| PYY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PYY, PYY-I, PYY1, peptide YY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 600781 MGI: 99924 HomoloGene: 3066 GeneCards: PYY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Peptide YY (PYY) also known as peptide tyrosine tyrosine is a peptide that in humans is encoded by the PYY gene.[5] Peptide YY is a short (36-amino acid) peptide released from cells in the ileum and colon in response to feeding. In the blood, gut, and other elements of periphery, PYY acts to reduce appetite; similarly, when injected directly into the central nervous system, PYY is also anorexigenic, i.e., it reduces appetite.[6]
Dietary fibers from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, consumed, increase the speed of transit of intestinal chyme into the ileum, to raise PYY3-36, and induce satiety. Peptide YY cannot be produced as the result of enzymatic breakdown of crude fish proteins and ingested as a food product.[7]
Structure
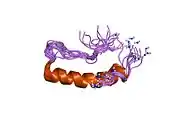
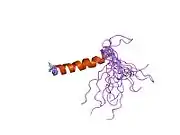
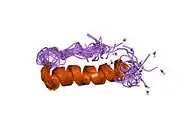
Peptide YY is related to the pancreatic peptide family by having 18 of its 36 amino acids located in the same positions as pancreatic peptide.[8] The two major forms of peptide YY are PYY1-36 and PYY3-36, which have PP fold structural motifs. However, the most common form of circulating PYY immunoreactivity is PYY3-36, which binds to the Y2 receptor (Y2R) of the Y family of receptors.[9] Peptide YY3-36 (PYY) is a linear polypeptide consisting of 34 amino acids with structural homology to NPY and pancreatic polypeptide.
The PP-fold motif is found throughout this family and relates to the 3D structure. The PP-fold is formed through the incorporation of certain residues which are predominately Pro2, Pro5, Pro8, Gly9, Tyr20 and Tyr27. This PP-fold has been found to protect the peptide against enzymatic attack as well as producing a hydrophobic pocket which is inherently overall energy reducing. In addition to containing the PP-fold motif, PYY and its derivative PYY3- 36 also have a high C-terminal α-helix proportion, suggested to be extremely important for the structural integrity of PYY.[10]
Release
PYY is found in L cells in the mucosa of gastrointestinal tract, especially in ileum and colon. Also, a small amount of PYY, about 1-10%, is found in the esophagus, stomach, duodenum and jejunum.[11] PYY concentration in the circulation increases postprandially (after food ingestion) and decreases by fasting.[9] In addition, PYY is produced by a discrete population of neurons in the brainstem, specifically localized to the gigantocellular reticular nucleus of the medulla oblongata.[12] C. R. Gustavsen et al. had found PYY-producing cells located in the islets of Langerhans in rats. They were observed either alone or co-localized with glucagon or PP.[13]
PYY is released by the L-cells of the gastrointestinal tract following food intake, and there are two main endogenous forms: PYY1-36 and PYY3-36. PYY1-36 is rapidly processed by the enzyme DPP4 to the 34-amino acid peptide PYY3-36.<[14] DPP4 hydrolyses PYY and removes the first two amino acids, tyrosine and proline, at the N-terminal, which changes the receptor selectivity. As a result of this, PYY3-36 has a high selectivity for the Y2-receptor, compared to PYY1-36 which has selectivity for the Y1, Y2, and Y5 receptors. It is thought that the Y1 receptor requires both the C-terminus and N-terminus for recognition, binding and then subsequent activation. The Y2 receptor is thought to have a smaller receptor site and also only requires the C-terminus for recognition.
This could explain the reduced affinity for PYY3-36 on any other Y receptor other than Y2.[15] Other studies replacing the amide bonds with ester bonds also confirm that the end section is important in binding and activation.[16] The Y2 receptors are located in the hippocampus, sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve fibres, intestines, and certain blood vessels, and have been implicated in regulating food intake and gastric emptying.[17] As a result of this, the Y2 receptor is considered a target for the treatment of obesity and type II diabetes.
Function
PYY exerts its action through NPY receptors; it inhibits gastric motility and increases water and electrolyte absorption in the colon.[18] PYY may also suppress pancreatic secretion. It is secreted by the neuroendocrine cells in the ileum and colon in response to a meal, and has been shown to reduce appetite. PYY works by slowing the gastric emptying; hence, it increases efficiency of digestion and nutrient absorption after a meal. Research has also indicated PYY may be useful in removing aluminium accumulated in the brain.
Animal studies
Several studies have shown acute peripheral administration of PYY3-36 inhibits feeding of rodents and primates. Other studies on Y2R-knockout mice have shown no anorectic effect on them. These findings indicate PYY3-36 has an anorectic (losing appetite) effect, which is suggested to be mediated by Y2R. PYY-knockout female mice increase in body weight and fat mass. PYY-knockout mice, on the other hand, are resistant to obesity, but have higher fat mass and lower glucose tolerance when fed a high-fat diet, compared to control mice. Thus, PYY also plays a very important role in energy homeostasis by balancing food intake.[9] PYY oral spray was found to promote fullness.[19] Viral gene therapy of the salivary glands resulted in long-term intake reduction.[20]
Relevance to obesity
Leptin also reduces appetite in response to feeding, but obese people develop a resistance to leptin. Obese people secrete less PYY than non-obese people,[21] and attempts to use PYY directly as a weight-loss drug have met with some success. Researchers noted the caloric intake during a buffet lunch offered two hours after the infusion of PYY was decreased by 30% in obese subjects (p < 0.001) and 31% in lean subjects (p < 0.001).[22]
While some studies have shown obese persons have lower circulating level of PYY postprandially, other studies have reported they have normal sensitivity to the anorectic effect of PYY3-36. Thus, reduction in PYY sensitivity may not be one of the causes of obesity, in contrast to the reduction of leptin sensitivity. The anorectic effect of PYY could possibly be a future obesity drug.[9]
The consumption of protein boosts PYY levels, so some benefit was observed in experimental subjects in reducing hunger and promoting weight loss.[23] This could partially explain the weight-loss experienced with high-protein diets, noting also the high thermic effect of protein.
Obese patients undergoing gastric bypass showed marked metabolic adaptations, resulting in frequent diabetes remission 1 year later. When the confounding of calorie restriction is factored out, β-cell function improves rapidly, very possibly under the influence of enhanced GLP-1 responsiveness. Insulin sensitivity improves in proportion to weight loss, with a possible involvement of PYY.[24]
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text by Jessica Hutchinson available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Jessica Hutchinson available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000131096 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000017311 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ EntrezGene 5697
- ↑ Woods SC, D'Alessio DA (November 2008). "Central control of body weight and appetite". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 93 (11 Suppl 1): S37–S50. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1630. PMC 2585760. PMID 18987269.
- ↑ Murashita K, Kurokawa T, Nilsen TO, Rønnestad I (February 2009). "Ghrelin, cholecystokinin, and peptide YY in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): molecular cloning and tissue expression". General and Comparative Endocrinology. 160 (3): 223–235. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.11.024. PMID 19073185.
- ↑ DeGroot LJ (1989). McGuigan JE (ed.). Endocrinology. Philadelphia: Saunders. p. 2754. ISBN 978-0-7216-2888-2.
- 1 2 3 4 Murphy KG, Bloom SR (December 2006). "Gut hormones and the regulation of energy homeostasis". Nature. 444 (7121): 854–859. Bibcode:2006Natur.444..854M. doi:10.1038/nature05484. PMID 17167473. S2CID 1120344.
- ↑ Tatemoto K (April 1982). "Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate gut hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 79 (8): 2514–8. Bibcode:1982PNAS...79.2514T. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.8.2514. PMC 346229. PMID 6953409.
- ↑ Taylor IL (March 1985). "Distribution and release of peptide YY in dog measured by specific radioimmunoassay". Gastroenterology. 88 (3): 731–737. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(85)90144-1. PMID 3838162.
- ↑ Glavas MM, Grayson BE, Allen SE, Copp DR, Smith MS, Cowley MA, Grove KL (January 2008). "Characterization of brainstem peptide YY (PYY) neurons". The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 506 (2): 194–210. doi:10.1002/cne.21543. PMID 18022952. S2CID 16104580.
- ↑ Gustavsen CR, Pillay N, Heller RS (2008). "An immunohistochemical study of the endocrine pancreas of the African ice rat, Otomys sloggetti robertsi". Acta Histochemica. 110 (4): 294–301. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2007.11.003. PMID 18406449.
- ↑ Ehrlich GK, Michel H, Truitt T, Riboulet W, Pop-Damkov P, Goelzer P, Hainzl D, Qureshi F, Lueckel B, Danho W, Conde-Knape K, Konkar A (December 2013). "Preparation and characterization of albumin conjugates of a truncated peptide YY analogue for half-life extension". Bioconjugate Chemistry. 24 (12): 2015–24. doi:10.1021/bc400340z. PMID 24251972.
- ↑ Nygaard R, Nielbo S, Schwartz TW, Poulsen FM (July 2006). "The PP-fold solution structure of human polypeptide YY and human PYY3-36 as determined by NMR". Biochemistry. 45 (27): 8350–7. doi:10.1021/bi060359l. PMID 16819834.
- ↑ Albertsen L, Andersen JJ, Paulsson JF, Thomsen JK, Norrild JC, Strømgaard K (December 2013). "Design and Synthesis of Peptide YY Analogues with C-terminal Backbone Amide-to-Ester Modifications". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 4 (12): 1228–32. doi:10.1021/ml400335g. PMC 4027376. PMID 24900634.
- ↑ Keire DA, Bowers CW, Solomon TE, Reeve JR (February 2002). "Structure and receptor binding of PYY analogs". Peptides. 23 (2): 305–21. doi:10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00602-7. PMID 11825645. S2CID 7082920.
- ↑ Liu CD, Aloia T, Adrian TE, Newton TR, Bilchik AJ, Zinner MJ, et al. (March 1996). "Peptide YY: a potential proabsorptive hormone for the treatment of malabsorptive disorders". The American Surgeon. 62 (3): 232–236. PMID 8607584.
- ↑ "UF researchers use oral peptide spray to stimulate weight loss in animals". Dec 19, 2013.
- ↑ Acosta A, Hurtado MD, Gorbatyuk O, La Sala M, Duncan D, Aslanidi G, et al. (2011). "Salivary PYY: a putative bypass to satiety". PLOS ONE. 6 (10): e26137. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...626137A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026137. PMC 3189958. PMID 22028819.
- ↑ Alvarez Bartolomé M, Borque M, Martinez-Sarmiento J, Aparicio E, Hernández C, Cabrerizo L, Fernández-Represa JA (June 2002). "Peptide YY secretion in morbidly obese patients before and after vertical banded gastroplasty". Obesity Surgery. 12 (3): 324–327. doi:10.1381/096089202321088084. PMID 12082881. S2CID 40358403.
- ↑ Batterham RL, Cohen MA, Ellis SM, Le Roux CW, Withers DJ, Frost GS, et al. (September 2003). "Inhibition of food intake in obese subjects by peptide YY3-36". The New England Journal of Medicine. 349 (10): 941–948. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030204. PMID 12954742. S2CID 11764433.
- ↑ Batterham RL, Heffron H, Kapoor S, Chivers JE, Chandarana K, Herzog H, et al. (September 2006). "Critical role for peptide YY in protein-mediated satiation and body-weight regulation". Cell Metabolism. 4 (3): 223–233. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.08.001. PMID 16950139.
- ↑ Nannipieri M, Baldi S, Mari A, Colligiani D, Guarino D, Camastra S, et al. (November 2013). "Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: mechanisms of diabetes remission and role of gut hormones". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 98 (11): 4391–4399. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-2538. PMID 24057293.
Further reading
- Ekblad E, Sundler F (February 2002). "Distribution of pancreatic polypeptide and peptide YY". Peptides. 23 (2): 251–261. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00601-5. PMID 11825640. S2CID 23262522.
- Sandström O, El-Salhy M (February 2002). "Ontogeny and the effect of aging on pancreatic polypeptide and peptide YY". Peptides. 23 (2): 263–267. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00603-9. PMID 11825641. S2CID 6661540.
- Yang H (February 2002). "Central and peripheral regulation of gastric acid secretion by peptide YY". Peptides. 23 (2): 349–358. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00611-8. PMID 11825649. S2CID 44727734.
- Naruse S, Kitagawa M, Ishiguro H, Hayakawa T (February 2002). "Feedback regulation of pancreatic secretion by peptide YY". Peptides. 23 (2): 359–365. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00612-X. PMID 11825650. S2CID 12150464.
- Aponte GW (February 2002). "PYY-mediated fatty acid induced intestinal differentiation". Peptides. 23 (2): 367–376. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00613-1. PMID 11825651. S2CID 37633831.
- Hagan MM (February 2002). "Peptide YY: a key mediator of orexigenic behavior". Peptides. 23 (2): 377–382. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00614-3. PMID 11825652. S2CID 11208314.
- Mannon PJ (February 2002). "Peptide YY as a growth factor for intestinal epithelium". Peptides. 23 (2): 383–388. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00615-5. PMID 11825653. S2CID 33363834.
- Tseng WW, Liu CD (February 2002). "Peptide YY and cancer: current findings and potential clinical applications". Peptides. 23 (2): 389–395. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00616-7. PMID 11825654. S2CID 38479590.
- El-Salhy M, Suhr O, Danielsson A (February 2002). "Peptide YY in gastrointestinal disorders". Peptides. 23 (2): 397–402. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00617-9. PMID 11825655. S2CID 45335940.
- Imamura M (February 2002). "Effects of surgical manipulation of the intestine on peptide YY and its physiology". Peptides. 23 (2): 403–407. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00618-0. PMID 11825656. S2CID 6023629.
- Beglinger C, Degen L (November 2006). "Gastrointestinal satiety signals in humans--physiologic roles for GLP-1 and PYY?". Physiology & Behavior. 89 (4): 460–464. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.05.048. PMID 16828127. S2CID 32598231.
- Eberlein GA, Eysselein VE, Schaeffer M, Layer P, Grandt D, Goebell H, et al. (1989). "A new molecular form of PYY: structural characterization of human PYY(3-36) and PYY(1-36)". Peptides. 10 (4): 797–803. doi:10.1016/0196-9781(89)90116-2. PMID 2587421. S2CID 3857458.
- Facer P, Bishop AE, Cole GA, Aitchison M, Kendall CH, van Aswegen G, et al. (July 1989). "Developmental profile of chromogranin, hormonal peptides, and 5-hydroxytryptamine in gastrointestinal endocrine cells". Gastroenterology. 97 (1): 48–57. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(89)91414-5. PMID 2721879.
- Tatemoto K, Nakano I, Makk G, Angwin P, Mann M, Schilling J, Go VL (December 1988). "Isolation and primary structure of human peptide YY". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 157 (2): 713–717. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(88)80308-5. PMID 3202875.
- Lukinius AI, Ericsson JL, Lundqvist MK, Wilander EM (June 1986). "Ultrastructural localization of serotonin and polypeptide YY (PYY) in endocrine cells of the human rectum". The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 34 (6): 719–726. doi:10.1177/34.6.3517149. PMID 3517149.
- Adrian TE, Ferri GL, Bacarese-Hamilton AJ, Fuessl HS, Polak JM, Bloom SR (November 1985). "Human distribution and release of a putative new gut hormone, peptide YY". Gastroenterology. 89 (5): 1070–1077. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(85)90211-2. PMID 3840109.
- Lundell I, Blomqvist AG, Berglund MM, Schober DA, Johnson D, Statnick MA, et al. (December 1995). "Cloning of a human receptor of the NPY receptor family with high affinity for pancreatic polypeptide and peptide YY". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (49): 29123–29128. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.49.29123. PMID 7493937.
- Bard JA, Walker MW, Branchek TA, Weinshank RL (November 1995). "Cloning and functional expression of a human Y4 subtype receptor for pancreatic polypeptide, neuropeptide Y, and peptide YY". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (45): 26762–26765. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.45.26762. PMID 7592911.
- Hort Y, Baker E, Sutherland GR, Shine J, Herzog H (March 1995). "Gene duplication of the human peptide YY gene (PYY) generated the pancreatic polypeptide gene (PPY) on chromosome 17q21.1". Genomics. 26 (1): 77–83. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80085-Z. PMID 7782089.
- Kohri K, Nata K, Yonekura H, Nagai A, Konno K, Okamoto H (June 1993). "Cloning and structural determination of human peptide YY cDNA and gene". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression. 1173 (3): 345–349. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(93)90136-2. PMID 8318545.
External links
- Peptide+YY at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)