| John Redmond Reservoir | |
|---|---|
 John Redmond Reservoir | |
| Location | Coffey County, Kansas |
| Coordinates | 38°15′05″N 95°48′10″W / 38.2515043°N 95.8029017°W[1] |
| Type | Reservoir |
| Primary inflows | Neosho River |
| Primary outflows | Neosho River |
| Catchment area | 3,015 sq mi (7,810 km2)[2] |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Managing agency | U.S. Army Corps of Engineers |
| Built | June 18, 1959 |
| First flooded | November 17, 1964 |
| Surface area | 9,400 acres (38 km2)[3] |
| Max. depth | 12 ft (3.7 m)[3] |
| Water volume | Full: 67,302 acre⋅ft (83,016,000 m3) Current (Jan. 2016): 88,024 acre⋅ft (108,576,000 m3)[4] |
| Shore length1 | 59 miles (95 km)[2] |
| Surface elevation | Full: 1,041 ft (317 m) Current (Jan. 2016): 1,043 ft (318 m)[4] |
| Islands | 3 on South section |
| Settlements | Burlington, New Strawn, Ottumwa |
| References | [2][1] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
John Redmond Reservoir is a reservoir on the Neosho River in eastern Kansas.[1] Built and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, it is used for flood control, recreation, water supply, and wildlife management.[5] It borders the Flint Hills National Wildlife Refuge to the northwest.[6]
History
The Neosho River valley flooded more than 50 times in the 30 years leading up to 1950 when the U.S. Congress authorized the flood control project that later became John Redmond Dam and Reservoir. It was authorized and awaiting construction during the Great Flood of 1951 which inundated downtown Burlington and Strawn where some locations had floodwater 30 feet (9.1 m) deep.[7]
Originally, Congress authorized the project under the Flood Control Act of 1950 as Strawn Dam in reference to Strawn, the town located where the reservoir is today. Strawn was relocated 6 miles (9.7 km) to the east on higher ground and renamed New Strawn at the time the dam was constructed. In 1958, Congress renamed the project John Redmond Dam and Reservoir in honor of the late John Redmond, the publisher of the Burlington Daily Republican who had been a long-time advocate for flood control and water conservation along the Neosho River. Redmond had died in 1953.[7]
The design and construction of the project was conducted by the Tulsa District of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers at a total cost of $29,264,000. The dam began to undergo construction on June 18, 1959 and went into service on November 17, 1964, several weeks before final completion, in order to protect the Neosho River valley from the expected winter and spring floods.[8]
During the Great Flood of 1993, floodwaters reached up to the top of the dam's release gates. The reservoir reached capacity in July 1993, necessitating the first release of the spillway.
Geography
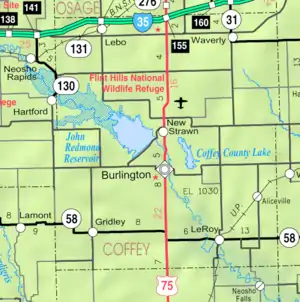
John Redmond Reservoir is located at 38°13′30″N 95°46′36″W / 38.22500°N 95.77667°W (38.2250209, -95.7766537) at an elevation of 1,041 feet (317 m).[4][1] It lies east of the Flint Hills on the Osage Plains in east-central Kansas.[6] The entirety of the reservoir lies within Coffey County.[9]
The reservoir is impounded at its southeastern end by John Redmond Dam.[9][10] The Neosho River is both the reservoir's primary inflow from the northwest and outflow to the southeast. Smaller tributaries include Hickory Creek and Kennedy Creek from the north as well as Buffalo Creek and Otter Creek from the west.[9]
U.S. Route 75 runs generally north-south east of the reservoir. 12th Road, a paved county road, runs east-west south of the reservoir.[9] Another paved county road, Embankment Road, runs northeast-southwest along the top of the dam.[9][11]
There are several settlements on or near the reservoir. The largest, Burlington, lies roughly 2 miles (3.2 km) southeast of the dam on the Neosho River. New Strawn is located immediately east of the reservoir at the northeast end of the dam. Ottumwa, which is unincorporated, sits on the reservoir's north shore.[9]
Hydrography
The surface area, surface elevation, and water volume of the reservoir fluctuate based on inflow and local climatic conditions. In terms of capacity, the Corps of Engineers vertically divides the reservoir into a set of pools based on volume and water level, and the reservoir is considered full when filled to the capacity of its conservation pool.[4] When full, John Redmond Reservoir has an approximate surface area of 9,400 acres (38 km2), a surface elevation of 1,041 feet (317 m), and a volume of 67,302 acre-feet (83,016,000 m3).[4][3] When filled to maximum capacity, it has a surface elevation of 1,073 feet (327 m) and a volume of 755,330 acre-feet (931,690,000 m3).[4]
The streambed underlying the reservoir has an elevation of 995 feet (303 m).[4]
Infrastructure
John Redmond Dam is an earth-fill embankment dam that stands 86.5 feet (26.4 m) above the streambed and 21,790 feet (6,640 m) long.[5] At its crest, the dam has an elevation of 1,081.5 feet (329.6 m).[4] A 664-foot (202 m) section of the dam at its northeast end is a concrete spillway that empties into the Neosho River channel. The spillway is an ogee weir controlled by 14 40-foot (12 m) by 35-foot (11 m) tainter gates. When the reservoir is filled to maximum capacity, the spillway has a discharge capacity of 578,000 cubic feet per second (16,400 m3/s). Additional outlet works include two 24-inch (61 cm) low-flow pipes with a capacity of 130 cubic feet per second (3.7 m3/s) at the spillway crest. An intake building for the Wolf Creek Generating Station is located below the dam. This serves as a secondary cooling source for the plant. The maximum capacity of the river channel below the dam is 15,000 cubic feet per second (420 m3/s).[5]
Management
The Tulsa District of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers manages John Redmond Dam and Reservoir for the purposes of flood control, recreation, water quality control, and water supply.[5] The Corps oversees recreational activities both on the reservoir surface and in the parks around it.[12]
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service manages 18,463 acres (74.72 km2) of land along the river northwest of the reservoir as the Flint Hills National Wildlife Refuge.[13] In addition, the Corps of Engineers has licensed the Kansas Department of Wildlife, Parks and Tourism (KDWP) to manage 1,637 acres (6.62 km2) on the reservoir's southwest shore as the Otter Creek Wildlife Area.[14] The Wildlife Area includes approximately 200 acres (81 ha) of riparian land, 465 acres (188 ha) of cropland, and 970 acres (390 ha) of native grassland.[15]
John Redmond Reservoir serves as a reserve water supply for the Wolf Creek Generating Station located 5 miles (8.0 km) east. During construction of the facility, a second reservoir, Coffey County Lake, was created to serve as a water source so a cooling tower would not be required. The water level of the Lake is kept above a mandatory level by pumping water from John Redmond when needed.
Parks and recreation
The Corps of Engineers manages three parks at the reservoir: Dam Site Park, Riverside East Park, and Riverside West Park.[12][16] Dam Site Park is located at the northeast end of the dam on the reservoir's eastern shore. Riverside East Park and Riverside West Park lie immediately below the dam on both sides of the Neosho River.[17] Both Dam Site and Riverside West host boat ramps. Dam Site and Riverside East each include hiking trails. All three parks include camping and picnic facilities.[16] In addition, the Corps manages three recreation areas which also provide boat ramps: the Otter Creek Recreational Area, located on the western shore at the southwest end of the dam, and the Strawn and Hartford Areas, both located upstream in the Flint Hills Wildlife Refuge.[12][17] The Otter Creek Area occupies 240 acres (97 ha) and is open for off-road vehicle use. Lastly, the Corps manages the Hickory Creek trail on the reservoir's north shore. The trail is open to hiking, horseback riding, and mountain biking.[18]
John Redmond Reservoir is open for sport-fishing.[12] Hunting is allowed, with restrictions, on the public land around the reservoir including in the Flint Hills Refuge.[17]
Wildlife
Fish species resident in the reservoir include channel and flathead catfish, crappie, walleye, and white bass.[12] One invasive species, the zebra mussel, is also present.[3] Game animals living on land around the reservoir include bobwhite quail, cottontail rabbits, mourning doves, prairie chickens, squirrels, turkeys, and whitetail deer.[12]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 "John Redmond Reservoir". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved January 15, 2021.
- 1 2 3 "John Redmond Report" (PDF). Kansas Water Office. Retrieved March 28, 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 "John Redmond Reservoir Fishing Information". Kansas Department of Wildlife, Parks and Tourism. Retrieved January 8, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "JRLK1: John Redmond Lake". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 "Pertinent Data". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- 1 2 "2003-2004 Official Transportation Map" (PDF). Kansas Department of Transportation. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- 1 2 "History of John Redmond Reservoir". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Archived from the original on August 17, 2019.
- ↑ "History Message". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Archived from the original on January 10, 2009. Retrieved March 28, 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "General Highway Map - Coffey County, Kansas". Kansas Department of Transportation. November 2008. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ↑ "John Redmond Dam". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ↑ "John Redmond Reservoir". Google Maps. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "John Redmond Reservoir Recreation". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ↑ "About the Refuge". U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ↑ "Otter Creek Wildlife Area at John Redmond Reservoir" (PDF). Kansas Department of Wildlife, Parks and Tourism. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ↑ "John Redmond Wildlife Area". Kansas Department of Wildlife, Parks and Tourism. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- 1 2 "John Redmond Reservoir". Corps Lakes Gateway. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- 1 2 3 "John Redmond Reservoir - Public Hunting Area [Map]" (PDF). U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ↑ "Welcome to John Redmond Reservoir". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
External links
- Flint Hills National Wildlife Refuge, U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service
- John Redmond Reservoir, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
- John Redmond/Otter Creek Wildlife Area, Kansas Department of Wildlife, Parks & Tourism