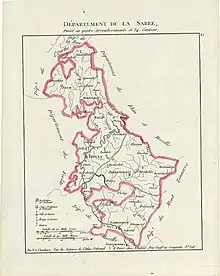
Sarre was a department in the First French Republic and First French Empire. Its territory is now part of Germany and Belgium. Named after the river Saar (French: Sarre), it was created in 1798 in the aftermath of the Treaty of Campo Formio of 18 October 1797 which ceded the left bank of the Rhine to France.
Despite its name it covered a much larger area than the historical area known as the Saarland. Prior to the French occupation of the area from 1793 onward, its territory had been divided between the Electorate of Trier, Nassau-Saarbrücken and the Electorate of the Palatinate (the Duchy of Zweibrücken and the County of Veldenz). Its territory is now part of the German states Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland as well as a tiny adjacent section of the Belgian province of Liège. Its capital was Trier.
The department was subdivided into the following arrondissements and cantons (situation in 1812):[1]
- Trier (French: Trèves), cantons Bernkastel, Büdlich, Konz, Pfalzel, Saarburg, Schweich, Trier and Wittlich.
- Birkenfeld, cantons: Baumholder, Birkenfeld, Grumbach, Hermeskeil, Herrstein, Kusel, Meisenheim, Rhaunen and Wadern.
- Prüm, cantons: Blankenheim, Daun, Gerolstein, Kyllburg, Lissendorf, Manderscheid, Prüm, Reifferscheid and Schönberg.
- Saarbrücken (French: Sarrebrück), cantons: Blieskastel, Lebach, Merzig, Ottweiler, Saarbrücken, Sankt Wendel and Waldmohr.
Its population in 1812 was 277,596, and its area was 493,513 hectares (1,219,500 acres).[1]
After Napoleon was defeated in 1814, most of the department became part of Prussia, with smaller parts assigned to Duchy of Oldenburg (Birkenfeld) and Bavaria. The cantons of Sankt Wendel and Baumholder were given to Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld as the Principality of Lichtenberg, which was sold to Prussia in 1834. The canton of Meisenheim was given to Hesse-Homburg, which was annexed to Prussia in 1866. France retained Saarbrücken but, after Waterloo, it was punished and it lost the town together with Saarlouis from nearby Moselle. The former Schönberg canton would later be included in the Eupen-Sankt Vith-Malmedy plebiscite area following World War I.
See also
References
- 1 2 Almanach Impérial an bissextil MDCCCXII, p. 463, accessed in Gallica 26 July 2013 (in French)