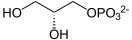
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2R)-2,3-Dihydroxypropyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
1,2,3-propanetriol, 1-(dihydrogen phosphate), (2R)- D-glycerol 1-phosphate L-glycerol 3-phosphate L-α-glycerophosphate L-α-phosphoglycerol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1723975 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.279 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Alpha-glycerophosphoric+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H7O6P | |
| Molar mass | 170.057 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related organophosphates |
Glycerol 1-phosphate Glycerol 2-phosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate[lower-alpha 1][lower-alpha 2] is the organic ion with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OPO32-. It is one of two stereoisomers of the ester of dibasic phosphoric acid (HOPO32-) and glycerol. It is a component of bacterial and eukaryotic glycerophospholipids.[2] From a historical reason, it is also known as L-glycerol 3-phosphate, D-glycerol 1-phosphate, L-α-glycerophosphoric acid.
Biosynthesis
Glycerol 3-phosphate is synthesized by reducing dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), an intermediate in glycolysis. The reduction is catalyzed by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. DHAP and thus glycerol 3-phosphate can also be synthesized from amino acids and citric acid cycle intermediates via the glyceroneogenesis pathway.
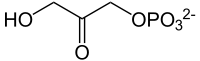 + NAD(P)H + H+ →
+ NAD(P)H + H+ →  + NAD(P)+
+ NAD(P)+
It is also synthesized by the phosphorylation of glycerol, which is generated by hydrolysis of fats. This esterification is catalyzed by glycerol kinase.
Metabolism and biological function

Glycerol 3-phosphate is a starting material for de novo synthesis of glycerolipids. In eukaryotes, it is first acylated on its sn-1 position by an ER- or mitochondrial membrane enzyme, glycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase. A second acyl group is subsequently installed on the sn-2 position making phosphatidic acids.
 + Acyl-CoA → Lysophosphatidic acid + CoA
+ Acyl-CoA → Lysophosphatidic acid + CoA
Glycerol-1-phosphatase catalyzes the hydrolysis of glycerol 3-phosphate to regenerate glycerol, allowing glycerol fermentation to produce glycerol from glucose through glycolysis pathway. A number of organisms express this enzyme.[2]
 + H2O →
+ H2O → 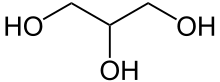 + Pi
+ Pi
Shuttle system
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenases are located both in the cytosol and the intermembrane face of mitochondrial inner membrane. Glycerol 3-phosphate (G3P) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) are molecules so small that they can permeate the mitochondrial outer membrane through porins and shuttle between two dehydrogenases. Using this shuttle system, NADH generated by cytosolic metabolisms including glycolysis is reoxidized to NAD+ reducing DHAP to G3P, and the reducing equivalent can be used for generating a proton gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane by coupling and oxidizing G3P and reducing quinone.
The Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle is an emergency back-up system to supply neurons' demand of energy.[3]
Dephosphorylation
Glycerol-3-phosphate was found to be a substrate for the enzyme phosphoglycolate phosphatase (PGP, or G3PP) in mammals in 2015.[2] G3PP activity has subsequently been suggested to have a regulatory role in central metabolism[2] and stress response.[4]
Glycerol 1-phosphate
Glycerol 1-phosphate, sometimes called as D-glycerol 3-phosphate, is the enantiomer of glycerol 3-phosphate. Eukaryotes use the 3-phosphate, or L-configuration, for glycerolipid backbone. The 1-phosphate is specifically found in archeal lipids.[5]
Notes
- ↑ This article uses stereospecific numbering where stereoconfiguration is not explicitly specified.
- ↑ Equally appropriate names in biochemical context include glycerol-3-phosphate, 3-O-phosphonoglycerol, 3-phosphoglycerol[1] and Gro3P.
- ↑ G. P. Moss (ed.). "Nomenclature of Phosphorus-Containing Compounds of Biochemical Importance". Archived from the original on 2016-12-08. Retrieved 2015-05-20.
- 1 2 3 4 Mugabo Y, Zhao S, Seifried A, Gezzar S, Al-Mass A, Zhang D, Lamontagne J, Attane C, Poursharifi P, Iglesias J, Joly E, Peyot ML, Gohla A, Murthy Madiraju SR, Prentki M (January 2016). "Identification of a mammalian glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase: Role in metabolism and signaling in pancreatic ß-cells and hepatocytes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (4): E430–E439. doi:10.1073/pnas.1514375113. PMC 4743820. PMID 26755581.
- ↑ "Neuronal Back-up System Discovered". August 30, 2022.
- ↑ Possik E, Schmitt C, Al-Mass A, Bai Y, Cote L, Morin J, Erb H, Oppong A, Kahloan W, Parker JA, Murthy Madiraju SR, Prentki M (January 2022). "Phosphoglycolate phosphatase homologs act as glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase to control stress and healthspan in C. elegans". Nature Communications. 177 (1): E177. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-27803-6. PMC 8752807. PMID 35017476.
- ↑ Caforio, Antonella; Driessen, Arnold J.M. (2017). "Archaeal phospholipids: Structural properties and biosynthesis" (PDF). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 1862 (11): 1325–1339. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.12.006. PMID 28007654.