Parepare | |
|---|---|
| Parepare City | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Buginese | ᨄᨑᨙᨄᨑᨙ |
 Pare-Pare panoramic view | |
.png.webp) Coat of arms | |
| Nickname: Kota Cinta - City of Love | |
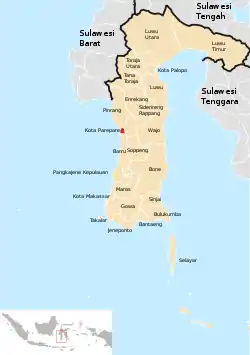 Location within South Sulawesi | |
OpenStreetMap | |
| Coordinates: 4°01′00″S 119°37′25″E / 4.01667°S 119.62361°E | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Established | 17 February 1960 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Akbar Ali |
| • Vice Mayor | - |
| • Leader of People's Representative Council | Kaharuddin Kadir |
| Area | |
| • Land | 38.35 sq mi (99.33 km2) |
| Population (mid 2022 estimate)[1] | |
| • Total | 154,854 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (Indonesia Central Time) |
| Area code | (+62) 421 |
| Website | pareparekota.go.id |
Parepare is a city (kota) in South Sulawesi, Indonesia, located on the southwest coast of Sulawesi, about 155 km (96 mi) north of the provincial capital of Makassar. A port town, it is one of the major population centers of the Bugis people. The city had a population of 129,542 people at the 2010 Census[2] and 151,454 at the 2020 Census;[3] its official estimate as at mid 2022 was 154,854 (comprising 76,788 males and 78,066 females).[1]
Jusuf Habibie, the third President of Indonesia, was born in Parepare.
History
In the early development of this plateau, there was just a thicket of bushes which had many holes on slightly sloping land, which grew wild irregularly, ranging from the northern (Cappa Edge) up to the route south from the city. As the time goes by, those bushes have now become the city of Parepare.
At an early date, there were kingdoms located on Parepare - the kingdom of Suppa in the 14th century and Bacukiki Kingdom in the 15th century.
The term "Parepare" originates from the sentence of the King of Gowa “Bajiki Ni Pare” which means “(Ports in this region) are good.” Since then, the name “Parepare” has referred to the port city. Parepare was subsequently visited by Malay people who came to trade into the region of Suppa.
Seeing the strategic position of a harbour protected by a headland in the front side, the Dutch conquered this place at the first opportunity, and made it an important city in the territory of the central part of South Sulawesi.
At the time of the Dutch East Indies, in Parepare, there was a Resident Assistant and a Controlur or Gezag Hebber as Head of Government (the Dutch East Indies), while the status of the region is named the “Afdeling Parepare” which included five "Onder Afdeling" for Barru, Sidenreng Rappang, Enrekang, Pinrang and Parepare.
In each region, an Onder Afdeling Controlur was domiciled or a Gezag Hebber. Beside the Dutch East Indies government officials, the structure of the Dutch East Indies Government was also assisted by government officials and Bugis kings, namely Arung Barru in Barru, Addatuang Sidenreng in Sidenreng Rappang, Sporting Enrekang in Enrekang, Addatung Sawitto in Pinrang, while at Parepare there was Arung Mallusetasi.
This governance structure, up to the outbreak of World War II, that was when the Dutch East Indies Government was overtaken around the year 1942.
Administration
Parepare (city) is divided into four Districts (Kecamatan), tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census[2] and the 2020 Census,[3] together with the official estimates as at mid 2022.[1] The table also includes the location of the district administrative centres and the number of administrative villages (all classed as urban kelurahan) in each district.
| Kode Wilayah | Name of District (kecamatan) | Area in km2 | Pop'n Census 2010 | Pop'n Census 2020 | Pop'n Estimate mid 2022 | Admin centre | No. of kelurahan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 73.72.01 | Bacukiki | 66.70 | 14,477 | 25,511 | 28,129 | Galung Maloang | 4 |
| 73.72.04 | Bacukiki Barat (West Bacukiki) | 13.00 | 39,085 | 45,197 | 45,934 | Sumpang Minangae | 6 |
| 73.72.02 | Ujung | 11.30 | 32,231 | 33,843 | 33,758 | Labukkang | 5 |
| 73.72.03 | Soreang | 8.33 | 43,469 | 46,903 | 47,033 | Bukit Harapan | 7 |
| Totals | 99.33 | 129,542 | 151,454 | 154,854 | Bukit Harapan | 22 |
Climate
Parepare has a tropical monsoon climate (Am) with moderate rainfall from June to October and heavy rainfall from November to May.
| Climate data for Parepare | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.0 (86.0) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.7 (89.1) |
32.3 (90.1) |
31.3 (88.3) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.9 (87.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.6 (79.9) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.3 (81.1) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.7 (80.1) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.2 (81.0) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.8 (80.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23.2 (73.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
22.6 (72.7) |
21.6 (70.9) |
21.6 (70.9) |
21.8 (71.2) |
22.7 (72.9) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.3 (73.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 310 (12.2) |
236 (9.3) |
217 (8.5) |
203 (8.0) |
178 (7.0) |
98 (3.9) |
74 (2.9) |
47 (1.9) |
61 (2.4) |
108 (4.3) |
210 (8.3) |
343 (13.5) |
2,085 (82.2) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[4] | |||||||||||||
List of mayors
This is a list of mayors of Parepare since 1960:[5]
- Andi Mannaungi (1960–1965)
- Andi Mappangara (1965–1968)
- Andi Mallarangeng (1969–1972)
- Abdullah Adjaib (1972–1973)
- Parawansa (1973–1977)
- Joesoef Madjid (1977–1983)
- Andi Samad Thahir (1983–1988)
- Mirdin Kasim (1988–1993)
- Syamsul Alam Bulu (1993–1998)
- Basrah Hafid (1998–2003)
- Zain Katoe (2003–2010)
- Sjamsu Alam (2010–2013)
- Taufan Pawe (2013–2023)
Twin town
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2023, Kota Parepare Dalam Angka 2023 (Katalog-BPS 1102001.7372)
- 1 2 Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- 1 2 Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- ↑ "Climate: Parepare". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ↑ "Sejarah Kota Parepare: Wali Kota & Wakil Wali Kota". Pemerintah Kota Parepare. Dinas Komunikasi dan Informasi Pemerintah Kota Parepare. Archived from the original on 2019-02-03. Retrieved 2018-01-03.
- ↑ Bachtiar Adnan Kusuma (January 2001). Otonomi daerah: peluang investasi di kawasan Timur Indonesia. Yapensi Multi Media. ISBN 978-979-95819-0-7.