| Perisinusoidal space | |
|---|---|
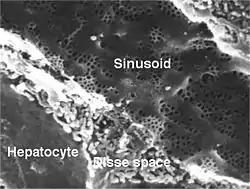 Sinusoid of a rat liver with fenestrated endothelial cells. Fenestrae are approx 100 nm diameter, and the sinusoidal width 5 µm. Scanning electron micrograph by Robin Fraser, University of Otago. | |
 Basic liver structure | |
| Details | |
| Location | Liver |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | spatium perisinusoideum |
| TH | H3.04.05.0.00012 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy | |
The perisinusoidal space (or space of Disse) is a location in the liver between a hepatocyte and a sinusoid. It contains the blood plasma. Microvilli of hepatocytes extend into this space, allowing proteins and other plasma components from the sinusoids to be absorbed by the hepatocytes. Fenestration and discontinuity of the endothelium facilitates this transport.[1] This space may be obliterated in liver disease, leading to decreased uptake by hepatocytes of nutrients and wastes such as bilirubin.
The perisinusoidal space also contains hepatic stellate cells (also known as Ito cells), which store fat or fat soluble vitamins including vitamin A). A variety of insults that cause inflammation can result in the cells transforming into myofibroblasts, resulting in collagen production, fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
The Space of Disse was named after German anatomist Joseph Disse (1852–1912).[2]
References
External links
- UIUC Histology Subject 1317
- Histology image: 22103loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Ultrastructure of the Cell: hepatocytes and sinusoids, sinusoid and space of Disse"
- Histology image: 15204loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Liver, Gall Bladder, and Pancreas: liver; sinusoids and Kupffer cells"
- Anatomy photo: digestive/mammal/liver5/liver7 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, liver (EM, Low)"