 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H25NO5 |
| Molar mass | 443.499 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
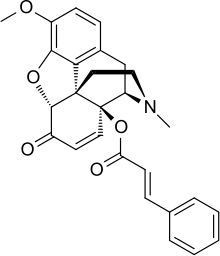
14-Cinnamoyloxycodeinone is the most potent example in a series of opiate analgesic drugs discovered in the 1960s, with over 100 times the potency of morphine.[1] It is a derivative of hydroxycodeinone, being the 14-cinnamate ester.[2] In another paper, Buckett assigns the potency as 177 with a range (depending on animal and test) of 101–310×.[3] It may be of interest to researchers that the allyl group in this compound and in allylprodine overlay very closely.
See also
References
- ↑ Lien EJ, Tong GL, Srulevitch DB, Dias C (1978). "QSAR of narcotic analgetic agents" (PDF). NIDA Research Monograph. 1978 (22): 186–96. PMID 30907. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-15. Retrieved 2011-06-01.
- ↑ Buckett WR (November 1965). "Some pharmacological studies with 14-cinnamoyloxycodeinone". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 17 (11): 759–60. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07602.x. PMID 4379812. S2CID 40424914.
- ↑ Buckett WR (December 1964). "The relationship between analgesic activity, acute toxicity and chemical structure in esters of 14-hydroxycodeinone". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 16: SUPPL:68–71T. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1964.tb07539.x. PMID 14265944. S2CID 23049905.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.