| Lambeth Palace | |
|---|---|
 Lambeth Palace, photographed looking east across the River Thames. Visible are the 15th-century Lollards' Tower at left, the Great Hall (with cupola) at centre, the late 15th-century brick gatehouse towards the right, and the 14th-century tower of St Mary-at-Lambeth on the far right. | |
| Type | Archbishop's palace |
| Location | Lambeth, London |
| Coordinates | 51°29′44″N 0°7′11″W / 51.49556°N 0.11972°W |
| Architectural style(s) | Tudor |
| Owner | See of Canterbury |
Listed Building – Grade I | |
| Official name | Lambeth Palace |
| Designated | 19 October 1951 |
| Reference no. | 1116399 |
| Official name | Lambeth Palace |
| Designated | 1 October 1987 |
| Reference no. | 1000818 |
 Location of Lambeth Palace in Greater London | |
Lambeth Palace is the official London residence of the archbishop of Canterbury. It is situated in north Lambeth, London, on the south bank of the River Thames, 400 yards (370 metres)[1] south-east of the Palace of Westminster, which houses Parliament, on the opposite bank.
History

While the original residence of the archbishop of Canterbury was in his episcopal see, Canterbury, Kent,[2] a site originally called the Manor of Lambeth or Lambeth House was acquired by the diocese around AD 1200 and has since served as the archbishop's London residence. The site is bounded by Lambeth Palace Road to the west and Lambeth Road to the south, but unlike all surrounding land is excluded from the parish of North Lambeth. The garden park is listed and resembles Archbishop's Park, a neighbouring public park; however, it was a larger area with a notable orchard until the early 19th century. The former church in front of its entrance has been converted to the Garden Museum. The south bank of the Thames along this reach, not part of historic London, developed slowly because the land was low and sodden: it was called Lambeth Marsh, as far downriver as the present Blackfriars Road. The name "Lambeth" embodies "hithe", a landing on the river: archbishops came and went by water, as did John Wycliff, who was tried here for heresy. In the Peasants' Revolt of 1381, the palace was attacked.
The oldest remaining part of the palace is the chapel which was built in the Early English Gothic architectural style. Lollards' Tower, which retains evidence of its use as a prison in the 17th century, dates from 1435 to 1440. The front is an early Tudor brick gatehouse built by Cardinal John Morton and completed in 1495. Cardinal Pole lay in state in the palace for 40 days after he died there in 1558. The fig tree in the palace courtyard is possibly grown from a slip taken from one of the White Marseille fig trees here for centuries (reputedly planted by Cardinal Pole). In 1786,[3] there were three ancient figs, two "nailed against the wall" and still noted in 1826 as "two uncommonly fine... traditionally reported to have been planted by Cardinal Pole, and fixed against that part of the palace believed to have been founded by him. They are of the white Marseilles sort, and still bear delicious fruit. ...On the south side of the building, in a small private garden, is another tree of the same kind and age."[4] By 1882, their place had been taken by several massive offshoots.[5] The notable orchard of the medieval period has somewhat given way to a mirroring public park adjoining and built-up roads of housing and offices. The palace gardens were listed grade II in October 1987.[6]
The great hall was completely ransacked, including the building material, by Cromwellian troops during the English Civil War. After the Restoration, it was completely rebuilt by Archbishop William Juxon in 1663 (dated) with a late Gothic hammerbeam roof. The choice of a hammerbeam roof was evocative, as it reflected the High-Church Anglican continuity with the Old Faith (the King's (Charles II) brother was an avowed Catholic) and served as a visual statement that the Interregnum was over. As with some Gothic details on University buildings of the same date, it is debated among architectural historians whether this is "Gothic survival" or an early work of the "Gothic Revival". The diarist Samuel Pepys recognised it as "a new old-fashioned hall".
The building is listed in the highest category, Grade I, for its architecture – its front gatehouse with its tall, crenellated gatehouse resembles Hampton Court Palace's gatehouse which is also of the Tudor period, however Morton's Gatehouse was at its very start, in the 1490s, rather than in the same generation as Cardinal Wolsey's wider, similarly partially stone-dressed deep red brick façade. While this is the most public-facing bit, it is not the oldest at north-west corner, the Water Tower or Lollards' Tower mentioned above is made of Kentish Ragstone with ashlar quoins and a brick turret is much older.[7]
Among the portraits of the archbishops in the palace are works by Hans Holbein, Anthony van Dyck, William Hogarth and Sir Joshua Reynolds.
New construction was added to the building in 1834 by Edward Blore (1787–1879), who rebuilt much of Buckingham Palace later, in neo-Gothic style and it fronts a spacious quadrangle. The buildings form the home of the archbishop, who is regarded as the first among equals in the Anglican Communion, and is ex officio a member of the House of Lords.
 Map of 1897, showing the palace opposite the river from Westminster Palace, with Lambeth Bridge and Westminster Bridge crossing the river
Map of 1897, showing the palace opposite the river from Westminster Palace, with Lambeth Bridge and Westminster Bridge crossing the river The Guard Room
The Guard Room The great hall with Cardinal Pole's fig tree in front
The great hall with Cardinal Pole's fig tree in front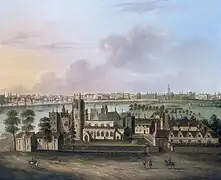 Lambeth Palace from the south c. 1685
Lambeth Palace from the south c. 1685 Lambeth Palace main entrance
Lambeth Palace main entrance The 19th-century range
The 19th-century range
Library

Within the palace precincts is Lambeth Palace Library, the official library of the archbishop of Canterbury, and the principal repository of records of the Church of England. It describes itself as "the largest religious collection outside of the Vatican".[8]
The library was founded as a public library by Archbishop Richard Bancroft in 1610, and was historically located within the main Palace complex. A new purpose-built library and repository opened in 2021. This is located at the far end of the Palace gardens, with its entrance on Lambeth Palace Road, and was designed by Wright & Wright. In addition to the existing library collections, it houses the archival collections of various Church of England institutions formerly held at the Church of England Record Centre (opened 1989) in Bermondsey.[9]
The library contains an extensive collection of material relating to ecclesiastical history, including the archives of the archbishops dating back to the 12th century, and those of other church bodies and of various Anglican missionary and charitable societies. Manuscripts include items dating back to the 9th century. The library also holds over 120,000 printed books. In 1996, when Sion College Library closed, Lambeth Palace Library acquired its important holdings of manuscripts, pamphlets, and pre-1850 printed books.
Topics covered by the collections range from the history of art and architecture to colonial and Commonwealth history, and numerous aspects of English social, political and economic history. The library is also an important resource for local history and genealogy. For online catalogues, see External links below.
Highlights of the collection

Notable items in the collections include:
- Mac Durnan Gospels (late 9th/early 10th centuries)
- Minuscule 473 (11th century)
- Minuscule 559 (11th century)
- Lambeth Apocalypse (12th century)
- The Romanesque Lambeth Bible (12th century)
- Lambeth Homilies (c.1200)
- Book of Hours of King Richard III (mid 15th century)
- A Short English Chronicle (mid 15th century)
- A rare copy of the Gutenberg Bible (1450s)
- Lambeth Choirbook (16th century)
- Book of Howth (late 16th century)
- Archives of the Commission for Building Fifty New Churches (1711–1759)
- Archives of the Incorporated Church Building Society (1818–1982)
St Mary-at-Lambeth
Immediately outside the gatehouse stands the former parish church of St Mary-at-Lambeth which was preserved by a campaign created by John and Rosemary Nicholson.[10] The tower dates from 1377 (repaired in 1834); while the body of the church was rebuilt in 1851 to the designs of Philip Hardwick.[6] Older monuments were preserved, including the tombs of some of the gardeners and plantsmen John Tradescant the elder and his son of the same name, and of Admiral William Bligh. St Mary's was deconsecrated in 1972, when the parish was absorbed into the surrounding parish of North Lambeth which has three active churches, the nearest being St Anselm's Church, Kennington Cross.[11][12] The Museum of Garden History (now the Garden Museum) opened in the building in 1977, taking advantage of its Tradescant associations.
During the renovation works of 2016, a previously unknown crypt was discovered, containing 30 coffins.[13] Amongst these were those of five archbishops of Canterbury—Richard Bancroft, Thomas Tenison, Matthew Hutton, Frederick Cornwallis, and John Moore—as well as that of John Bettesworth, Dean of the Arches.
Resident community
Lambeth Palace is home to the Community of Saint Anselm, an Anglican religious order that is under the patronage of the archbishop of Canterbury.[14]
See also
- Old Palace, Canterbury, within the precincts of Canterbury Cathedral, is the residence of the archbishop when in Canterbury
- List of palaces
- Palace of Whitehall
References
- ↑ Google (20 March 2015). "Lambeth Palace" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- ↑ Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and its People. Silver, Burdett. p. 37.
- ↑ Andrew Coltee Ducarel, History and Antiquities of the Palace of Lambeth, 1786 (as Biblioteca Topographica Britannica, vol. II pt 5, 1790)
- ↑ Thomas Allen, The History and Antiquities of the Parish of Lambeth 1826:229, paraphrasing Ducarel.
- ↑ "It were a grave omission to pass over unnoticed the 'Lambeth fig-trees.' Two of extraordinary size, supposed to have been planted by Cardinal Pole, formerly stood near the east end of the old garden front: they have long ago died, but three or four thriving offshoots, now grown into venerable trees, may still be seen basking on the sunny side of the Great Hall" (John Cave-Browne, Lambeth palace and its associations, 1882:310); "It was Cardinal Pole who is said to have planted the two fig-trees in Lambeth garden, which were still to be seen in 1806, while slips taken from the original plants are now flourishing trees." (Robert Sangster Rait and Caroline C. Morewood, English episcopal palaces (province of Canterbury), 1910:74)
- 1 2 Historic England. "Lambeth Palace (Grade II) (1000818)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- ↑ Historic England. "Lambeth Palace (Grade I) (1116399)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- ↑ "Lambeth Palace". The Archbishop of Canterbury. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ↑ "New Library News". Lambeth Palace Library. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ↑ "History of the Garden Museum". Garden Museum. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ↑ Map of North Lambeth parish A Church Near You church finder - Church of England
- ↑ Lambeth Mission St Mary Archived 31 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine A Church Near You church finder - Church of England
- ↑ Brinkhurst-Cuff, Charlie (16 April 2017). "Remains of five archbishops found near Lambeth Palace". The Guardian. Retrieved 16 April 2017.
- ↑ Lodge, Carey (18 September 2015). "Archbishop Welby launches monastic community at Lambeth Palace". Christian Today. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
Bibliography
- Palmer, Richard; Brown, Michelle P., eds. (2010). Lambeth Palace Library: Treasures from the Collections of the Archbishops of Canterbury. London: Scala. ISBN 9781857596274.
- Stourton, James (2012). Great Houses of London. London: Frances Lincoln. ISBN 978-0-7112-3366-9.
- Tatton-Brown, Tim (2000). Lambeth Palace: a history of the Archbishops of Canterbury and their houses. London: SPCK. ISBN 0-281-05347-2.
External links
- Official website
- Lambeth Palace Library official website
- Detailed architectural description – from the Survey of London online
- Library catalogue of printed books
- Library catalogue of manuscripts and archives