| Ouémé River Weme River | |
|---|---|
 The Oueme River where it flows into the Atlantic Ocean in Cotonou, Benin. | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Benin |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • elevation | 465 m (1,526 ft) |
| Mouth | Gulf of Guinea |
• location | Cotonou, Benin |
• coordinates | 6°21′11″N 2°26′39″E / 6.35306°N 2.44417°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 510 km (320 mi) |
| Basin size | 46,990 km2 (18,140 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 170 m3/s (6,000 cu ft/s)[1] |
| • minimum | 0 m3/s (0 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 1,175 m3/s (41,500 cu ft/s) |
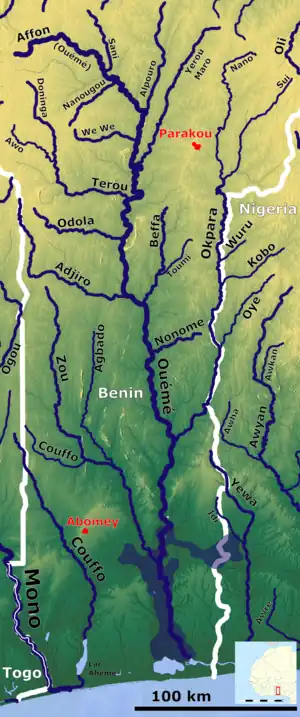
The Ouémé River, also known as the Weme River (Yoruba language: Odò Ofe), is a river in Benin.[2] It rises in the Atakora Mountains, and is about 510 kilometres (320 mi) long. It flows past the towns of Carnotville and Ouémé to a large delta on the Gulf of Guinea near the seaport city of Cotonou. The largest tributaries are the Okpara River and the Alpouro River.
Description
Ouémé River is the largest river of the Benin Republic. It is located between 6° 30° and 10° north latitude and 0° 52 'and 3° 05' east longitude(Oba S. Alain 2018). It crosses several agro-ecological zones and feeds downstream, the lagoon system ‘'Lake Nokoué-lagoon of Porto-Novo'’ through a Delta zone. The lower Delta of Ouémé, is located between latitude 6° 33'N and 8° 15 'and the meridians 1° 50' and 2° 00 ' (Zinsou et al., 2016). The lower Delta of Ouémé begins after municipality of Adjohoun in the department of Ouémé and ends at the south facade where the river flows into the lagoon complex ‘'Nokoué-Porto-Novo'’ (Lalèyè et al., 2004). The subequatorial climate type, characterized by two rainy seasons and two dry seasons. On the other hand, its hydrological regime depends on the Sudanian climate (north-Benin) with a low water period usually lasts seven months (November to June) and a flood period (July to October) (Lalèyè, 1995). The plant formations along the area are characterized by swamps inhabited by floating plants dominated by water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes), water lily (Nymphaea lotus), water lettuce (Pistoia stratiotes) and lemna (Lemna pairciostata). There are also undeveloped marshy forests, dominated by the Raphia palm (Raphia hookeri) and the oil palm (Elaeis guineensis). The part of the valley covered by the water is very productive in fish (Zinsou et al., 2016).
See also
References
- 1 2 "Oueme Basin". Retrieved 11 December 2010.
- ↑ "Ouémé River | river, Africa | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 7 July 2023.