| Hyperthyroxinemia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hyperthyroxinaemia |
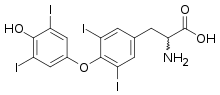 | |
| Thyroxine | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Hyperthyroxinemia is a thyroid disease where the serum levels of thyroxine are higher than expected.[1] Thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine (T4) is produced by the thyroid gland.
The term is sometimes used to refer to hyperthyroidism, but hyperthyroidism is a more general term. [2]
When the level of thyroxine (T4) in the blood exceeds normal range, it can lead to symptoms such as irritability and unexplained weight loss.[3]
Types include:
- Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia
- Familial euthyroid hyperthyroxinemia
- Thyroid hormone resistance syndrome
References
- ↑ "four/000051350""at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "four/000051350""at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "Hyperthyroxinemia". MrLabTest. Retrieved 15 June 2023.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.