Native name: तिहन्यु Nickname: Tihanyu | |
|---|---|
 Katchal Island | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Bay of Bengal |
| Coordinates | 7°57′N 93°23′E / 7.95°N 93.38°E |
| Archipelago | Nicobar Islands |
| Adjacent to | Indian Ocean |
| Total islands | 1 |
| Major islands |
|
| Area | 146.5 km2 (56.6 sq mi)[1] |
| Length | 17 km (10.6 mi) |
| Width | 16 km (9.9 mi) |
| Coastline | 83.3 km (51.76 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 227 m (745 ft)[2] |
| Administration | |
| District | Nicobar |
| Island group | Nicobar Islands |
| Subdivisions of India | Nancowry Subdivision |
| Largest settlement | Mildera (pop. 1250) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 2685 (2011) |
| Pop. density | 18.3/km2 (47.4/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Hindu, Nicobarese |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
| PIN | 744301 |
| Telephone code | 03192 |
| ISO code | IN-AN-00[3] |
| Official website | www |
| Literacy | 84.4% |
| Avg. summer temperature | 32.0 °C (89.6 °F) |
| Avg. winter temperature | 28.0 °C (82.4 °F) |
| Sex ratio | ♂/♀ |
| Census Code | 35.638.0002 |
| Official Languages | Hindi, English, Tamil Katchal (regional) |
Katchal (Hindi: कत्चल, Nicobarese: तिहन्यु, Tihnyu) is one of the Nicobar Islands, India.
History
Katchal Island was previously known as Tihanyu. Due to the remote location and lack of exposure with the rest of the world, outsiders economically exploited the innocent islanders for a long time. To stop their economic exploitation, the Government of India declared the Nicobar Islands an Aboriginal Tribal Reserve Area (ATRA) on 2 April 1957. This made the Nicobar Islands inaccessible to outsiders and currently even Indian nationals need a special tribal pass to visit the islands. Only Government Servants (outsiders) posted to Katchal Islands are allowed to stay in the island.
Nicobar Islands have experienced all kinds of external influences for centuries, because they are located along an ancient international sea trade route and have been known to voyagers and scholars since ancient times. Due to this, the islands have been receiving external influences, which have affected their culture and race over the centuries. According to recent history, an archeological inscription dating to AD 1059 says that Nicobar was part of the overseas kingdom of Tamil Chola King of Tanjore. In 1869, the British took possession of the Nicobar Islands from the Danes and made them a part of modern India.
At sunrise on 1 January 2000, Katchal Island was in the news. Many voyagers had converged on it for a glimpse of the millennium's first sunrise.[4][5]
Katchal was one of the worst affected islands during the December 26th 2004 Tsunami. The tsunami devastated the Island, disturbing the socio-economic set-up of its inhabitants. Of the 5,000 people missing (5000 is official - actual is more) in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, 1,549 were believed to be from Katchal.
To support the local population a sizable number of Govt. Staffs were posted to this Island prior to the Tsunami day. Most of the staff went missing as majority of the Govt. provided Staff Quarters were situated very close to the sea shore and a very few managed to escape to the nearby hill. To cite an example - not a single teacher out of 47 posted here prior on 26-12-2004 was found alive.
Some people managed to escape the waters by clinging over to coconut tree tops. Of the 344 people reported dead, only one body could be identified. Either the bodies were decomposed beyond recognition or there were no survivors to claim them.[6]
Geography
Its area is 146.5 km2 (56.6 sq mi). It is approximately 1,600 km (990 mi) away from mainland (India) and 305 km (190 mi) south to capital Port Blair. The highest peak of Katchal is 227 m (745 ft) high.[2] The hills of Katchal are composed of calcareous sandstone and marble slates, and in the tropical forest of Katchal there are many pythons, black monkeys and pigs.
Demography
Katchal Island is home to both indigenous and non-indigenous people. Katchal is inhabited by Nicobari Tribes and Migrated Tamilians (For Rubber plantation workers under Sastri-Srimao Bandaranayaka Pact of 1964). After the tsunami almost all the tribal chiefs and their heirs were killed, leaving the tribes virtually headless. Katchal[7] is the largest island of the central group of islands and had 35 villages (of which six were main villages). After the tsunami, the natives regrouped and formed five tribal villages in the island viz. E-Wall, Meenakshi Ram Nagar, Japan Tikrey, Sallo Tikrey, and Upper Katchal. Mildera is another village in the island inhabited by non tribal people (Tamil repatriates and Ranchi communities).[8] Languages spoken in Katchal are Nicobarese, Hindi, Tamil, Telugu and Santali.
Administration
Katchal Island belongs to the township of Nancowry of Katchal tehsil.[9][10] The Island is not open to tourists and special permission is required from the local administration at Port Blair.
Facilities
These are the facilities on the island: Health: Primary Health Center: 1 Secondary Health Center: 3 Education: Primary School - 6 ( Kindergarten to 5th Standard), Middle School - 2 ( 6th to 8th Standard), Senior Secondary School - 1 (11th to 12th Standard) Govt.: Water supply is adequate and sufficient. Power station which is electrified and has plans to augment the DG (Diesel Generators) capacity at Katchal Islands by 3x128 KW DG Sets. 9 km of roads (Pucca road). Police Station:1[11] Jetty: 1, A Berthable Jetty at Nirma Nagar Communication: Wireless Local Loop Phones and PSTN phones. Mobile phone signal strength is currently very low. Information Technology: Connected by VSAT under E-Governance project of A & N Administration for speeding up the developmental works and effective monitoring.
Economics
According to initial estimates, 112 hectares (277 acres) of land has been rendered useless due to salination after the tsunami, and 3.54 lakh coconut and an equal number of Supari (betel nut) trees destroyed. Currently, The villagers are engaged in coconut, betelnut and arecanut trade. In 1968, rubber plantation and subsequently red oil palm plantation were established here.
Flora and fauna
Birds found:
- White-rumped munia
- Indian white-eye
- Red-whiskered bulbul
- Orange thrush
- Grey wagtail
- Purple-rumped sunbird
- Asian paradise flycatcher
- Emerald dove
- White-breasted sea eagle
- Pied triller
- Shikra
- Long-tailed parakeet
- White-collared kingfisher
- Black-naped oriole
- Black-naped monarch
- Brown shrike
- Pied imperial pigeon
- Pacific reef egret
- Plume-toed swiftlet
- Andaman green pigeon
Image gallery
 Map
Map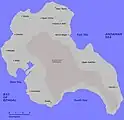 1990 Map of Katchal Island
1990 Map of Katchal Island
References
- ↑ "Islandwise Area and Population - 2011 Census" (PDF). Government of Andaman.
- 1 2 Sailing Directions (Enroute), Pub. 173: India and the Bay of Bengal (PDF). Sailing Directions. United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. 2017. p. 293.
- ↑ Registration Plate Numbers added to ISO Code
- ↑ Gautam Singh (2 January 2000). "Millennium sunrise eludes Katchal island". The Tribune. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ↑ "Stamp Featuring 1st Sunrise of the Millennium". Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ↑ Life as Medical Officer @ Katchal-Post Tsunami Archived 2013-01-04 at archive.today
- ↑ "Katchal Pincode 744304". Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- ↑ Kathchal Map
- ↑ Tehsils
- ↑ "Andaman & Nicobar Administration Web site". Archived from the original on 2018-12-13. Retrieved 2008-03-06.
- ↑ Katchal Archived 2009-04-09 at the Wayback Machine
 Andaman and Nicobar Islands travel guide from Wikivoyage
Andaman and Nicobar Islands travel guide from Wikivoyage