| Reticulate whipray | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Superorder: | Batoidea |
| Order: | Myliobatiformes |
| Family: | Dasyatidae |
| Genus: | Himantura |
| Species: | H. uarnak |
| Binomial name | |
| Himantura uarnak (Forsskål, 1775) or (J. F. Gmelin, 1789) | |
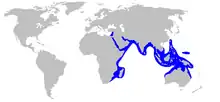 | |
| Range of the reticulate whipray | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The reticulate whipray or honeycomb stingray (Himantura uarnak) is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It inhabits coastal waters in the western Indian Ocean including the Red Sea, Natal and the Arabian Sea; also a Lessepsian transmigrant in the eastern Mediterranean. A large species reaching 2 m (6.6 ft) in width, the reticulate whipray has a diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc and an extremely long tail without fin folds. Both its common and scientific names refer to its ornate dorsal color pattern of many small, close-set dark spots or reticulations on a lighter background. However, the reticulate whipray is only one of several large spotted stingrays in the Indo-Pacific which, coupled with the variability of its coloration with age and locality, has resulted in a great deal of taxonomic confusion.
Often encountered resting on the bottom during daytime, the reticulate whipray is a predator of bottom-dwelling invertebrates and bony fishes. Like other stingrays, it is aplacental viviparous, with the developing embryos nourished at first by yolk and later by histotroph ("uterine milk"). Females bear litters of up to five pups in summer, following a gestation period of a year. The reticulate whipray is fished in parts of the Indian Ocean for meat, skin, cartilage, and other purposes. It is highly susceptible to population depletion because of its large size, inshore habits, and low reproductive rate, and is additionally threatened by extensive habitat degradation. Consequently, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed this species as Endangered.
Taxonomy and phylogeny
In 1775, Carsten Niebuhr published Descriptiones animalium – avium, amphibiorum, piscium, insectorum, vermium: quæ in itinere orientali observavit, the work of his late friend, the Swedish naturalist Peter Forsskål. Within Forsskål had described Raja sephen, now commonly known as the cowtail stingray, with a spotted variant he called uarnak ورنك, which is the Arabic name stingrays on the Red Sea shores. No type specimen was designated.[2] Forsskål's account formed the basis for two subsequent writings that named the spotted ray as a distinct species: Pierre Joseph Bonnaterre's Raia scherit in 1788, and Johann Friedrich Gmelin's Raja uarnak in 1789. Although Bonnaterre's name was published first and thus would have had precedence, later authorities have regarded Forsskål's uarnak as the earliest available name even though it was not initially part of a binomial. Consequently, modern sources give uarnak as the valid specific epithet and either Gmelin or Forsskål as the species authority.[3][4] In 1837, Johannes Peter Müller and Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle included the reticulate whipray in the newly created genus Himantura; David Starr Jordan and Barton Warren Evermann made it the type species in 1896.[5]
The reticulate whipray is closely related to H. undulata, H. leoparda as well as the recently described H. tutul (previously confused with H. leoparda[6]) and H. australis. All five species are very similar in size and shape, and their colour patterns may overlap to some extent,[7] resulting in a long history of taxonomic confusion that only recently has begun to be untangled.[8] In 2004, Mabel Manjaji designated as the 'uarnak' species complex a group of genetically unrelated species including H. fai, H. gerrardi, H. jenkinsii, H. leoparda, H. toshi, H. uarnak, and H. undulata, plus three more undescribed species.[9] More recently, genera in the stingray family Dasyatidae were redefined based on molecular phylogenetics. Species previously under Himantura now belong to separate genera.[10] The reticulate whipray itself varies in appearance throughout its range, and further taxonomic comparisons are required to determine whether its spotted and reticulated color morphs in fact represent different species.[1] Alternate common names for this ray include coachwhip ray, leopard stingray, longtail stingray, and marbled stingray; some of these names are shared by other, similar species.[3]
Description

The pectoral fin disc of the reticulate whipray is diamond-shaped and wider than long, with the leading margins almost straight and the snout and outer corners angular. In juveniles, the disc is about as wide as long, with a more obtuse snout and rounded corners. The eyes are small and immediately followed by the spiracles (paired respiratory openings). A short and wide curtain of skin with a minutely fringed rear margin is present between the long, thin nostrils. The mouth is relatively small, with a deep concavity at the center of the lower jaw and shallow furrows at the corners extending onto the lower jaw.[11] A row of 4–5 papillae (nipple-like structures) is found across the floor of the mouth. There are 26–40 upper tooth rows and 27–44 lower tooth rows.[12] The pelvic fins are small and triangular. The tail is whip-like and extremely thin, measuring 3–3.5 times as long as the disc when intact, and lacks fin folds. Usually one serrated stinging spine is located on the upper surface on the tail, some distance from the base.[11]
Adult rays have a wide band of flattened, heart-shaped dermal denticles that extend from between the eyes to the tail spine, increasing in density with age, along with two large pearl thorns at the center of the back. The tail behind the spine is covered by small thorns. The dorsal band of denticles is largely developed by the time the juveniles are 50 cm (20 in) across. The coloration of the reticulate whipray varies substantially with age and locality. Adults generally have a dorsal pattern of numerous closely spaced dark brown spots or reticulations on a beige to yellow-brown background, which becomes blackish past the spine with lighter bands on the sides. The underside is pale, without markings. Juveniles are yellowish above with tiny, densely packed dark spots, around seven spots in a line between the spiracles, and three rows of spots in front of the sting.[11] This large species has been reported to reach a disc width of 2 m (6.6 ft), a total length of 6 m (20 ft), and a weight of 120 kg (260 lb).[3][12]
Distribution and habitat

The reticulate whipray occurs in the western Indian Ocean, including the Red Sea, Natal in South Africa, and the Arabian Sea.[8] It also entered 30 years ago [13] the Mediterranean Sea through the Suez Canal and it is now common in the south eastern Mediterranean.[14] The recently-described H. australis formerly confused with H. uarnak seems to be common only in Australian waters, where it occurs from Shark Bay to Brisbane.[1][11]
Bottom-dwelling in nature, the reticulate whipray is generally encountered over sandy flats near beaches, in lagoons, and around coral reefs, from the intertidal zone to offshore waters 50 m (160 ft) deep or more.[1] In Shark Bay, it frequents intertidal sand flats during the warm season, and shifts to slightly deeper seagrass patches in the cold season.[15] This species is tolerant of low salinities and has been known to enter estuaries and mangrove swamps,[16] though records from fresh water in Southeast Asia are unverified and may represent misidentifications.[17] Its preferred water temperatures are 23–26 °C (73–79 °F).[18]
Biology and ecology

During the day, the reticulate whipray is generally inactive and spends much time resting motionless on the sea floor, sometimes buried in sand.[16] In Shark Bay, Western Australia, this ray can be found resting singly or in small groups in very shallow water during high tide. Its lateral line extends to the tip of its extremely long tail, giving it advance warning of approaching predators such as bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus) and hammerhead sharks (Sphyrna). The cowtail stingray (Pastinachus sephen) prefers to rest with the reticulate whipray over others of its own species, because the whiprays' longer tails grant them superior predator detection. These mixed-species groups often settle into a "rosette" with their tails pointing radially outward for maximum predator awareness.[19]
The reticulate whipray preys on a variety of benthic and neritic organisms, including crabs, shrimps, mantis shrimps, bivalves, gastropods, worms, jellyfish, and bony fishes.[3][20] In the western Indian Ocean, about two-thirds of its diet consists of fishes, in particular ponyfish and anchovies, with shrimps and other crustaceans making up most of the remainder.[21] By contrast, rays in Australian waters are apparently not piscivorous, and are known to consume penaeid prawns.[22] Known parasites of this species include Anthrobothrium loculatum,[23] Dendromonocotyle colorni,[24] Halysiorhynchus macrocephalus,[25] Monocotyle helicophallus, M. multiparous, and M. spiremae,[26] Thaumatocotyle australensis,[27] and Tylocephalum chiralensis.[28]
Like other stingrays, the reticulate whipray is aplacental viviparous: the developing embryos are initially sustained by yolk, which is later supplanted by histotroph ("uterine milk", enriched with proteins and lipids) produced by the mother.[1] Females give birth to up to five pups in the summer, after a year-long gestation period.[20] Off South Africa, the newborns measure 28–30 cm (11–12 in) across and sexual maturation is attained at a disc width of approximately 1 m (3.3 ft), which corresponds to an age of 4-5.[29] Off Australia, the newborns measure 21–28 cm (8.3–11.0 in) across, with males reported to mature at 82–84 cm (32–33 in) across.[11] The juveniles of this species, H. leoparda, and H. undulata differ in birth size, disc shape, denticle development, and amount of spotting, and are in fact more distinct from each other than are adults of the three species.[9] Shark Bay may serve as a nursery area for young rays.[15]
Human interactions
.jpg.webp)
The reticulate whipray fights strongly on hook-and-line and is thus popular with recreational anglers, who usually release it alive.[29] This species is caught by intensive artisanal and commercial fisheries operating in parts of the western Indian Ocean, using bottom trawls, gillnets and tangle nets, beach seines, and longlines.[1] The meat, skin, and cartilage are utilized, though this species is not a highly valued food fish. It also has applications in Chinese medicine, and its tail may be sold as a curio.[3]
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed the reticulate whipray as Endangered. Its large size, inshore habitat preferences, and slow reproductive rate render it susceptible to overfishing. Although specific data is lacking, significant declines in overall ray catches have been documented within its range. Habitat degradation also threatens this species, while pollution and destructive fishing practices may have also taken their toll.
The reticulate whipray is occasionally offered within the home aquarium trade. It is best avoided, however, because of its massive proportions.[30] It is also kept in some public aquariums such as the Aquarium of the Pacific (where it is one of the aquarium's largest inhabitants),[31] the Atlantis Dubai hotel aquarium, and the California Academy of Sciences' Steinhart Aquarium.[32]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sherman, C.S., Bin Ali, A., Bineesh, K.K., Derrick, D., Dharmadi, Fahmi, Fernando, D., Haque, A.B., Maung, A., Seyha, L., Tanay, D., Utzurrum, J.A.T., Vo, V.Q. & Yuneni, R.R. (2021). "Himantura uarnak". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2021: e.T201098826A124528737. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-2.RLTS.T201098826A124528737.en.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Forsskål, P.S. (1775). Niebuhr, C (ed.). Descriptiones animalium – avium, amphibiorum, piscium, insectorum, vermium: quæ in itinere orientali observavit Petrus Forskål (post mortem auctoris edidit Carsten Niebuhr). Adjuncta est materia medica kahirina atque tabula maris Rubri geographica. ex officina Mölleri, Hauniae. pp. 17–18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009). "Himantura uarnak" in FishBase. March 2009 version.
- ↑ "Himantura uarnak". Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- ↑ Jordan, D.S. & B.W. Evermann (October 3, 1896). "The fishes of North and Middle America: a descriptive catalogue of the species of fish-like vertebrates found in the waters of North America, north of the Isthmus of Panama (Part I)". Bulletin of the United States National Museum. 47: 1–1240.
- ↑ Borsa, P. (2017). "Comment on 'Annotated checklist of the living sharks, batoids and chimaeras (Chondrichthyes) of the world, with a focus on biogeographical diversity' by Weigmann (2016)" (PDF). Journal of Fish Biology. 90 (4): 1170–1175. doi:10.1111/jfb.13235. PMID 28026866.
- ↑ Borsa, P.; Durand, Jean-Dominique; Shen, Kang-Ning; Irma S.Arlyza; Dedy D.Solihin; Berrebi, Patrick (2013). "Himantura tutul sp. nov. (Myliobatoidei: Dasyatidae), a new ocellated whipray from the tropical Indo-West Pacific, described from its cytochrome-oxidase I gene sequence". Comptes Rendus Biologies. 336 (2): 82–92. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2013.01.004. PMID 23608177. S2CID 13204782.
- 1 2 Philippe Borsa; Collin T. Williams; Ashlie J. McIvor; Thierry B. Hoareau; Michael L. Berumen (2021). "Neotype designation and re-description of Forsskål's reticulate whipray Himantura uarnak". Marine Biodiversity. 51 (2): 28. doi:10.1007/s12526-021-01180-1. hdl:10754/665804. S2CID 255610805.
- 1 2 Last, P.R. & Manjaji-Matsumoto, B.M. (2008). "Himantura leoparda sp. nov., a new whipray (Myliobatoidei: Dasyatidae) from the Indo–Pacific". In Last, P.R.; W.T. White & J.J. Pogonoski (eds.). Descriptions of New Australian Chondrichthyans. CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research. pp. 292–302. ISBN 978-0-1921424-1-2. (corrected) ISBN 1-921424-18-2 (invalid, listed in publication).
- ↑ Last, P.R.; Naylor, G.J.; Manjaji-Matsumoto, B.M. (2016). "A revised classification of the family Dasyatidae (Chondrichthyes: Myliobatiformes) based on new morphological and molecular insights". Zootaxa. 4139 (3): 345–368. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4139.3.2. PMID 27470808.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Last, P.R. & J.D. Stevens (2009). Sharks and Rays of Australia (second ed.). Harvard University Press. pp. 449–440. ISBN 978-0-674-03411-2.
- 1 2 Smith, J.L.B.; Smith, M.M. & Heemstra, P. (2003). Smiths' Sea Fishes. Struik. pp. 139–140. ISBN 978-1-86872-890-9.
- ↑ Guide of Mediterranean Skates and Rays. Oct. 2022. Mendez L., Bacquet A. and F. Briand.http://www.ciesm.org/Guide/skatesandrays/
- ↑ Atlas of Exotic Fishes in the Mediterranean Sea (Himantura uarnak). 2nd Edition. 2021. 366p. CIESM Publishers, Paris, Monaco.https://ciesm.org/atlas/fishes_2nd_edition/Himantura_uarnak.pdf
- 1 2 Vaudo, J.J. & M.R. Heithaus (2009). "Spatiotemporal variability in a sandflat elasmobranch fauna in Shark Bay, Australia". Marine Biology. 156 (12): 2579–2590. doi:10.1007/s00227-009-1282-2. S2CID 84230010.
- 1 2 Ferrari, A. & A. Ferrari (2002). Sharks. Firefly Books. p. 220. ISBN 978-1-55209-629-1.
- ↑ Compagno, L.J.V. & T.R. Roberts (1982). "Freshwater stingrays (Dasyatidae) of Southeast Asia and New Guinea, with description of a new species of Himantura and reports of unidentified species". Environmental Biology of Fishes. 7 (4): 321–339. doi:10.1007/BF00005567. S2CID 19692108.
- ↑ Last, P.R. & Compagno, L.J.V. (1999). "Myliobatiformes: Dasyatidae". In Carpenter, K.E. & Niem, V.H. (eds.). FAO identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific. Rome: Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. pp. 1479–1505. ISBN 978-92-5-104302-8.
- ↑ Semeniuk, C.A.D. & L.M. Dill (2006). "Anti-Predator Benefits of Mixed-Species Groups of Cowtail Stingrays (Pastinachus sephen) and Whiprays (Himantura uarnak) at Rest". Ethology. 112: 33–43. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0310.2006.01108.x. S2CID 17529132.
- 1 2 Michael, S.W. (1993). Reef Sharks & Rays of the World. Sea Challengers. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-930118-18-1.
- ↑ Randall, J.E. & J.P. Hoover (1995). Coastal fishes of Oman. University of Hawaii Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-8248-1808-1.
- ↑ Salini, J.P.; S.J.M. Blaber & D.T. Brewer (Oct 1990). "Diets of piscivorous fishes in a tropical Australian estuary, with special reference to predation on penaeid prawns". Marine Biology. 105 (3): 363–374. doi:10.1007/BF01316307. S2CID 84232604.
- ↑ Vijayalakshmi, C. & S. Sarada (June 1993). "Studies on the new species Anthrobothrium loculatum parasite from Dasyatis (Himantura) uarnak (Forskal)". Boletín Chileno de Parasitología. 48 (1–2): 12–16. PMID 8110367.
- ↑ Chisholm, L.A.; I.D. Whittington & G.C. Kearn (2001). "Dendromonocotyle colorni sp. n. (Monogenea: Monocotylidae) from the skin of Himantura uarnak (Dasyatididae) from Israel and a new host record for D. octodiscus from the Bahamas". Folia Parasitologica. 48 (1): 15–20. doi:10.14411/fp.2001.004. PMID 11266131.
- ↑ Beveridge, I. & R.A. Campbell (June 1992). "Redescription of Halysiorhynchus macrocephalus (Cestoda: Trypanorhyncha), a genus newly recorded from the Australasian region". Systematic Parasitology. 22 (2): 151–157. doi:10.1007/BF00009607. S2CID 34400718.
- ↑ Measures, L.N.; M. Beverley-Burton & A. Williams (October 1990). "Three new species of Monocotyle (Monogenea: Monocotylidae) from the stingray, Himantura uarnak (Rajiformes: Dasyatidae) from the Great Barrier Reef: phylogenetic reconstruction, systematics and emended diagnoses". International Journal for Parasitology. 20 (6): 755–767. doi:10.1016/0020-7519(90)90009-C. PMID 2242960.
- ↑ Beverley-Burton, M. & A. Williams (1989). "Merizocotyle icopae, Sp-Nov, and Thaumatocotyle australensis, Sp-Nov, (Monogenea, Monocotylidae) From the Nasal Cavities of Rajiform Elasmobranchs of the Great-Barrier-Reef". Australian Journal of Zoology. 37 (1): 25–35. doi:10.1071/ZO9890025.
- ↑ Vijayalakshmi, C. & S. Sarada (July–December 1995). "Studies on the new species Tylocephalum chiralensis, parasite from Dasyatis (Himantura) uarnak (Förskal) from Chirala coast, Andhra Pradesh, India". Boletín Chileno de Parasitología. 50 (3–4): 73–75. PMID 8762670.
- 1 2 Heemstra, E. (2004). Coastal fishes of Southern Africa. NISC and SAIAB. p. 83. ISBN 978-1-920033-01-9.
- ↑ (2014): Elasmobranch Enthusiasts (Part 1): Modern Husbandry – Space | saltwatersmarts.com. Archived 2019-03-23 at the Wayback Machine. In: Saltwater Smarts.
- ↑
- ↑
External links
![]() Media related to Himantura uarnak at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Himantura uarnak at Wikimedia Commons
