myelin
English
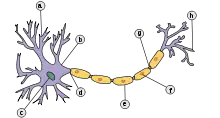
Neuron, with myelin sheath labeled as e
Etymology
myelo- + -in. From Ancient Greek μυελός (muelós, “marrow”).
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /ˈmaɪəlɪn/
Noun
myelin (countable and uncountable, plural myelins)
- (neuroanatomy) A white, fatty material, composed of lipids and lipoproteins, that surrounds the axons of nerves.
- 1868 January, Edmund Montgomery, “On the Formation of so-called Cells in Animal Bodies”, in The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, page 203:
- As the result of prolonged action of water upon myelin, bird's-nests-cells are also said to be produced, and we are certain we have seen, as the result of such prolonged action of water, the appearances thus compared.
- 2018 December 13, Carl Zimmer, “Narrower Skulls, Oblong Brains: How Neanderthal DNA Still Shapes Us”, in The New York Times, →ISSN:
- This gene controls the production of an insulating sleeve that wraps around neurons. Known as myelin, it is crucial for long-range communication in the brain.
Derived terms
- demyelination
- myelinate
- myelinated
- myelination
- myelin basic protein
- myelinic
- myelinisation
- myelinization
- myelinogenesis
- myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein
- myelinolysis
- myelinopathy
- myelinophagia
- myelin protein zero
- myelin sheath
- nonmyelin
Related terms
Translations
white, fatty material, composed of lipids and lipoproteins
|
Further reading
- “myelin”, in Webster’s Revised Unabridged Dictionary, Springfield, Mass.: G. & C. Merriam, 1913, →OCLC.
- “myelin”, in The Century Dictionary […], New York, N.Y.: The Century Co., 1911, →OCLC.
Anagrams
Czech
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): [ˈmɪjɛlɪn]
- IPA(key): [ˈmɪjɛliːn]
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.