| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Dioxetane | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,3-Dioxacyclobutane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 60.052 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
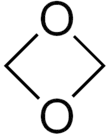
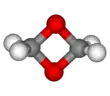
1,3-Dioxetane (1,3-dioxacyclobutane) is a heterocyclic organic compound with formula C2O2H4, whose backbone is a four-member ring of alternating oxygen and carbon atoms. It can be viewed as a dimer of formaldehyde (COH2).
Derivatives of 1,3-dioxetane are rarely encountered as intermediates in the literature. Usually, they are prepared via [2+2] cycloadditions of two carbonyl compounds. Molecular orbital theory calculations suggest that they should be more stable than the 1,2-isomers, which are more intensively studied.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Cordier, C.; Leach, S.; Nelson, A. (2014). Science of Synthesis: Houben-Weyl Methods of Molecular Transformations Vol. 29: Acetals: Hal/X and O/O, S, Se, Te. Georg Thieme Verlag. p. 407. ISBN 9783131720412.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.