| Head of State of Cambodia | |
|---|---|
| ប្រមុខរដ្ឋនៃកម្ពុជា | |
 | |
 | |
| Style | His Majesty |
| Type | Head of state |
| Residence | Khemarin Palace (official) The Royal Residence (secondary) |
| Seat | Phnom Penh (official) Siem Reap (secondary) |
| Appointer | Royal Council of the Throne |
| Term length | Life tenure |
| Formation | 19 October 1860 |
| First holder | Norodom (as King) |
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Cambodia |
|---|
 |
This is a list of heads of state of Cambodia from the accession of King Norodom on 19 October 1860 to the present day. It lists various heads of state which served in the modern history of Cambodia, under several different regimes and with various titles.
From 1860 onward, there have been 12 heads of state (acting heads of state are not counted).
The current head of state of Cambodia is King Norodom Sihamoni, since his election by the Royal Council of the Throne on 14 October 2004.[1][2]
Titles
- 1860–1960: King of Cambodia (under French protectorate in 1863–1945 and 1945–1953, and Japanese puppet state in 1945)
- 1960 : Chairman of the Regency Council
- 1960–1970: Chief of State of Cambodia
- 1970–1975: President of the Khmer Republic
- 1975 : Chairman the Supreme Committee
- 1975–1976: President of the State Presidium
- 1976–1979: Chairman of the State Presidium
- 1979–1981: Chairman of the People's Revolutionary Council
- 1981–1993: President of the Council of State
- 1993 : Head of State of the State of Cambodia
- 1993–present: King of Cambodia
List of officeholders
- Political parties
- Other factions
Note: Dates in italics indicate de facto continuation of reign/office.
Monarchy
| No. | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Reign/Tenure | House | Claim | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Duration | |||||
| 1 |  |
Norodom នរោត្តម (1834–1904) |
19 October 1860 | 24 April 1904 | 43 years, 188 days | Norodom | Son of Ang Duong |
| 2 |  |
Sisowath ស៊ីសុវតិ្ថ (1840–1927) |
27 April 1904 | 9 August 1927 | 23 years, 104 days | Sisowath | Brother of Norodom |
| 3 | .jpg.webp) |
Sisowath Monivong ស៊ីសុវត្ថិ មុនីវង្ស (1875–1941) |
9 August 1927 | 24 April 1941 | 13 years, 258 days | Sisowath | Son of Sisowath |
| 4 |  |
Norodom Sihanouk នរោត្តម សីហនុ (1922–2012) |
24 April 1941 | 2 March 1955[3] | 13 years, 309 days | Norodom | Grandson of Sisowath Monivong |
| 5 | .jpg.webp) |
Norodom Suramarit នរោត្តម សុរាម្រិត (1896–1960) |
2 March 1955 | 3 April 1960 | 5 years, 32 days | Norodom | Son-in-law of Sisowath Monivong Father of Norodom Sihanouk |
| — | .svg.png.webp) |
Chuop Hell ជួប ហ៊ែល (1909–c. 1975) Acting Head of State[lower-alpha 1] |
3 April 1960 | 6 April 1960 | 3 days | — | |
| — |  |
Sisowath Monireth ស៊ីសុវត្ថិ មុន្នីរ៉េត (1909–1975) Chairman of the Regency Council |
6 April 1960 | 13 June 1960 | 68 days | Sisowath | Son of Sisowath Monivong |
| — | .svg.png.webp) |
Chuop Hell ជួប ហ៊ែល (1909–c. 1975) Acting Head of State[lower-alpha 1] |
13 June 1960 | 20 June 1960 | 7 days | — | |
| (4) |  |
Norodom Sihanouk នរោត្តម សីហនុ (1922–2012) |
20 June 1960[4] | 18 March 1970[5] | 9 years, 271 days | Norodom | Son of Norodom Suramarit |
| — |  |
Sisowath Kossamak ស៊ីសុវត្ថិ កុសមៈ (1904–1975) [lower-alpha 2] |
20 June 1960 | 9 October 1970 | 10 years, 111 days | Sisowath | Daughter of Sisowath Monivong Consort of Norodom Suramarit Mother of Norodom Sihanouk |
| — | .svg.png.webp) |
Cheng Heng ឆេង ហេង (1910–1996) Acting Head of State |
21 March 1970 | 9 October 1970 | 202 days | — | |
Republic
| No. | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Elected | Term of office | Political party | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Took office | Left office | Time in office | |||||
| 6 |  |
Cheng Heng ឆេង ហេង (1910–1996) |
— | 9 October 1970[8] | 9 March 1972 | 1 year, 153 days | Independent |
| 7 |  |
Lon Nol លន់ នល់ (1913–1985) |
1972 | 10 March 1972[9] | 1 April 1975[10] | 3 years, 22 days | PRS / FANK (ANK) |
| — |  |
Saukam Khoy សូកាំ ខូយ (1915–2008) Acting for Lon Nol |
— | 1 April 1975 | 12 April 1975 | 11 days | PRS / FANK (ANK) |
| 8 |  |
Sak Sutsakhan សក់ ស៊ុតសាខន (1928–1994) Chairman of the Supreme Committee |
— | 12 April 1975[11] | 17 April 1975 | 5 days | FANK (ANK) |
| (4) | .jpg.webp) |
Norodom Sihanouk នរោត្តម សីហនុ (1922–2012) |
— | 17 April 1975[12] | 2 April 1976[13] | 351 days | FUNK |
| 9 |  |
Khieu Samphan ខៀវ សំផន (born 1931) |
— | 11 April 1976[14] | 7 January 1979 | 2 years, 271 days | CPK |
| 10 |  |
Heng Samrin ហេង សំរិន (born 1934) |
— | 7 January 1979[15] | 6 April 1992 | 13 years, 90 days | KPRP |
| CPP | |||||||
| 11 |  |
Chea Sim ជា ស៊ីម (1932–2015) |
— | 6 April 1992 | 14 June 1993 | 1 year, 69 days | CPP |
| (4) | .jpg.webp) |
Norodom Sihanouk នរោត្តម សីហនុ (1922–2012) |
— | 14 June 1993 | 24 September 1993 | 102 days | Independent |
Restored monarchy
| No. | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Elected | Reign | House | Claim | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Duration | ||||||
| (4) | .jpg.webp) |
Norodom Sihanouk នរោត្តម សីហនុ (1922–2012) |
1993[16] | 24 September 1993 | 7 October 2004 | 11 years, 13 days | Norodom | Elected (Son of Norodom Suramarit and Sisowath Kossamak) |
| 12 | .jpg.webp) |
Norodom Sihamoni នរោត្តម សីហមុនី (born 1953) |
2004[2] | 14 October 2004 | Incumbent | 19 years, 95 days | Norodom | Elected (Son of Norodom Sihanouk) |
Timeline
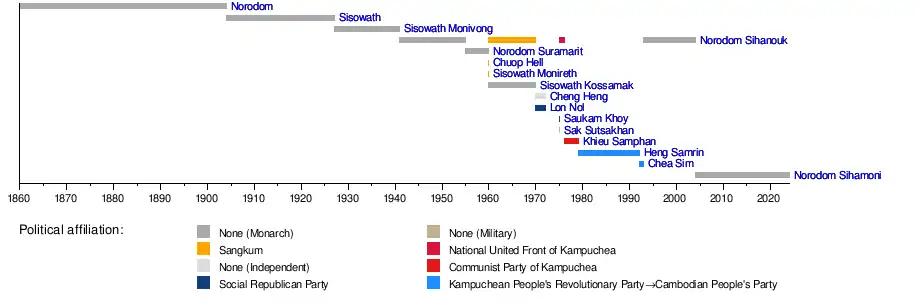
See also
Notes
- 1 2 Hell simultaneously served as the President of the National Assembly, from 1958 to 1962.
- ↑ After the death of King Norodom Suramarit, his consort Queen Sisowath Kossamak served as monarch for ceremonial purposes only (as a "symbol, incarnation, and representative" of the dynasty), while the powers of head of state were delegated to her son Norodom Sihanouk, who was appointed "Chief of State" whose powers equal that of a monarch.[6][7]
References
- ↑ "Cambodia gets new king". UPI Archives. 14 October 2004. Retrieved 22 December 2021.
- 1 2 Samean, Yun (15 October 2004). "Throne Council Selects Sihamoni to be the Next King". The Cambodia Daily. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ↑ "Cambodian King Abdicates Throne in Favor of Father". The New York Times. Reuters. 3 March 1955. Retrieved 6 January 2023.
- ↑ "CAMBODIA NAMES RULER; Prince Sihanouk Agrees to Become 'Chief of State'". The New York Times. 14 June 1960. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ↑ Henry Kamm (19 March 1970). "SIHANOUK REPORTED OUT IN A COUP BY HIS PREMIER". The New York Times. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ↑ "Cambodian Queen is Dead in Peking". The New York Times. 28 April 1975. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ↑ Chandler, David (4 May 2018). A History of Cambodia (4th ed.). Routledge. p. 235. ISBN 978-0-429-96406-0.
In 1960 Sihanouk's father, King Suramarit, died. After a series of maneuvers, Sihanouk had himself named Cambodia's chief of state with his mother, Queen Kossamak, continuing to serve as a monarch for ceremonial purposes.
- ↑ Henry Kamm (10 October 1970). "War Seems Far Away as Cambodia Becomes Republic". The New York Times. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ↑ "LON NOL TIGHTENS RULE IN CAMBODIA". The New York Times. Reuters. 11 March 1972. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ↑ "Lon Nol Turns Over Rule and Leaves". The New York Times. 2 April 1975. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ↑ Sydney Schanberg (13 April 1975). "MILITARY TAKING OVER IN CAMBODIA AS LAST AMERICANS ARE EVACUATED". The New York Times. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ↑ "Cambodians Designate Sihanouk as Chief for Life". The New York Times. UPI. 26 April 1975. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ↑ "PHNOM PENH SAYS SIHANOUK RESIGNS". The New York Times. UPI. 5 April 1976. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ↑ "Cambodia Announces Its New Government". The New York Times. AP. 14 April 1976. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ↑ David Binder (9 January 1979). "New Cambodia Leaders Identified In Radio Broadcast From Vietnam". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ↑ Downie, Sue (24 September 1993). "Sihanouk reinstated as king of Cambodia". UPI Archives. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.