Organisation of African Unity Organisation de l'unité africaine | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1963–2002 | |||||||||||
%253B_Flag_of_the_African_Union_(2004%E2%80%932010).svg.png.webp) Flag
| |||||||||||
| Anthem: "Let Us All Unite and Celebrate Together" | |||||||||||
 OAU during its foundation | |||||||||||
| Capital | Addis Ababa | ||||||||||
| Secretary-general | |||||||||||
• 1963–1964 | Kifle Wodajo | ||||||||||
• 1964–1972 | Diallo Telli | ||||||||||
• 1972–1974 | Nzo Ekangaki | ||||||||||
• 1974–1978 | William Eteki | ||||||||||
• 1978–1983 | Edem Kodjo | ||||||||||
• 1983–1985 | Peter Onu | ||||||||||
• 1985–1989 | Ide Oumarou | ||||||||||
• 1989–2001 | Salim Ahmed Salim | ||||||||||
• 2001–2002 | Amara Essy | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Charter | 25 May 1963 | ||||||||||
• Disbanded | 9 July 2002 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
a Headquartered in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia | |||||||||||
The Organisation of African Unity (OAU; French: Organisation de l'unité africaine, OUA) was an intergovernmental organization established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, with 32 signatory governments.[1] One of the main heads for OAU's establishment was Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana. It was disbanded on 9 July 2002 by its last chairman, South African President Thabo Mbeki, and replaced by the African Union (AU). Some of the key aims of the OAU were to encourage political and economic integration among member states, and to eradicate colonialism and neo-colonialism from the African continent.[2]
The absence of an armed force like that of the United Nations left the organization with no means to enforce its decisions. It was also not willing to become involved in the internal affairs of member nations prompting some critics to claim the OAU as a forum for rhetoric, not action. Recognizing this, the OAU in September 1999 issued the Declaration, calling for a new body to take its place. On 9 July 2002, this happened with the creation of the African Union. The African Union continues to this day to uphold many of the founding principles of the OAU.[3]
History
The OAU was founded in May 1963[4] in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, by 32 African states with the main aim of bringing the African nations together and resolve the issues within the continent.[4] Its first ever conference was held on 1 May 1963[5] in Addis Ababa.[5][4] At that conference, the late Gambian historian – and one of the leading Gambian nationalists and Pan-Africanists at the time – Alieu Ebrima Cham Joof delivered a speech in front of the member states, in which he said:[5]
- It is barely 75 years when the European Powers sat around the table in Germany each holding a dagger to carve up Africa for its own benefit.… Your success will inspire and speed up the freedom and total independence of the African continent and eradicate imperialism and colonialism from the continent and eventually neo-colonialism from the globe… Your failure, which no true African in Africa is praying for, will prolong our struggle with bitterness and disappointment. I, therefore, adjure that you ignore any suggestion outside Africa and holding that the present civilization, which some of the big powered are boasting of, sprang up from Africa, and realising that the entire world has something earthly to learn from Africa, you would endeavour your utmost to come to agreement, save Africa from the clutches of neo-colonialism and resurrect African dignity, manhood and national stability.
Aims
The OAU had the following primary aims:

- To co-ordinate and intensify the co-operation of African states in order to achieve a better life for the people of Africa.[1]
- To defend the sovereignty, territorial integrity and independence of African states.
- The OAU was also dedicated to the eradication of all forms of colonialism and white minority rule as, when it was established, there were several states that had not yet won their independence or were white minority-ruled. South Africa and Angola were two such countries. The OAU proposed two ways of ridding the continent of colonialism and white minority rule. First, it would defend the interests of independent countries and help to pursue the independence those of still-colonised ones. Secondly, it would remain neutral in terms of world affairs, preventing its members from being controlled once more by outside powers.
A Liberation Committee was established to aid independence movements and look after the interests of already-independent states. The OAU also aimed to stay neutral in terms of global politics, which would prevent them from being controlled once more by outside forces – an especial danger with the Cold War.
| History of the African Union |
|---|
The OAU had other aims, too:
- Ensure that all Africans enjoyed human rights.
- Raise the living standards of all Africans.
- Settle arguments and disputes between members – not through fighting but rather peaceful and diplomatic negotiation.[6]
Soon after achieving independence, a number of African states expressed a growing desire for more unity within the continent. Not everyone was agreed on how this unity could be achieved, however, and two opinionated groups emerged in this respect:
- The Casablanca bloc, led by Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana, wanted a federation of all African countries. Aside from Ghana, it comprised also Algeria, Guinea, Morocco, Egypt, Mali and Libya. Founded in 1961, its members were described as "progressive states".
- The Monrovian bloc, led by Senghor of Senegal, felt that unity should be achieved gradually, through economic cooperation. It did not support the notion of a political federation. Its other members were Nigeria, Liberia, Ethiopia, and most of the former French colonies.
Some of the initial discussions took place at Sanniquellie, Liberia. The dispute was eventually resolved when Ethiopian emperor Haile Selassie I invited the two groups to Addis Ababa, where the OAU and its headquarters were subsequently established. The Charter of the Organisation was signed by 32 independent African states.
At the time of the OAU's disbanding, 53 out of the 54 African states were members; Morocco left on 12 November 1984 following the admission of the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic as the government of Western Sahara in 1982.[7]
Criticism and praise
The organisation was widely derided as a bureaucratic "talking shop" with little power. It struggled to enforce its decisions, and its lack of armed force made intervention exceedingly difficult. Civil wars in Nigeria and Angola continued unabated for years, and the OAU could do nothing to stop them.
The policy of non-interference in the affairs of member states also limited the effectiveness of the OAU. Thus, when human rights were violated, as in Uganda under Idi Amin in the 1970s, the OAU was powerless to stop them.
The Organisation was praised by Ghanaian former United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan for bringing Africans together. Nevertheless, critics argue that, in its 39 years of existence, the OAU did little to protect the rights and liberties of African citizens from their own political leaders, often dubbing it as a "Dictators' Club"[8] or "Dictators' Trade Union".
The OAU was, however, successful in some respects. Many of its members were members of the UN, too, and they stood together within the latter organisation to safeguard African interests – especially in respect of lingering colonialism. Its pursuit of African unity, therefore, was in some ways successful.
Total unity was difficult to achieve, however, as the OAU was largely divided. The former French colonies, still dependent on France, had formed the Monrovia Group, and there was a further split between those that supported the United States and those that supported the USSR in the Cold War of ideologies. The pro-Socialist faction was led by Ghana's Kwame Nkrumah, while Félix Houphouët-Boigny of the Ivory Coast led the pro-capitalists. Because of these divisions, it was difficult for the OAU to take action against states involved in internal conflicts because it could rarely reach an agreement on what was to be done.
The OAU did play a pivotal role in eradicating colonialism and white minority rule in Africa. It gave weapons, training and military bases to rebel groups fighting white minority and colonial rule. Groups such as the ANC and PAC, fighting apartheid, and ZANU and ZAPU, fighting to topple the government of Rhodesia, were aided in their endeavours by the OAU. African harbours were closed to the South African government, and South African aircraft were prohibited from flying over the rest of the continent. The UN was convinced by the OAU to expel South Africa from bodies such as the World Health Organization.
The OAU also worked with the UN to ease refugee problems. It set up the African Development Bank for economic projects intended to make Africa financially stronger. Although all African countries eventually won their independence, it remained difficult for them to become totally independent of their former colonisers. There was often continued reliance on the former colonial powers for economic aid, which often came with strings attached: loans had to be paid back at high interest-rates, and goods had to be sold to the aiders at low rates.
The US and Soviet Union intervened in post-colonial Africa in pursuit of their own objectives. Help was sometimes provided in the form of technology and aid-workers. Despite the fight to keep "Westerners" (colonialists) out of African affairs, the OAU failed to achieve to meet goals set up to advocate African affairs. The Organisation still heavily depended on Western help (military and economic) to intervene in African affairs, despite African leaders' displeasure at dealing with the international community, especially Western countries.
Agencies
Autonomous specialised agencies, working under the auspices of the OAU, were:
- Pan-African Telecommunications Union (PATU)
- Pan-African Postal Union (PAPU)
- Pan-African News Agency (PANA)
- Union of African National Television and Radio Organisations (URTNA)
- Union of African Railways (UAR)
- Organisation of African Trade Union Unity (OATUU)
- Supreme Council for Sports in Africa
- African Civil Aviation Commission
List of chairpersons
List of secretaries-general
OAU summits

| International opposition to apartheid in South Africa |
|---|
 |
|---|
| Host City | Host Country | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Addis Ababa | 22–25 May 1963 | |
| Cairo | 17–21 July 1964 | |
| Accra | 21–26 October 1965 | |
| Addis Ababa | 5–9 November 1966 | |
| Kinshasa | 11–14 September 1967 | |
| Algiers | 13–16 September 1968 | |
| Addis Ababa | 6–10 September 1969 | |
| Addis Ababa | 1–3 September 1970 | |
| Addis Ababa | 21–23 June 1971 | |
| Rabat | 12–15 June 1972 | |
| Addis Ababa | 27–28 May 1973 | |
| Mogadishu | 1974 | |
| Kampala | 28 July–1 August 1975 | |
| Port Louis | 2–6 July 1976 | |
| Libreville | 2–5 July 1977 | |
| Khartoum | 18–22 July 1978 | |
| Monrovia | 17–20 July 1979 | |
| Freetown | 1–4 July 1980 | |
| Nairobi | 24–27 June 1981 | |
| Addis Ababa | 6–12 June 1983 | |
| Addis Ababa | 12–15 November 1984 | |
| Addis Ababa | 18–20 July 1985 | |
| Addis Ababa | 28–30 July 1986 | |
| Addis Ababa | 27–29 July- 1987 | |
| Addis Ababa | Extraordinary Summit: October 1987 | |
| Addis Ababa | 25–28 May 1988 | |
| Addis Ababa | 24–26 July 1989 | |
| Addis Ababa | 9–11 July 1990 | |
| Abuja | 3–5 July 1991 | |
| Dakar | 29 June – 1 July 1992 | |
| Cairo | 28–30 June 1993 | |
| Tunis | 13–15 June 1994 | |
| Addis Ababa | 26–28 June 1995 | |
| Yaoundé | 8–10 June 1996 | |
| Harare | 2–4 June 1997 | |
| Ouagadougou | 8–10 June 1998 | |
| Algiers | 12–14 July 1999 | |
| Sirte | Extraordinary Summit 6–9 September 1999 | |
| Lomé | 10–12 July 2000 | |
| Lusaka | 9–11 July 2001, the last OAU summit |
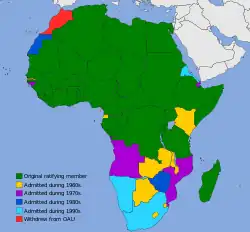
OAU members by date of admission (53 states)
| Date | Countries | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 25 May 1963 | ||
| 1971–97 Zaire | ||
| From 1975 Benin | ||
| From 1985 Côte d'Ivoire | ||
| Withdrew 12 November 1984, protesting the membership of Western Sahara. However, Morocco joined the African Union in January 2017, 33 years after its withdrawal.[9] | ||
| Tanganyika and Zanzibar merged 26 April 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar, which was renamed Tanzania on 1 November 1964. | ||
| From 1984 Burkina Faso | ||
| Tanganyika and Zanzibar merged 26 April 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar, which was renamed Tanzania 1 November 1964. | ||
| 13 December 1963 | ||
| 13 July 1964 | ||
| 16 December 1964 | ||
| October 1965 | ||
| 31 October 1966 | ||
| August 1968 | ||
| 24 September 1968 | ||
| 12 October 1968 | ||
| 19 November 1973 | ||
| 11 February 1975 | ||
| 18 July 1975 | ||
| 29 June 1976 | ||
| 27 June 1977 | ||
| 1 June 1980 | ||
| 22 February 1982 | ||
| 3 June 1990 | ||
| 24 May 1993 | ||
| 6 June 1994 |
See also
- African Parliamentary Union (APU), another inter-parliamentary institution only of some African countries (non-members are Eritrea, Seychelles, Comoros, Mauritius, Madagascar, Tanzania, Zimbabwe, Malawi, Mozambique, Botswana, South Africa, Swaziland, Lesotho, Sahrawi Republic)[10]
- Africa Day
- Bamako Convention
- Casablanca Group
- Convention Governing the Specific Aspects of Refugee Problems in Africa
- List of Linguistic Rights in Constitutions (Africa)
- Monrovia Group
- MPAIAC
- Pan-Africanism
References
- 1 2 "Department of International Relations and Cooperation – South Africa". dfa.gov.za. Archived from the original on 4 February 2012. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
- ↑ "African Union (See also – Organization of African Unity (OAU)) Archives". Question of Palestine. Retrieved 27 May 2021.
- ↑ Beverton, Alys (10 May 2009). "Organization of African Unity (1963–2002)". Retrieved 27 May 2021.
- 1 2 3 Jaynes, Gerald D., Encyclopedia of African American Society, Volume 1 (contributors: Thomson Gale (Firm), Sage Publications), (2005), p. 672, ISBN 978-0761927648 Archived 18 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 3 "Message to the Founding Fathers of the OAU at their First Conference at Addis Ababa 1st May 1963 – Alhaji A E Cham-Joof". The Point Newspaper, 29 June 2006. Archived 23 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Elias, T. O. (1965). "The Charter of the Organization of African Unity". The American Journal of International Law. 59 (2): 243–267. doi:10.2307/2196967. ISSN 0002-9300. JSTOR 2196967. S2CID 146867168.
- ↑ Beverton, Alys (10 May 2009). "Organization of African Unity (1963–2002)". blackpast.org.
- ↑ Reynolds, Paul (8 July 2002). "BBC News – World – Africa – African Union replaces dictators' club". news.bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
- ↑ "Morocco rejoins the African Union after 33 years". Al Jazeera. 31 January 2017. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ↑ "African Parliamentary Union". Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
Further reading
- OAU After Twenty Years. Praeger (1984); ISBN 0-03-062473-8;
- Terry M. Mays, Africa's First Peacekeeping Operation: The OAU in Chad, 1981–1982, Praeger (2002); ISBN 0-275-97606-8
- Chaloka Beyani, Chris Stringer, African Exodus: Refugee Crisis, Human Rights, & the 1969 OAU Convention. Lawyers Committee for Human Rights (1995); ISBN 0-934143-73-0
- CEC.rwanda2.free.fr, Report on the Rwandan genocide in 2000.
- Black-king.net, Emperor Haile Selassie of Ethiopia speaks at the OAU conference, Addis Ababa, 1963
