ⲉⲃⲓⲏⲛ
Coptic
Etymology
From Demotic 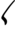
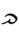
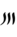
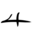
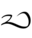 (ꜣbyn, “poor man”). Ultimately borrowed from Canaanite *ʾabyōn-,[1]
whence also Hebrew אֶבְיוֹן (ʾeḇyōn, “poor, needy”). Related to Ugaritic 𐎀𐎁𐎊𐎐 (ảbyn /ʾabyānu/, “poor, impoverished”).[2]
(ꜣbyn, “poor man”). Ultimately borrowed from Canaanite *ʾabyōn-,[1]
whence also Hebrew אֶבְיוֹן (ʾeḇyōn, “poor, needy”). Related to Ugaritic 𐎀𐎁𐎊𐎐 (ảbyn /ʾabyānu/, “poor, impoverished”).[2]
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /(ʔ)əβˈjeːn/
Noun
ⲉⲃⲓⲏⲛ • (ebiēn) m or f
Adjective
ⲉⲃⲓⲏⲛ • (ebiēn)
References
- Wilson-Wright, Aren M., Huehnergard, John (2021) “How to Kill a Dragon in Northwest Semitic: Three Linguistic Observations regarding Ugaritic ltn and Hebrew liwyātān”, in Vetus Testamentum, volume 72, number 1, Brill, : “Normally, the suffix *-ān becomes -ôn in Biblical Hebrew with the operation of the Canaanite shift (e.g., *ʔabyān- > ʔebyôn “poor”).”
- Bordreuil, Pierre, Pardee, Dennis (2009) A Manual of Ugaritic, Penn State Press, →ISBN, page 293: “ʾABYN adjective 'destitute, poor' /ʾabyānu/”
- Janet H. Johnson, editor (2001), The Demotic Dictionary of the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago, volume ꜣ (02.1), Chicago: The University of Chicago, page 18
- Černý, Jaroslav (1976) Coptic Etymological Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, →ISBN, page 32
- Crum, Walter E. (1939) A Coptic Dictionary, Oxford: Clarendon Press, →ISBN, page 53
- “ꜣbjn (lemma ID d73)”, in Thesaurus Linguae Aegyptiae, Corpus issue 17, Web app version 2.01 edition, Tonio Sebastian Richter & Daniel A. Werning by order of the Berlin-Brandenburgische Akademie der Wissenschaften and Hans-Werner Fischer-Elfert & Peter Dils by order of the Sächsische Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Leipzig, 2004–15 December 2022
- Vycichl, Werner (1983) Dictionnaire Étymologique de la Langue Copte, Leuven: Peeters, →ISBN, page 38
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.