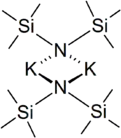 | |
amide_unsolvated_from_crystal.png.webp) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Potassium 1,1,1-trimethyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)silanaminide | |
| Other names
Potassium hexamethyldisilazide
Potassium hexamethylsilazane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | KHMDS |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.102.263 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UN number | 3263 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KSi 2C 6NH 18 | |
| Molar mass | 199.4831 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White, opaque crystals |
| Reacts | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Danger | |
| H314[2] | |
| P280, P305+P351+P338, P310[2] | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (commonly abbreviated as KHMDS, Potassium(K) HexaMethylDiSilazide) or potassium hexamethyldisilazane[1] is the chemical compound with the formula ((CH3)3Si)2NK. It is a strong, non-nucleophilic base with an approximate pKa of 26 (compare to lithium diisopropylamide, at 36).
Structure
In the solid state, the unsolvated compound is dimeric, with two potassium and two nitrogen atoms forming a square. This compound is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents and conducts electricity poorly in solution and in the melt. This is attributed to very strong ion pairing.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 "Potassium Hexamethyldisilazane". sigmaaldrich.com. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- 1 2 Potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide, Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Tesh, Kris F.; Hanusa, Timothy P.; Huffman, John C. (1990). "Ion pairing in [bis(trimethylsilyl)amido]potassium: The x-ray crystal structure of unsolvated [KN(SiMe3)2]2". Inorg. Chem. 29 (8): 1584–1586. doi:10.1021/ic00333a029.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.