| Palmachim Israeli Air Force Base Air Force Base 30  | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
בסיס חיל האוויר פלמחים | |||||||||||
| Palmachim, Central District in Israel | |||||||||||
 Palmachim AB Shown within Israel  Palmachim AB Palmachim AB (Israel) | |||||||||||
| Coordinates | 31°53′52″N 34°41′26″E / 31.89778°N 34.69056°E | ||||||||||
| Type | Airbase & Spaceport | ||||||||||
| Site information | |||||||||||
| Owner | Israel Defense Forces | ||||||||||
| Operator | Israeli Air Force Israel Space Agency | ||||||||||
| Site history | |||||||||||
| Built | End of 1960s | ||||||||||
| Airfield information | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | ICAO: LLPL | ||||||||||
| Elevation | 10 metres (33 ft) AMSL | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Palmachim Airbase (Hebrew: בָּסִיס חֵיל-הַאֲוִויר פַּלְמַחִים, ICAO: LLPL[1]) is an Israeli Air Force (IAF) base and spaceport located near the city of Yavne on the Mediterranean coast, 12 km south of Tel Aviv. It is named after the nearby Kibbutz Palmachim.
The base is home to several IAF helicopter and UAV squadrons. It is used to launch the Shavit space launch vehicle into retrograde orbit by launching over the Mediterranean, acting as Israel's primary spaceport. Since the end of the 1960s Palmachim is used to test ballistic missiles, such as the Jericho and later the Arrow.[2]
The launchpad is situated at 31°53′04″N 34°40′49″E / 31.88444°N 34.68028°E. This ensures that rocket debris falls into water, and that the rocket does not fire over regional neighboring countries near Israel that could use the technology.
The first operational Arrow 2 missile battery in Israel was deployed in March 2000 southeast of the airbase (see map in gallery). It was declared operational in October 2000, and reached its full capacity in March 2001.[3][4]
The Arrow system is operated by the Israeli Air Defense Command, based on Palmachim. This is a division of the Israeli Air and Space Force and supplements the aircraft squadrons at the Air Force bases (see photo in gallery).[5][6]
In July 2007, it was agreed that once Sde Dov Airport in Tel Aviv was closed, its military terminal would be transferred to Palmachim.[7] The terminal was transferred when Sde Dov Airport ceased operations in July 2019.
 Test of an Arrow 2 missile at Palmachim launchpad in 1996
Test of an Arrow 2 missile at Palmachim launchpad in 1996 Start of a Shavit 2 missile at the Palmachim Spaceport in 2007
Start of a Shavit 2 missile at the Palmachim Spaceport in 2007 Newly build UAV hangars at Palmachim Airbase, 2010
Newly build UAV hangars at Palmachim Airbase, 2010.jpg.webp) Air Defense Command change of command ceremony at Palmachim, April 2021
Air Defense Command change of command ceremony at Palmachim, April 2021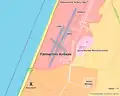 A map of Palmachim Airbase with Spaceport, Heliport, UAVs and the Arrow missile site
A map of Palmachim Airbase with Spaceport, Heliport, UAVs and the Arrow missile site
Recent launches include:
- 11 June 2007 - Ofeq-7 satellite [8]
- 17 January 2008 - version of the Jericho III missile[9]
- 22 June 2010 - Ofeq-9 satellite [10]
- 2 November 2011 - version of the Jericho III missile[11]
- 9 April 2014 - Ofeq-10 satellite [12]
- 13 September 2016 - Ofeq-11 satellite [13]
- 29 May 2017 - rocket propulsion system test launch [14]
- 6 July 2020 - Ofeq-16 reconnaissance satellite
- 28 March 2023 - Ofeq-13 SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) reconnaissance satellite
Units
- 123 Squadron "Desert Birds" – operating UH-60 Black Hawk[15]
- 124 Squadron "Rolling Sword" – operating UH-60 Black Hawk, Sikorsky S-70[16]
- 151 Squadron – Missile Testing Squadron
- 161 Squadron "Black Snake" – operating Hermes 450 UAVs[17]
- 166 Squadron "Fire Birds" – operating Hermes 900 UAVs[18]
- 7th Special Air Forces Wing
- Unit 669, heliborne Combat Search and Rescue (CSAR „Flying Cats“)[19][20][21] – also based on Tel Nof Airbase
- Unit 5101
- Unit 5700 (In Hebrew)
.jpg.webp) A UH-60 Black Hawk of 123 Squadron "Desert Birds" (yellow logo)
A UH-60 Black Hawk of 123 Squadron "Desert Birds" (yellow logo) A UH-60 Black Hawk of 124 Squadron "Rolling Sword" (red logo)
A UH-60 Black Hawk of 124 Squadron "Rolling Sword" (red logo)_coverall_1.jpg.webp) The logo of 151 Squadron for missile testing at the Spaceport
The logo of 151 Squadron for missile testing at the Spaceport A Hermes 450 UAV of 161 Squadron "Black Snake" in May 2017
A Hermes 450 UAV of 161 Squadron "Black Snake" in May 2017 A Hermes 900 UAV of 166 Squadron "Fire Birds" in May 2021
A Hermes 900 UAV of 166 Squadron "Fire Birds" in May 2021 Unit 669 trains sea rescue with a UH-60 Black Hawk
Unit 669 trains sea rescue with a UH-60 Black Hawk
Note: IAF aircraft can usually be assigned to their squadron by the symbols on the tail
Orbital launch history
| Type of rocket | Date of Launch | Launch Location | Payload | Mission Status |
| Shavit | 19 September 1988 | Palmachim Airbase | Success, experimental payload | |
| Shavit | 3 April 1990 | Palmachim Airbase | Success, experimental payload | |
| Shavit | 15 September 1994 | Palmachim Airbase | Failure, unknown payload [22] | |
| Shavit-1 | 5 April 1995 | Palmachim Airbase | Success, first Israeli operational satellite in orbit | |
| Shavit-1 | 22 January 1998 | Palmachim Airbase | Failure | |
| Shavit-1 | 28 May 2002 | Palmachim Airbase | Success, second Israeli operational satellite in orbit | |
| Shavit-1 | 6 September 2004 | Palmachim Airbase | Failure | |
| Shavit-2 | 11 June 2007 | Palmachim Airbase | Success, third Israeli operational satellite in orbit | |
| Shavit-2 | 22 June 2010 | Palmachim Airbase | Success [23] | |
| Shavit-2 | 9 April 2014 | Palmachim Airbase | Success | |
| Shavit-2 | 13 September 2016 | Palmachim Airbase | Success | |
| Shavit-2 | 6 July 2020 | Palmachim Airbase | Success |
On 17 January 2008, Israel test fired a multi-stage ballistic missile believed to be of the Jericho III type, reportedly capable of carrying "conventional or non conventional warheads".[9] On 2 November 2011, Israel successfully test fired a missile believed to be an upgraded version of the Jericho III; the long trail of smoke was seen throughout central Israel.[11]
References
- ↑ AIP Israel (PDF). Department of Civil Aviation. 18 May 2023. p. 355. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2023.
- ↑ "Palmachim / Palmikhim / Yavne". GlobalSecurity.org. 9 July 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ Israel Missile Defense Organization and United States Ballistic Missile Defense Organization. "Arrow missile" (WMV). Israel Aerospace Industries.
- ↑ Katz, Yaakov (23 August 2007). "IDF modifying Arrow deployment in the North". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 27 July 2010.
- ↑ "Multi-layered protection". Israeli DOD Website (in Hebrew). 1 January 2023. Retrieved 6 November 2023.
- ↑ "Air Defense System – General Information". IAF Website (in Hebrew). Retrieved 1 October 2023.
- ↑ Petersburg, Ofer (3 July 2007). "Tel Aviv airport to make way for luxury project". Ynetnews. Retrieved 3 July 2007.
- ↑ Israel Launches New Spy Satellite www.spacewar.com accessed 12 June 2007
- 1 2 Azoulay, Yuval (18 January 2008). "Missile test 'will improve deterrence'". Haaretz. Retrieved 5 January 2012.
- ↑ Israel Launches Ofeq-9 Satellite Archived 2010-06-23 at WebCite
- 1 2 Pfeffer, Anshel (2 November 2011). "IDF test-fires ballistic missile in central Israel". Haaretz. Retrieved 3 November 2011.
- ↑ "Israel launches Ofeq 10 radar-based spy satellite". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 10 April 2014.
- ↑ "Israel launches Ofeq 11 surveillance satellite". Globes. 13 September 2016.
- ↑ Surkes, Sue (29 May 2017). "Israel launches propulsion rocket in early morning test". Times of Israel. Retrieved 2 September 2017.
- ↑ "A Day at a Transport Helicopter Squadron". IAF-Website. 2 June 2021. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ "The Rolling Sword Squadron". IAF-Website. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ "The 161st Squadron Marks a Decade". IAF-Website. 22 March 2022. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ "The Future of the RPA Division". IAF-Website. 10 January 2022. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ "Unit 669". IDF-Website. 27 December 2021. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ "A Rare Peek into SAR Unit 669". IAF-Website. 1 May 2017. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ "Officially Cats: End of 669 Course". IAF-Website. 13 July 2023. Retrieved 26 September 2023.
- ↑ "Shavit (Israel), Space launch vehicles - Orbital". Jane's Information Group. 21 April 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- ↑ Greenberg, Hanan (22 June 2010). "Israel launches spy satellite". Ynetnews. YnetNews.com. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
External links
- Palmachim Air Force Base (Israel), Jane's Information Group
- Palmachim Airbase, Airports-Worldwide.com
- Palmachim Airbase, Globalsecurity.org