 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
ammonium phosphate | |
| Other names
triammonium phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.709 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
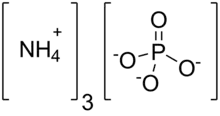
| (NH4)3PO4 | |
| Molar mass | 149.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | White, tetrahedral crystals |
| 58.0 g/100 mL (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Insoluble in acetone[2] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H319 | |
| P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P305+P351+P338, P330, P337+P313, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1671.9 kJ/mol |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Trisodium phosphate Tripotassium phosphate |
Related compounds |
Diammonium phosphate Monoammonium phosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Ammonium phosphate is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)3PO4. It is the ammonium salt of orthophosphoric acid. A related "double salt", (NH4)3PO4.(NH4)2HPO4 is also recognized but is impractical to use. Both triammonium salts evolve ammonia. In contrast to the unstable nature of the triammonium salts, the diammonium phosphate (NH4)2HPO4 and monoammonium salt (NH4)H2PO4 are stable materials that are commonly used as fertilizers to provide plants with fixed nitrogen and phosphorus.[3]
Preparation of triammonium phosphate
Triammonium phosphate can be prepared in the laboratory by treating 85% phosphoric acid with 30% ammonia solution:
- H3PO4 + 3 NH3 → (NH4)3PO4
(NH4)3PO4 is a colorless, crystalline solid. The solid, which has the odor of ammonia, is readily soluble in water. The salt converts to diammonium hydrogen phosphate (NH4)2HPO4.
See also
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 4–42, 5–19. ISBN 978-0-8493-0594-8.
- ↑ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 4–41. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ↑ Schrödter, Klaus; Bettermann, Gerhard; Staffel, Thomas; Wahl, Friedrich; Klein, Thomas; Hofmann, Thomas (2008). "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3. ISBN 978-3527306732.
