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone) and tetrahydrogestrinone (THG; δ9,11-17α-ethyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone).
See also
References
- ↑ Baddeley GV, Carpio H, Edwards JA (1966). "Steroids. CCLXXXVIII.1The Synthesis of 18-Methylprogesterone and Related Compounds2". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 31 (4): 1026–1032. doi:10.1021/jo01342a009. ISSN 0022-3263.
- ↑ Strike DP, Herbst D, Smith H (May 1967). "Totally Synthetic Hormones. XVI.(1) The Conversion of Estr-4-en-17-ol to Testosterone and the Total Synthesis of Some 18-Methylandrostane and 18-Methylpregnane Derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (3): 446–451. doi:10.1021/jm00315a034. PMID 22185150.
- ↑ Rees R, Strike DP, Smith H (September 1967). "Totally synthetic steroid hormones. XVII. Further studies on the synthesis of dl-18-methylandrostane and dl-18-methylpregnane derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (5): 783–789. doi:10.1021/jm00317a006. PMID 6048483.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.