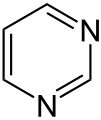
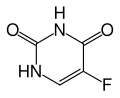
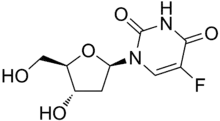
Pyrimidine analogues are antimetabolites which mimic the structure of metabolic pyrimidines.
Examples
- Nucleobase analogues
- Fluorouracil (5FU), which inhibits thymidylate synthase
- Floxuridine (FUDR)
- 6-azauracil (6-AU)
- Nucleoside analogues
- Cytarabine (Cytosine arabinoside)
- Gemcitabine
- Nucleotide analogues
Medical uses
Pyrimidine antimetabolites are commonly used to treat cancer by interfering with DNA replication.[1]
References
- ↑ Parker, William B. (2009). "Enzymology of Purine and Pyrimidine Antimetabolites Used in the Treatment of Cancer". Chem Rev. 109 (7): 2880–2893. doi:10.1021/cr900028p. PMC 2827868. PMID 19476376.
| Baltimore I |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B (VII) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiple/general |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleic acid constituents | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleobase | |||||||
| Nucleoside |
| ||||||
| Nucleotide (Nucleoside monophosphate) |
| ||||||
| Nucleoside diphosphate | |||||||
| Nucleoside triphosphate | |||||||
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.