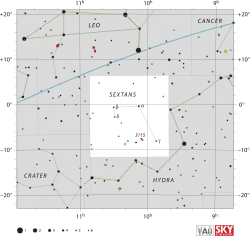
| Constellation | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | Sex |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Sextantis, Sextansis |
| Pronunciation | /ˈsɛkstənz/, genitive /sɛksˈtæntɪs/ |
| Symbolism | the Sextant |
| Right ascension | 09h 41m 04.8653s–10h 51m 30.2447s[1] |
| Declination | 6.4327669°–−11.6621428°[1] |
| Quadrant | SQ2 |
| Area | 314 sq. deg. (47th) |
| Main stars | 3 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 28 |
| Stars with planets | 5 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 0 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 5 |
| Brightest star | α Sex (4.49m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | Sextantids |
| Bordering constellations | Leo Hydra Crater |
| Visible at latitudes between +80° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of April. | |
Sextans is a faint, minor equatorial constellation which was introduced in 1687 by Polish astronomer Johannes Hevelius. Its name is Latin for the astronomical sextant, an instrument that Hevelius made frequent use of in his observations.
Notable features
Sextans as a constellation covers a rather dim, sparse region of the sky. It has only one star above the fifth magnitude, namely α Sextantis at 4.49m. Altogether, there are 38 stars that are brighter than or equal to apparent magnitude 6.5.[lower-alpha 1][3] John Flamsteed labeled 41 stars for the constellation.[4] Francis Baily intended to give Bayer designations to some of the stars but because none of them were above magnitude 4.5, he left them unlettered.[4] Rather, it was Benjamin Apthorp Gould who lettered some of the stars. He labeled the five brightest stars using Greek letters Alpha (α) to Epsilon (ε) in his Uranometria Argentina.[4]
Stars

Bright Stars
- Alpha Sextantis is an ageing A-type star of spectral class A0 III[5] located 280±20 light-years away[6] from the Solar System. At the age of 385 million years,[7] it is exhausting hydrogen at its core and leaving the main sequence.
- γ Sextantis is the second brightest star in the constellation with an apparent magnitude of 5.05. It is a binary star consisting of two A-type main-sequence stars with classes of A1 V and A4 V respectively.[8] The stars take 77.55 years to circle each other in an eccentric orbit[9] and the system is located 280±10 light-years away from the Solar System.[6] The separation of the stars is four-tenths of an arcsecond,[9] making it difficult to observe without the use of a telescope with an aperture of 30 cm.
- β Sextantis is slightly fainter at magnitude 5.07;[10] it is said to be 364±10 light-years distant.[11] Beta Sextantis is a B-type main-sequence star of spectral class B6 V and it has been used as a standard in the MK spectral classification system.[12] It is suspected to be a Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable with a period of 15.4 days.[13]
The constellation contains a few double stars including 35 and 40 Sextantis. There are a few notable variable stars, including 25, 23 Sextantis, and LHS 292. NGC 3115, an edge-on lenticular galaxy, is the only noteworthy deep-sky object. It also lies near the ecliptic, which causes the Moon, and some of the planets to occasionally pass through it for brief periods of time.
The constellation is the location of the field studied by the COSMOS project, undertaken by the Hubble Space Telescope.
COSMOS project
 COSMOS-Gr30 is a particularly dense region in space that contains 10 individual galaxies[14]
COSMOS-Gr30 is a particularly dense region in space that contains 10 individual galaxies[14] Cosmos Redshift 7, brightest galaxy in the early universe, is located in the constellation Sextans (artist concept)
Cosmos Redshift 7, brightest galaxy in the early universe, is located in the constellation Sextans (artist concept)
Sextans B is a fairly bright dwarf irregular galaxy at magnitude 6.6, 4.3 million light-years from Earth. It is part of the Local Group of galaxies.[15]
CL J1001+0220 is as of 2016 the most distant-known galaxy cluster at redshift z=2.506, 11.1 billion light-years from Earth.[16]
In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy (at z = 6.60) found in Sextans. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.[17][18]
Depictions of the constellation
 The constellation Sextans as depicted in Johann Doppelmayr's Atlas Coelestis, c. 1730 (Plate 19, Southern Celestial Hemisphere).
The constellation Sextans as depicted in Johann Doppelmayr's Atlas Coelestis, c. 1730 (Plate 19, Southern Celestial Hemisphere). Sextans and other constellations seen around Hydra. From Urania's Mirror (1825)
Sextans and other constellations seen around Hydra. From Urania's Mirror (1825)
See also
References
- 1 2 IAU, The Constellations, Sextans.
- ↑ Bortle, John E. (February 2001). "The Bortle Dark-Sky Scale". Sky & Telescope. Sky Publishing Corporation. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ↑ Ridpath, Ian. "Constellations: Lacerta–Vulpecula". Star Tales. Self-published. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 Wagman, Morton (2003). Lost Stars: Lost, Missing and Troublesome Stars from the Catalogues of Johannes Bayer, Nicholas Louis de Lacaille, John Flamsteed, and Sundry Others. Blacksburg, VA: The McDonald & Woodward Publishing Company. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-939923-78-6.
- ↑ Cowley, A.; Cowley, C.; Jaschek, M.; Jaschek, C. (April 1969). "A study of the bright stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications". The Astronomical Journal. 74: 375. Bibcode:1969AJ.....74..375C. doi:10.1086/110819. ISSN 0004-6256. S2CID 121555804.
- 1 2 van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ↑ Monier, Richard; Bowman, Dominic M.; Lebreton, Yveline; Deal, Morgan (2023). "The Unexpected Optical and Ultraviolet Variability of the Standard Star α Sex (HD 87887)". The Astronomical Journal. 166 (2): 73. arXiv:2306.08551. Bibcode:2023AJ....166...73M. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/acdee4.
- ↑ Edwards, T. W. (April 1976), "MK classification for visual binary components", Astronomical Journal, 81: 245–249, Bibcode:1976AJ.....81..245E, doi:10.1086/111879.
- 1 2 Heintz, W. D. (March 1982), "Orbits of 16 visual binaries", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 47: 569–573, Bibcode:1982A&AS...47..569H.
- ↑ Crawford, D. L.; et al. (1971), "Four-color, H-beta, and UBV photometry for bright B-type stars in the northern hemisphere", The Astronomical Journal, 76: 1058, Bibcode:1971AJ.....76.1058C, doi:10.1086/111220.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Mathys, G.; et al. (March 1986), "Photometric variability of some early-type stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 63 (3): 403–416, Bibcode:1986A&AS...63..403M.
- ↑ Kholopov, P. N.; et al. (April 1989), "The 69th Name-List of Variable Stars", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars, 3323 (3323): 1, Bibcode:1989IBVS.3323....1K.
- ↑ "A gigantic cosmic bubble". www.eso.org. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- ↑ Levy 2005, p. 178.
- ↑ Wang, Tao; Elbaz, David; Daddi, Emanuele; Finoguenov, Alexis; Liu, Daizhong; Schrieber, Corenin; Martin, Sergio; Strazzullo, Veronica; Valentino, Francesco; van Der Burg, Remco; Zanella, Anita; Cisela, Laure; Gobat, Raphael; Le Brun, Amandine; Pannella, Maurilio; Sargent, Mark; Shu, Xinwen; Tan, Qinghua; Cappelluti, Nico; Li, Xanxia (2016). "Discovery of a galaxy cluster with a violently starbursting core at z=2.506". The Astrophysical Journal. 828 (1): 56. arXiv:1604.07404. Bibcode:2016ApJ...828...56W. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/828/1/56. S2CID 8771287.
- ↑ Sobral, David; Matthee, Jorryt; Darvish, Behnam; Schaerer, Daniel; Mobasher, Bahram; Röttgering, Huub J. A.; Santos, Sérgio; Hemmati, Shoubaneh (4 June 2015). "Evidence For POPIII-Like Stellar Populations In The Most Luminous LYMAN-α Emitters At The Epoch Of Re-Ionisation: Spectroscopic Confirmation". The Astrophysical Journal. 808 (2): 139. arXiv:1504.01734. Bibcode:2015ApJ...808..139S. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/808/2/139. S2CID 18471887.
- ↑ Overbye, Dennis (17 June 2015). "Astronomers Report Finding Earliest Stars That Enriched Cosmos". New York Times. Retrieved 17 June 2015.
- "Sextans". The Constellations. International Astronomical Union.
- Levy, David H. (2005). Deep Sky Objects. Prometheus Books. ISBN 1-59102-361-0.
- Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0-00-725120-9. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0-691-13556-4.