 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate | |
| Other names
TMSOTf Trimethylsilyl triflate TMS triflate Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid trimethylsilyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.136 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
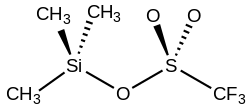
| C4H9F3O3SSi | |
| Molar mass | 222.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.225 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf) is an organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiO3SCF3. It is a colorless moisture-sensitive liquid. It is the trifluoromethanesulfonate derivative of trimethylsilyl.[1] It is mainly used to activate ketones and aldehydes in organic synthesis.
Reactions
TMSOTf is quite sensitive toward hydrolysis:
- (CH3)3SiO3SCF3 + H2O → (CH3)3SiOH + HO3SCF3
It is far more electrophilic than trimethylsilyl chloride.
Related to its tendency to hydrolyze, tmsOTf is effective for silylation of alcohols:[2]
- (CH3)3SiO3SCF3 + ROH + Et3N → ROSi(CH3)3Si + [Et3NH]O3SCF3
A common use of (CH3)3SiO3SCF3 is for the preparation of silyl enol ethers.[3][4] One example involves the synthesis of the silyl enol ether of camphor:
It was also used in Takahashi Taxol total synthesis and in chemical glycosylation reactions.[5]
Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate has a variety of other specialized uses. It has been use to install tert-alkyl groups on phosphine (R = alkyl):[6]
- PH3 + R3C–OAc + Me3SiOTf → [(R3C)2PH2]OTf
Deprotection of Boc-protected amines can be achieved using trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate and triethylamine or 2,6-lutidine.[7][8]
References
- ↑ Joseph Sweeney; Gemma Perkins; Enrique Aguilar; Manuel A. Fernández‐Rodríguez; Rodolfo Marquez; Eric Amigues; Ricardo Lopez‐Gonzalez (2018). "Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt338. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ↑ Boeckman, Robert; Tusch, Douglas J.; Biegasiewicz, Kyle F. (2015). "(S)-1,1-Diphenylprolinol Trimethylsilyl Ether". Organic Syntheses. 92: 309–319. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.092.0309.
- ↑ Umemoto, Teruo; Tomita, Kyoichi; Kawada, Kosuke (1990). "N-Fluoropyridinium Triflate: An Electrophilic Fluorinating Agent". Organic Syntheses. 69: 129. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.069.0129.
- ↑ Efficient Stereoselective Synthesis of Proanthocyanidin Trimers with TMSOTf-Catalyzed Intermolecular Condensation. Akiko Saito, Akira Tanaka, Makoto Ubukata and Noriyuki Nakajima, Synlett, 2004, volume 6, pages 1069-1073, doi:10.1055/s-2004-822905
- ↑ Love, Kerry R.; Seeberger, Peter H. (2005). "Synthesis and Use of Glycosyl Phosphates as Glycosyl Donors". Organic Syntheses. 81: 225. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.081.0225.
- ↑ Barber, Thomas; Argent, Stephen P.; Ball, Liam T. (2020-05-15). "Expanding Ligand Space: Preparation, Characterization, and Synthetic Applications of Air-Stable, Odorless Di- tert -alkylphosphine Surrogates". ACS Catalysis. 10 (10): 5454–5461. doi:10.1021/acscatal.0c01414. ISSN 2155-5435. S2CID 219017552.
- ↑ Kuehne, Martin E.; Xu, Feng (1 December 1998). "Syntheses of Strychnan- and Aspidospermatan-Type Alkaloids. 10. An Enantioselective Synthesis of (−)-Strychnine through the Wieland−Gumlich Aldehyde". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 63 (25): 9427–9433. doi:10.1021/jo9813989.
- ↑ Doi, Takayuki; Numajiri, Yoshitaka; Munakata, Asami; Takahashi, Takashi (1 February 2006). "Total Synthesis of Apratoxin A". Organic Letters. 8 (3): 531–534. doi:10.1021/ol052907d. PMID 16435877.
