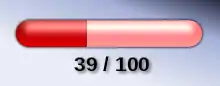
Health is a video game or tabletop game quality that determines the maximum amount of damage or fatigue something takes before leaving the main game. In role-playing games, this typically takes the form of hit points (HP), a numerical attribute representing the health of a character or object.[1][2] The game character can be a player character, a boss, or a mob. Health can also be attributed to destructible elements of the game environment or inanimate objects such as vehicles and their individual parts. In video games, health is often represented by visual elements such as a numerical fraction, a health bar or a series of small icons, though it may also be represented acoustically, such as through a character's heartbeat.
Mechanics
In video games, as in tabletop role-playing games, an object usually loses health as a result of being attacked.[3][4] Protection points or armor help them to reduce the damage taken.[3] Characters acting as tanks usually have more health and armor.[2][5] In many games, particularly role-playing video games, the player starts with a small number of health and defense points,[6] but can increase them by gaining the required number of experience points and raising the character's level.[7][8]
In game design, it is considered important to clearly show that the player's character (or other object that they control) is losing health. In his book Level Up!: The Guide to Great Video Game Design, game designer Scott Rogers wrote that "health should deplete in an obvious manner, because with every hit, a player is closer to losing their life". As examples of visualizing health loss, Rogers cited Arthur of Ghosts 'n Goblins, who loses a piece of armor with each sustained hit, as well as the cars in the Grand Theft Auto series, in which smoke begins to flow from the hood after the car takes a significant amount of damage.[9]
The use of health points simplifies the game development process (since developers do not need to create complex damage systems), allows computers to simplify calculations associated with the game, and makes it easier for the player to understand the game.[10] However, more complex and realistic damage systems are used in a number of games. In Dwarf Fortress, instead of health points, dwarves have separate body parts, each of which can be damaged.[11] The Fallout games use health points, but allow characters to inflict damage to different parts of the enemy's body, which affects gameplay.[12][13] For example, if a leg is injured, the character can get a fracture, which will reduce their movement speed,[14] and if their arm is injured, the character can drop their weapon.[12] Health can also serve as a plot element. In Assassin's Creed, if the protagonist takes too much damage, thus departing from the "correct" route, the game ends and returns the player to the nearest checkpoint.[15]
In some games such as The Legend of Zelda and Monster Hunter, only the player's health points are visible. This is done so that the player does not know how many blows still need to be delivered, which makes the game less predictable.[16] Contrariwise, other games such as the Street Fighter series have both the player's and the opponent's health meters clearly visible, which allows the player to understand how successful their combat strategy is and how many remaining blows need to be inflicted on the enemy.[17]
Regeneration
Players can often restore a character's health by using various items such as potions, food or first-aid kits.[18] In role-playing video games, the player often can also restore a character's health by visiting a doctor or resting at an inn.[19] A number of games incorporate a mechanic known as "life steal" or "life leech", which allows a character to restore health by siphoning it from an enemy.[20][21][22][23][24][25] Methods for replenishing health differ from each other and are dependent on the game's genre. In more dynamic action games, it is important to quickly restore a character's health, while role-playing games feature slower-paced methods of health restoration to achieve realism.[26]
A number of games incorporate a regeneration system that automatically replenishes health if the character does not take damage. This makes the game easier to play by giving the player the opportunity to restore the character's health after a difficult battle. This system may allow the player to safely run through dangerous parts of the game without consequence.[27]
Tag team games often regenerate part of the health of a resting character.[28]
Armor class
In some role-playing games, armor class (abbreviated AC; also known as defense) is a derived statistic that indicates how difficult it is to land a successful blow on a character with an attack; it can also indicate damage reduction to a character's health. AC is typically a representation of a character's physical defenses such as their ability to dodge attacks and their protective equipment.[29][30][31] Armor class is a mechanic that can be used as part of health and combat game balancing.[32] AC "is roughly equivalent to defensive dodging in war games".[29]
Presentation
The health indicator can be represented in various ways.[15] The most basic forms are fractions and health bars,[33] as well as various icons such as hearts or shields.[34] More recent games can use a nonlinear health bar, where earlier hits take off more damage than later ones, in order to make the game appear more exciting.[35]
The indicator can be combined with other elements of the game interface. Doom uses a character portrait located at the bottom of the screen as such an indicator, in addition to a numerical health percentage display. If the hero takes damage, his face will appear increasingly pained and blood-covered.[36] The health point indicator can also be part of the character. In Dead Space, it is located on the main character's costume.[37] In Trespasser, it is represented as a tattoo on the main character's chest.[38] In Half-Life: Alyx, a VR game, the indicator is located on the back of the player's non-dominant hand, requiring the player to physically look at their tracked hand to check their health.[39] The character's condition can be conveyed through sound. In Dungeons of Daggorath, the frequency of the player character's audible heartbeat is dependent on how much damage has been received.[40] Silent Hill uses a similar system, but transmits the heartbeat via vibrations from the DualShock controller.[41]
The player character's health point indicator often occupies a significant position in the game's heads-up display. In The Legend of Zelda, it occupies one third of the HUD.[42] However, a number of games do without such an indicator. In the Super Mario series, the player character initially only has one health point, and the character's appearance is used to signify the number of health points; if the character collects a Super Mushroom, they grow in size and gain an additional health point.[43] In a number of first-person shooters, such as Call of Duty or Halo, the numerical value of the character's health points is hidden from the player. However, when the player character receives a large amount of damage, the game screen (or the part of the screen to which damage was dealt) is painted red, often including drops of blood, which simulates the effect of real-life injury. As health is restored, these effects gradually disappear.[44]
History
Hit points
The term "hit points" was coined by Dungeons & Dragons co-creator Dave Arneson.[45][46][47] While developing the tabletop role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons with Gary Gygax based on the latter's previous game Chainmail, Arneson felt that it was more interesting for players to manage small squads than a large army. This also allowed them to act out the role of each squad member. However, this approach had one drawback: according to the rules of Chainmail, the player rolls the dice during each battle, and depending on the number rolled, the character either kills the enemy or is killed. Because players did not want to lose the characters they had become accustomed to, Arneson created a "hit point" system based on similar mechanics previously used in the wargames Don't Give Up the Ship and Ironclads.[45][47][48][49] According to this system, each character has a certain number of hit points, which decreases with each blow dealt to them. This allows the character to survive several hits from an enemy.[45]
Some of the first home computer games to use hit points are Rogue (1980),[50] in which health is represented by a fraction,[51] and Dungeons of Daggorath (1982), which includes an audible heartbeat influenced by the player character's condition.[40] Action games also began moving away from one-hit deaths to health systems allowing players to take multiple hits, such as SNK's arcade shoot 'em up game Ozma Wars (1979) numerically representing an energy supply that depletes when taking hits and Mattel's Intellivision game Tron: Deadly Discs (1982) allowing players to take multiple hits at the cost of reducing maneuverability.[52]
Health meter
Before the introduction of health meters, action video games typically used a lives system in which the player could only take damage once, but could continue the game at the expense of a life. The introduction of health meters granted players the right to make mistakes and allowed game developers to influence a game's difficulty by adjusting the damage an enemy character inflicts.[53]
Data East's Flash Boy (1981) for the arcade DECO Cassette System, a scrolling action game based on the manga and anime series Astro Boy (1952–1968), has an energy bar that gradually depletes over time and some of which can be sacrificed for temporary invincibility.[54] Punch-Out!! (1983), an arcade boxing game developed by Nintendo, has a stamina meter that replenishes every time the player successfully strikes the opponent and decreases if the player fails to dodge the opponent's blow; if the meter is fully depleted, the player character loses consciousness.[55]
Yie Ar Kung-Fu (1984), an arcade fighting game developed by Konami, replaced the point-scoring system of Karate Champ (1984) with a health meter system. Each fighter has a health meter, which depletes as they take hits; once a fighter's health meter is fully depleted, it leads to a knockout. Yie Ar Kung-Fu established health meters as a standard feature in fighting games.[56] Kung-Fu Master (1984), an arcade beat 'em up developed by Irem, uses a health meter to represent player health, with the bar depleting when taking damage. In addition to the player character having a health meter, the bosses also have health meters, which leads to the game temporarily becoming a one-on-one fighting game during boss battles.[57][58] Kung-Fu Master established health meters as a standard feature in side-scrolling action games such as beat 'em ups.[58]
Health meters also began being used to represent hit points in role-playing video games, starting with The Black Onyx (1984), developed by Bullet-Proof Software. This inspired the use of a health bar in Hydlide (1984), an action role-playing game by T&E Soft, which took it a step further with a regenerating health bar.[59] Namco's arcade action role-playing title Dragon Buster (1984) further popularized the use of a health bar in role-playing games.[53]
Regeneration
The 1982 Apple II platform game Crisis Mountain displays health as a number from 3 (full) to 0 (dead), and health gradually regenerates over time.[60] In Hydlide (1984) and the Ys series,[61][62] the character's health (represented as both hit points and a health meter) are restored when the character does not move.[63][64] Halo: Combat Evolved (2001) is credited with popularizing the use of regeneration in first-person shooters.[65] However, according to GamesRadar+'s Jeff Dunn, regeneration in its current form was introduced in The Getaway (2002), as Halo: Combat Evolved only used shield regeneration.[61]
Defense
Arneson is also credited for the term "armor class" which was used in Chainmail and then Dungeons & Dragons;[66][67] "although armor class might have been inspired by the rules in Don't Give Up the Ship!, there is not an explicit attribute with that name in the game's rules. [...] It seems more likely that Arneson's house rules for armor class never made it into the final published version of the wargame".[48] However, many role-playing games that followed Dungeons & Dragons moved away from the term "armor class" and simply replaced the term with "defense".[48]
See also
- Magic (game terminology)
- Experience point
- Medical state, a real-world indicator of health status for hospital patients
References
- ↑ Fullerton 2014, pp. 79, 130.
- 1 2 Moore 2011, p. 91.
- 1 2 Fullerton 2014, p. 130.
- ↑ Brathwaite & Schreiber 2009, p. 225.
- ↑ Schwab 2009, p. 85.
- ↑ Adams 2010, p. 408.
- ↑ Kremers 2009, p. 378.
- ↑ Moore 2011, p. 142.
- ↑ Rogers 2010, pp. 276–277.
- ↑ Adams & Dormans 2012, p. 290.
- ↑ Adams, Tarn (27 February 2008). "Interview: The Making Of Dwarf Fortress". Gamasutra (Interview). Interviewed by Josh Harris. Archived from the original on 2013-11-12. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- 1 2 Burford, GB (August 21, 2015). "Fallout 3 Isn't Really an RPG". Kotaku. Archived from the original on October 30, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ↑ Stapleton, Dan (July 2, 2010). "Exclusive Fallout: New Vegas trait revealed". PC Gamer. Archived from the original on April 25, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ↑ Hernandez, Patricia (January 4, 2016). "Fallout 3 Beaten in Under 15 Minutes, A New World Record". Kotaku. Archived from the original on August 23, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- 1 2 Rogers 2010, p. 172.
- ↑ Martindale, Jon (October 3, 2012). "Let's Kill off Health Bars". Kit Guru Gaming. Archived from the original on May 28, 2015. Retrieved November 21, 2014.
- ↑ Novak 2013, p. 31.
- ↑ Moore 2011, pp. 151, 194.
- ↑ Duggan 2011, pp. 109, 141.
- ↑ Tan, Maurice (January 13, 2012). "A starter's guide to Robot Entertainment's Hero Academy". Destructoid. Archived from the original on August 25, 2012. Retrieved August 25, 2012.
- ↑ Onyett, Charles (June 19, 2012). "Dota 2: Playing the Phantom Assassin". IGN. Archived from the original on June 22, 2012. Retrieved August 25, 2012.
- ↑ Carter, Chris (June 17, 2013). "Impressions: League of Legends: Aatrox". Destructoid. Archived from the original on October 29, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ↑ Goldfarb, Andrew (September 14, 2012). "Diablo III Reducing Inferno Difficulty". IGN. Archived from the original on November 1, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ↑ Hancock, Patrick (June 27, 2013). "Review: Rogue Legacy". Destructoid. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved July 5, 2013.
- ↑ Carter, Chris (March 14, 2013). "God of War: Ascension single and multiplayer guide". Destructoid. Archived from the original on October 21, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ↑ Fullerton 2014, p. 79.
- ↑ Moriarty, Jonathan (December 2, 2010). "Video Game Basics: The Health Bar". Baltimoregamer.com. Archived from the original on 28 April 2012. Retrieved November 21, 2014.
- ↑ "CAPCOM: STREET FIGHTER X TEKKEN | Official Web Manual".
- 1 2 Adams 2010, p. 466.
- ↑ Howley, Greg (2019-04-26). "Beyond Hit Points: The Evolution of RPG Combat Mechanics". GeekDad. Archived from the original on 2022-02-23. Retrieved 2022-02-23.
- ↑ Mackay, Daniel (2017). The Fantasy Role-Playing Game: A New Performing Art. McFarland. p. 173. ISBN 9780786450473.
- ↑ Schreiber, Ian; Romero, Brenda (2021). Game Balance. CRC Press. ISBN 9781351643412.
- ↑ Moore 2011, p. 46.
- ↑ Rogers 2010, pp. 172, 276.
- ↑ "Guilty Gear Strive: Damage Scaling Explained". 17 June 2021.
- ↑ Zwiezen, Zack (4 February 2019). "The Weird Story Behind Doom's Rare "Ouch Face"". Kotaku Australia. Retrieved 12 June 2023.
- ↑ Antista, Chris (August 17, 2010). "The 10 most creative life bars". GamesRadar+. p. 2. Archived from the original on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ Pearson, Craig (May 16, 2007). "PC Feature Long Play: Trespasser". PC Gamer UK. Future Publishing Limited. Archived from the original on September 9, 2007. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
- ↑ "Half-Life: Alyx Wiki Guide, Chapter 2: The Quarantine Zone". IGN. 2020-03-26. Archived from the original on 2020-08-08.
- 1 2 Barton, Matt (February 23, 2007). "The History of Computer Role-Playing Games Part 1: The Early Years (1980–1983)". Gamasutra. Archived from the original on April 19, 2007. Retrieved August 14, 2020.
- ↑ Rogers 2010, pp. 166–167.
- ↑ Schell 2008, p. 237.
- ↑ Saunders & Novak 2012, p. 231.
- ↑ Rogers 2010, p. 173.
- 1 2 3 Rausch, Allen (August 19, 2004). "Dave Arneson Interview". GameSpy. Archived from the original on August 22, 2004. Retrieved January 9, 2014.
- ↑ Carreker 2012, p. 334.
- 1 2 Fannon 1999, p. 249.
- 1 2 3 Tresca 2010, p. 53-54.
- ↑ https://www.blackgate.com/2013/03/25/weird-of-oz-huffs-about-hit-points/
- ↑ Costikyan 2013, p. 46.
- ↑ "Rogue Instruction Manual © 1985 EPYX, Inc". Archived from the original on 2016-07-31.
- ↑ Ragan, Jess (June 15, 2006). "Playing With Power: Great Ideas That Have Changed Gaming Forever". 1UP.com. Archived from the original on 2006-06-17. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- 1 2 "Gaming's most important evolutions". GamesRadar. October 8, 2010. Archived from the original on January 18, 2016. Retrieved August 14, 2020.
- ↑ John Szczepaniak (2014). "Flash Boy". The Untold History of Japanese Game Developers (DVD) (in English and Japanese). Hardcore Gaming 101. Event occurs at 1:34:00.
- ↑ "Glass Joe Boxes Clever". Computer + Video Games. Future Publishing: 47. August 1984. Archived from the original on 2017-10-22. Retrieved 2015-01-02.
- ↑ Good, Owen S. (24 November 2019). "Yie Ar Kung Fu, one of the earliest fighting games, comes to Switch and PS4". Polygon. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ↑ Lendino, Jamie (27 September 2020). Attract Mode: The Rise and Fall of Coin-Op Arcade Games. Steel Gear Press. pp. 289–290. Archived from the original on 14 February 2023. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
Like Thomas, the end bosses all had health meters, so the game would momentarily become a one-on-one fighter
- 1 2 Williams, Andrew (16 March 2017). History of Digital Games: Developments in Art, Design and Interaction. CRC Press. pp. 143–146. ISBN 978-1-317-50381-1.
- ↑ Szczepaniak, John (November 2015). The Untold History of Japanese Game Developers. Vol. 2 (First ed.). S.M.G Szczepaniak. p. 32. ISBN 978-1518818745.
- ↑ "Crisis Mountain Apple II Manual" (PDF). 1982. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-06-26. Retrieved 2021-02-06.
- 1 2 Dunn, Jeff (November 15, 2012). "Stop, Drop, and Heal: The history of regenerating health". GamesRadar. Archived from the original on January 8, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Sulliven, Lucas (March 10, 2014). "Top 7… Games you didn't know did it first". GamesRadar+. Archived from the original on January 8, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Greene, Robert (August 1, 2017). "Hydlide". Hardcore Gaming 101. Archived from the original on August 26, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ↑ Szczepaniak, John (July 7, 2011). "Falcom: Legacy of Ys". GamesTM (111): 152–159 [153]. Archived from the original on April 23, 2016. Retrieved April 7, 2016.(cf. Szczepaniak, John (July 8, 2011). "History of Ys interviews". Hardcore Gaming 101. Archived from the original on 16 May 2019. Retrieved 6 September 2011.)
- ↑ Rogers 2010, p. 277.
- ↑ Rogers, Scott (2014). Level Up! The Guide to Great Video Game Design (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 237. ISBN 9781118877197.
- ↑ "Dungeons & Deceptions: The First D&D Players Push Back On The Legend Of Gary Gygax". Kotaku. August 26, 2019. Archived from the original on 2020-06-29. Retrieved 2022-02-23.
Bibliography
- Adams, Ernest (2010). Fundamentals of Game Design. New Riders. ISBN 978-0132104753.
- Adams, Ernest; Dormans, Joris (2012). Game Mechanics: Advanced Game Design. New Riders. ISBN 978-0132946681.
- Brathwaite, Brenda; Schreiber, Ian (2009). Challenges for Game Designers. Course Technology. ISBN 978-1584505808.
- Carreker, Dan (2012). The Game Developer's Dictionary: A Multidisciplinary Lexicon for Professionals and Students. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1435460829.
- Costikyan, Greg (2013). Uncertainty in Games. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0262018968.
- Duggan, Michael (2011). RPG Maker for Teens. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1435459670.
- Fannon, Sean Patrick (1999). Fantasy Roleplaying Gamer's Bible. Obsidian Studios Corporation. ISBN 0967442907.
- Fullerton, Tracy (2014). Game Design Workshop: A Playcentric Approach to Creating Innovative Games. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1482217179.
- Kremers, Rudolph (2009). Level Design: Concept, Theory, and Practice. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1439876954.
- Moore, Michael (2011). Basics of Game Design. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1568814339.
- Novak, Jeannie (2013). The Official GameSalad Guide to Game Development. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1285712666.
- Rogers, Scott (2010). Level Up!: The Guide to Great Video Game Design. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0470970928.
- Saunders, Kevin; Novak, Jeannie (2012). Game Development Essentials: Game Interface Design. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1285401379.
- Schell, Jesse (2008). The Art of Game Design: A Book of Lenses. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0123694966.
- Schwab, Brian (2009). AI Game Engine Programming. Course Technology. ISBN 978-1584506287.
- Tresca, Michael (2010). The Evolution of Fantasy Role-Playing Games. McFarland & Company. ISBN 978-0786460090.
External links
 Media related to HP bar at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to HP bar at Wikimedia Commons