Havelberg | |
|---|---|
 Church of Saint Lawrence seen across the Havel River | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Havelberg within Stendal district 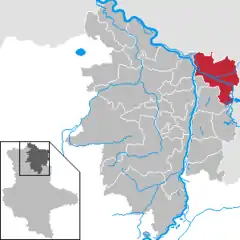 | |
 Havelberg 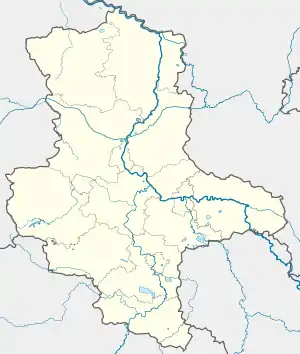 Havelberg | |
| Coordinates: 52°49′30″N 12°4′28″E / 52.82500°N 12.07444°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Saxony-Anhalt |
| District | Stendal |
| Subdivisions | 14 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2022–29) | Mathias Bölt[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 149.13 km2 (57.58 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 26 m (85 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 6,397 |
| • Density | 43/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 39532–39539 |
| Dialling codes | 039387 and 039382 |
| Vehicle registration | SDL |
| Website | havelberg.de |
Havelberg (German pronunciation: [ˈhaːfl̩ˌbɛʁk] ⓘ) is a town in the district of Stendal, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the Havel, and part of the town is built on an island in the centre of the river. The two parts were incorporated as a town in 1875. It has a population of 6,436 (2020).
History



The Bishopric of Havelberg was founded in 946, by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (then a prince), but the bishop tended to live in either Plattenburg or Wittstock, a few miles north of Havelberg.[3] An early bishop was Anselm of Havelberg. The Slavic revolt of 983 brought Havelberg under the control of the pagan Wends. The city was not restored to Christian, German rule until 1147 with the Wendish Crusade. Havelberg is home to a former monastery, now used as the Prignitz Museum, which was established in 1904. In 1359 Havelberg became a member of the Hanseatic League and developed into a trade center with a booming economy.[4] Havelberg remained a member of the Hanseatic League until 1559.[5]
Havelberg was part of Brandenburg for most of its history. Havelberg was formerly a strong fortress, but during the Thirty Years' War it was taken from the Danish by the imperial troops in 1627. Recaptured by the Swedes in 1631, and again in 1635 and 1636, it was in 1637 retaken by the Saxons.[3]
When the German states where dissolved in East Germany in 1952, Havelberg became part of the district of Magdeburg.
When the German states were refounded during German Reunification in 1990, the whole district of Magdeburg became part of Saxony-Anhalt, including the formerly Brandenburgian town of Havelberg.
Sights
Havelberg has a historical centre with many well-preserved wooden buildings, e.g. in Kirchstraße and Scabellstraße. The St. Mary's Cathedral was founded in 1170 and transformed into an impressive gothic building from 1279-1330.[6] It is on a hill offering a beautiful view of the old town centre where St. Laurentius, a parish church which was built around 1300, deserves a visit. The oldest house is Beguinenhaus at Salzmarkt (Salt Market) built from sandstone in 1390 with a stone relief which was carved around 1400 above the entrance.[7]
Notable people
- Bruno Keil (1859–1916), classical philologist.
- Singer Annett Louisan was born here in 1977.
- Gustav Gerneth (1905–2019), oldest living man at the time of his death.
References
- ↑ Bürgermeisterwahlen in den Gemeinden, Endgültige Ergebnisse, Statistisches Landesamt Sachsen-Anhalt, accessed 10 November 2022.
- ↑ "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden – Stand: 31. Dezember 2021" (PDF) (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Sachsen-Anhalt. June 2022.
- 1 2 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Havelberg". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 13 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 79.
- ↑ Matthias Puhle: Die Hanse - 16 Städtebilder aus Sachsen-Anhalt, p. 53. Dößel (Saalekreis) 2008
- ↑ "Tourist-Information der Hansestadt Stendal: Altmärkischer Hansebund".
- ↑ Karl Baedeker GmbH: Deutschland 2000, p. 203. Ostfildern 2000
- ↑ Matthias Puhle: Die Hanse - 16 Städtebilder aus Sachsen-Anhalt, p. 55. Dößel (Saalekreis) 2008