| Inferior rectus | |
|---|---|
 The inferior rectus muscle, is shown in this superior view of the eye, along with its axis of rotation. The other muscle is the superior oblique muscle, which angles around the trochlea. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | common tendinous ring at the orbital apex |
| Insertion | 6.8 mm inferior to the corneal limbus |
| Artery | inferior muscular branch of the ophthalmic artery, infraorbital artery |
| Vein | inferior muscular branch of the ophthalmic vein |
| Nerve | inferior branch of oculomotor nerve |
| Actions | depression, adduction, extorsion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus rectus inferior bulbi |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.011 |
| TA2 | 2043 |
| FMA | 49036 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The inferior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit near the eye. It is one of the four recti muscles in the group of extraocular muscles. It originates from the common tendinous ring, and inserts into the anteroinferior surface of the eye. It depresses the eye (downwards).
Structure
The inferior rectus muscle originates from the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn).[1] It inserts into the anteroinferior surface of the eye.[2] This insertion has a width of around 10.5 mm.[2] It is around 7 mm from the corneal limbus.[2]
Blood supply
The inferior rectus muscle is supplied by an inferior muscular branch of the ophthalmic artery.[1] It may also be supplied by a branch of the infraorbital artery.[1] It is drained by the corresponding veins: the inferior muscular branch of the ophthalmic vein, and sometimes a branch of the infraorbital vein.[1]
Nerve supply
The inferior rectus muscle is supplied by the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve (III).[1]
Development
The inferior rectus muscle develops from the embryonic mesoderm in the orbit of the skull.[1][3] This is similar to the other extraocular muscles.[3]
Relations
The insertion of the inferior rectus muscle is around 6 mm from the insertion of the medial rectus muscle, and around 8 mm from the insertion of the lateral rectus muscle.[2] A parasympathetic branch that supplies the ciliary muscles of the pupil passes close to the inferior rectus muscle.[1]
Variation
Very rarely, the inferior rectus muscle may be congenitally absent.[3][4] This may cause inferior rectus palsy, where the eye cannot be depressed.[3]
Function
The inferior rectus muscle depresses, adducts, and helps extort the eye.[1] It is the only muscle that is capable of depressing the pupil when it is in a fully abducted position.[5]
Clinical significance
Strabismus
If the inferior rectus muscle is damaged, weak, or paralysed, this can cause strabismus.[1][6] This can lead to elevation of the eye, as the superior rectus muscle remains stronger.[6] For minor cases, prism glasses can be used to gradually realign the eye.[6] Alternatively for serious cases, it may be surgically corrected by slightly weakening the superior rectus muscle (opposite) - this reduces the elevation of the eye, and corrects the strabismus.[6] This procedure may lead to overcorrection of the strabismus, but is otherwise generally successful.[7]
Surgery
Any surgery on the inferior rectus muscle may damage the parasympathetic branches to the ciliary muscles of the pupil.[1] This may cause problems with control of the pupil.[1] Nearby blood vessels and nerves may also be damaged.[1]
Additional images
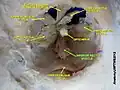 Inferior rectus muscle
Inferior rectus muscle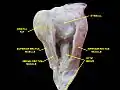 Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Shumway, Caleb L.; Motlagh, Mahsaw; Wade, Matthew (2021), "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Eye Inferior Rectus Muscle", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30085520, retrieved 2021-09-27
- 1 2 3 4 Apt, L (1980). "An anatomical reevaluation of rectus muscle insertions". Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society. 78: 365–375. ISSN 0065-9533. PMC 1312149. PMID 7257065.
- 1 2 3 4 Astle, William F; Hill, Vivian E; Ells, Anna L; Chi, Nguyen Thi Thanh; Martinovic, Elaine (2003-10-01). "Congenital absence of the inferior rectus muscle—diagnosis and management". Journal of American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 7 (5): 339–344. doi:10.1016/S1091-8531(03)00214-3. ISSN 1091-8531. PMID 14566316.
- ↑ Ingham, Peter N.; McGOVERN, Stephen T.; Crompton, John L. (1986). "Congenital Absence of the Inferior Rectus Muscle". Australian and New Zealand Journal of Ophthalmology. 14 (4): 355–358. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9071.1986.tb00471.x. ISSN 1440-1606. PMID 3814423.
- ↑ "Eye Theory". Cim.ucdavis.edu. Archived from the original on 2014-05-27. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- 1 2 3 4 Paysse, Evelyn A.; Saunders, Richard A.; Coats, David K. (2000-06-01). "Surgical management of strabismus after rupture of the inferior rectus muscle". Journal of American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 4 (3): 164–167. doi:10.1016/S1091-8531(00)70007-3. ISSN 1091-8531. PMID 10849393.
- ↑ Sprunger, Derek T.; Helveston, Eugene M. (1993-05-01). "Progressive Overcorrection After Inferior Rectus Recession". Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology & Strabismus. 30 (3): 145–148. doi:10.3928/0191-3913-19930501-04. PMID 8350221.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 29:01-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbit5)
- Diagram at mun.ca