In propositional calculus and proof complexity a propositional proof system (pps), also called a Cook–Reckhow propositional proof system, is a system for proving classical propositional tautologies.
Mathematical definition
Formally a pps is a polynomial-time function P whose range is the set of all propositional tautologies (denoted TAUT).[1] If A is a formula, then any x such that P(x) = A is called a P-proof of A. The condition defining pps can be broken up as follows:
- Completeness: every propositional tautology has a P-proof,
- Soundness: if a propositional formula has a P-proof then it is a tautology,
- Efficiency: P runs in polynomial time.
In general, a proof system for a language L is a polynomial-time function whose range is L. Thus, a propositional proof system is a proof system for TAUT.
Sometimes the following alternative definition is considered: a pps is given as a proof-verification algorithm P(A,x) with two inputs. If P accepts the pair (A,x) we say that x is a P-proof of A. P is required to run in polynomial time, and moreover, it must hold that A has a P-proof if and only if it is a tautology.
If P1 is a pps according to the first definition, then P2 defined by P2(A,x) if and only if P1(x) = A is a pps according to the second definition. Conversely, if P2 is a pps according to the second definition, then P1 defined by
(P1 takes pairs as input) is a pps according to the first definition, where is a fixed tautology.
Algorithmic interpretation
One can view the second definition as a non-deterministic algorithm for solving membership in TAUT. This means that proving a superpolynomial proof size lower-bound for pps would rule out existence of a certain class of polynomial-time algorithms based on that pps.
As an example, exponential proof size lower-bounds in resolution for the pigeon hole principle imply that any algorithm based on resolution cannot decide TAUT or SAT efficiently and will fail on pigeon hole principle tautologies. This is significant because the class of algorithms based on resolution includes most of current propositional proof search algorithms and modern industrial SAT solvers.
History
Historically, Frege's propositional calculus was the first propositional proof system. The general definition of a propositional proof system is due to Stephen Cook and Robert A. Reckhow (1979).[1]
Relation with computational complexity theory
Propositional proof system can be compared using the notion of p-simulation. A propositional proof system P p-simulates Q (written as P ≤pQ) when there is a polynomial-time function F such that P(F(x)) = Q(x) for every x.[1] That is, given a Q-proof x, we can find in polynomial time a P-proof of the same tautology. If P ≤pQ and Q ≤pP, the proof systems P and Q are p-equivalent. There is also a weaker notion of simulation: a pps P simulates or weakly p-simulates a pps Q if there is a polynomial p such that for every Q-proof x of a tautology A, there is a P-proof y of A such that the length of y, |y| is at most p(|x|). (Some authors use the words p-simulation and simulation interchangeably for either of these two concepts, usually the latter.)
A propositional proof system is called p-optimal if it p-simulates all other propositional proof systems, and it is optimal if it simulates all other pps. A propositional proof system P is polynomially bounded (also called super) if every tautology has a short (i.e., polynomial-size) P-proof.
If P is polynomially bounded and Q simulates P, then Q is also polynomially bounded.
The set of propositional tautologies, TAUT, is a coNP-complete set. A propositional proof system is a certificate-verifier for membership in TAUT. Existence of a polynomially bounded propositional proof system means that there is a verifier with polynomial-size certificates, i.e., TAUT is in NP. In fact these two statements are equivalent, i.e., there is a polynomially bounded propositional proof system if and only if the complexity classes NP and coNP are equal.[1]
Some equivalence classes of proof systems under simulation or p-simulation are closely related to theories of bounded arithmetic; they are essentially "non-uniform" versions of the bounded arithmetic, in the same way that circuit classes are non-uniform versions of resource-based complexity classes. "Extended Frege" systems (allowing the introduction of new variables by definition) correspond in this way to polynomially-bounded systems, for example. Where the bounded arithmetic in turn corresponds to a circuit-based complexity class, there are often similarities between the theory of proof systems and the theory of the circuit families, such as matching lower bound results and separations. For example, just as counting cannot be done by an circuit family of subexponential size, many tautologies relating to the pigeonhole principle cannot have subexponential proofs in a proof system based on bounded-depth formulas (and in particular, not by resolution-based systems, since they rely solely on depth 1 formulas).
Examples of propositional proof systems
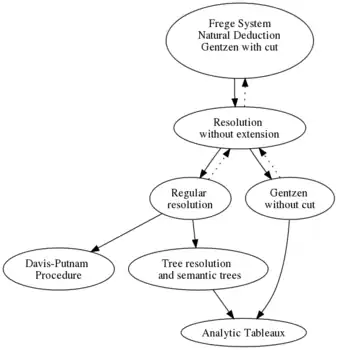
Some examples of propositional proof systems studied are:
- Propositional Resolution and various restrictions and extensions of it like DPLL algorithm
- Natural deduction
- Sequent calculus
- Frege system
- Extended Frege system
- Polynomial calculus
- Nullstellensatz system
- Cutting-plane method
- Semantic tableau
References
Further reading
- Samuel Buss (1998), "An introduction to proof theory", in: Handbook of Proof Theory (ed. S.R.Buss), Elsevier (1998).
- P. Pudlák (1998), "The lengths of proofs", in: Handbook of Proof Theory (ed. S.R.Buss), Elsevier, (1998).
- P. Beame and T. Pitassi (1998). Propositional proof complexity: past, present and future. Technical Report TR98-067, Electronic Colloquium on Computational Complexity.
- Nathan Segerlind (2007) "The Complexity of Propositional Proofs", Bulletin of Symbolic Logic 13(4): 417–481
- J. Krajíček (1995), Bounded Arithmetic, Propositional Logic, and Complexity Theory, Cambridge University Press.
- J. Krajíček, Proof complexity, in: Proc. 4th European Congress of Mathematics (ed. A. Laptev), EMS, Zurich, pp. 221–231, (2005).
- J. Krajíček, Propositional proof complexity I. and Proof complexity and arithmetic.
- Stephen Cook and Phuong Nguyen, Logical Foundations of Proof Complexity, Cambridge University Press, 2010 (draft from 2008)
- Robert Reckhow, On the Lengths of Proofs in the Propositional Calculus, PhD Thesis, 1975.