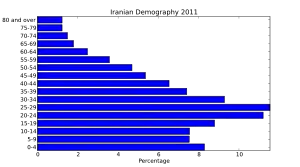
For health issues in Iran see Health in Iran.
Healthcare in Iran is based on three pillars: the public-governmental system, the private sector, and NGOs.[1] The healthcare and medical sector's market value in Iran was almost US$24 billion in 2002 and is forecast to rise to US$96 billion in 2017.[2] With a population of 80 million (2017), Iran is one of the most populous countries in West Asia. The country faces the common problem of other young demographic nations in the region, which is keeping pace with growth of an already huge demand for various public services. The young population will soon be old enough to start new families, which will boost the population growth rate and subsequently the need for public health infrastructures and services. Total healthcare spending is expected to rise from $24.3 billion in 2008, to $96 billion by 2017, reflecting the increasing demand on medical services.[3] Total health spending was equivalent to 6% of GDP in Iran in 2017.[4] About 90% of Iranians have some form of health insurance.[5] Iran is also the only country with a legal organ trade.[6][7] However, the legal character of organ donations is deemed to be a gifting of organs and not their sale and purchase.[8]
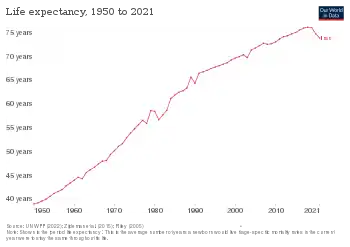
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as of 2000, Iran ranks 58 in healthcare and 93 in health-system performance.[9] In 2016, Bloomberg News ranked Iran 30th most efficient healthcare system ahead of the United States and Brazil.[10] The report shows life expectancy in Iran is 75.5 years and per capita spending on healthcare is $346.[11][10] The health status of Iranians has improved over the last two decades. Iran has been able to extend public health preventive services through the establishment of an extensive Primary Health Care Network.[12] As a result, child and maternal mortality rates have fallen significantly, and life expectancy at birth has risen remarkably. Infant (IMR) and under-five (U5MR) mortality have decreased to 28.6 and 35.6 per 1,000 live births respectively in 2000, compared to an IMR of 122 per 1,000 and a U5MR of 191 per 1,000 in 1970.[13] Immunization of children is accessible to most of the urban and rural population.[4]
Health services
| IRAN: Healthcare (Source: EIU)[4] | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy, average (years) | 70.0 | 70.3 | 70.6 | 70.9 | 71.1 | 71.4 |
| Healthcare spending (% of GDP) | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| Healthcare spending ($ per head) | 113 | 132 | 150 | 191 | 223 | 261 |
The largest healthcare delivery network is owned and run by the Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME) through its network of health establishments and medical schools in the country. MOHME is in charge of provision of healthcare services through its network, medical insurance, medical education, supervision and regulation of the healthcare system in the country, policymaking, production and distribution of pharmaceuticals, and research and development. Additionally, there are other parallel organisations such as Medical Services Insurance Organizations (MSIO) that have been established to act as a relief foundation as well as an insurance firm. Some hospitals, such as Mahak for children's cancer, are run by charitable foundations.
According to the last census that Statistical Centre of Iran undertook in 2003, Iran possesses 730 medical establishments (e.g. hospitals, clinics) with a total of 110,797 beds, of which 488 (77,300 beds) are directly affiliated and run by the MOHME and 120 (11,301 beds) owned by the private sector and the rest belong to other organisations, such as the Social Security Organization of Iran (SSO). There were about seven nurses and 17 hospital beds per 10,000 population.[4]
An extensive network of public clinics offers primary health care at low cost. In rural areas, each village or group of villages has a "health house" staffed by community health workers, locals trained in preventive healthcare methods such as nutrition, family planning, taking blood pressure, prenatal care, immunization, and monitoring environmental conditions such as water quality. Each health house is equipped with an examination room and sleeping quarters, and has a staff of one man and one or more women, all of whom are from the villages they serve. These are the population's first point of contact with the health care system. Those with more complex illnesses are referred to rural health centers, which are staffed by a physician, technician, and administrator. Similar primary health posts also exist in urban areas. Those in need of more complex care, including surgical services, are referred to hospitals. Iran's primary healthcare system has been rated as "excellent" by UNICEF.[14]
The Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME) operates public hospitals, both general and specialty hospitals, throughout Iran. Public hospitals are typically under the direct management of universities.[15] In most large cities, well-to-do persons use private clinics and hospitals that charge high fees.[4] In 2000, 94% of the population could access local health services, according to the WHO. Access ranged from 86% in rural areas to 100% in urban areas.[4] Between 80% and 94% of the population could access affordable essential medicines in 1999.[4]
Coverage
The Social Security Organization is responsible for insuring employed citizens in urban areas and their dependents, with the exception of government workers. All salaried and wage workers are covered, as are self-employed persons who voluntarily join. It also insures many old-age pensioners. The Medical Service Insurance Organization covers government employees, students, and inhabitants of rural areas. The Imam Khomeini Relief Foundation insures the poor who are not covered by other insurance schemes, while the Military Personnel Insurance Organization provides health insurance to members of the armed forces. Beyond these schemes, there are a number of private and semi-public insurance programs that cover the more affluent members of society.[5]
More than 90% of the population has health insurance, and the government has made universal coverage by 2018 a priority.[15] In general, health insurance covers 70% of the cost of drugs on the insurers' coverage list, and 90% of public hospital costs, with extra provision for those with rare diseases or in remote areas.[5][15]
Since 2009, a new government plan called "the comprehensive insurance plan" provides basic coverage to all Iranians.[16]
Workforce
Iran has been very successful in training/educating the necessary human resources for its health system. The system of almost 30 years ago where the country was facing a shortage of all kinds of skilled personnel in the health and medical sector has been completely changed into one in which the necessary professionals now completely suffice the country's needs. There are now 488 government funded hospitals in Iran. There were 0.5-1.1 physicians per 1000 population in 2004 according to various estimates (about 46 percent of physicians were women).[17]
| Medical Schools | 51 |
| Medical Students | 1 million |
| Professors of Medicine | 20,000 |
| Hospital Beds | 120,000 |
| Village Clinics | 20,000 |
| Doctors | 100,000 |
| Nurses | 170,000 |


.jpg.webp)





However, access and availability of health care continues to be somewhat limited in lesser developed provinces where the health indices are also lower as compared to national averages. The country is in an epidemiologic transition and faces double burden of the diseases. New emerging threats should also be considered. The demographic and epidemiological transition underway will have a significant effect on the pattern of morbidity and mortality in the near and distance future, especially as it affects the emergence of chronic non-communicable diseases and the health problems of an aging population.
Development
Although overall improvements have been achieved in all health areas since the 1979 revolution, the present challenging economic conditions of the country, combined with rapid advances in medical technology and information technology, individuals’ expectations, and the young demographic of the population will undoubtedly challenge the sustainability of past improving trends.
Medical tourism
Medical tourism in Iran is a very progressed and talented field. Medical tourism is about going abroad for getting medical treatment or a treatment that is not provided in your own country or at least it is not as efficient as it should be. People from more developed countries would travel to other countries to get their treatment with lower price. Its estimated that by using medical tourism in Iran a foreigner can save up to 50% on their treatment.
Medical tourism in Iran, has a high potential of attracting tourists for medical services. Apart from the price which is considerably lower, comparing to other countries being in the same region, the quality of medical services in Iran are quite pleasing. Iran has a really well educated and experienced medical staff. Medical specialists are highly professional and supported by a qualified nursing system. Iran also has a really active team of medical researchers.[18]
In 2012, 30,000 people visited Iran each year to receive medical treatment.[19][20] Most health tourists were from Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Iraq, Turkey, Kuwait, Oman and Pakistan.[21]
Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry in Iran began in its modern form in 1920 when the Pasteur Institute of Iran was founded. Iran has a well-developed pharmaceutical production capability, however, the country still relies on imports for raw materials and many specialized drugs. The standards regarding pharmaceutical products are determined and modified by the Pharmacopeia Council. As of 2019, Iran says it produces 80-90% of the raw materials needed inside the country.[22] These include microplates, omeprazole, tamsulosin hydrochloride, naltrexone base, sitagliptin phosphate, and pioglitazone in various sizes.[23]
Iran's Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME) has a mission to provide access to sufficient quantities of safe, effective and high quality medicines that are affordable for the entire population. Since the 1979 revolution, Iran has adopted a full generic-based National Drug Policy (NDP), with local production of essential drugs and vaccines as one of the main goals.[24]
Although over 85 percent of the population use an insurance system to reimburse their drug expenses, the government heavily subsidizes pharmaceutical production/importation in order to increase affordability of medicines, which tends also to increase overconsumption, overprescription and misuse of drugs, much like the abuse of pharmaceutical opioids in Iran such as the heavily prescribed codeine for moderate to severe pain. The regulatory environment of the country is rather strict on the import of drugs and pharmaceuticals towards companies that intend to enter into the market for the first time. The Ministry of Health and Medical Education is the main stakeholder of pharmaceutical affairs in the country.
Market
In 2006, 55 pharmaceutical companies in Iran produce more than 96 percent (quantitatively) of medicines on the market, worth $1.2 billion annually.[25] Iran's pharmaceutical market is estimated to be worth $1.87 billion (2008), $2.31 billion (2009), $3.26 billion (2011), $3,57 billion (2013) and $3.65bn by 2013 (projected).[3][26][27][28]
The drug market in Iran is heavily in favour of generic medicines, which contributed US$1.23bn to the total in 2009, with patented drugs at US$817mn and OTC medicines at US$262mn.[27]
The market share of local production (value-wise) has declined from 85.2% to 63.4% over the past 8 (Iranian) years (2009). In this period the value of importation has jumped from 14.8% to 36.6%. The government imposes 90% tariff on the import of drugs.
In 2009, 1.8 million units of pharmaceutical products worth $1.2 billion were imported into Iran.[29]
As of 2015, Iran's share of global biotechnology products market is half a billion US dollar.[30]
In 2010, 50% of raw materials and chemicals used in the drug manufacturing sector were imported.[31] In 2019, Iranian companies were able to produce 80-90% of the raw materials needed inside the country.[22]
Products
Iran has produced a wide range of pharmaceuticals for the treatment of cancer, diabetes, infection and depression.[32]
Iran is the first country in the East Mediterranean region which has the technical and scientific capability to export vaccines to various world countries.[33] Iran will gain self-sufficiency in vaccine production by 2014.[34] As of 2019, Iran produced 8 out of the 18 main vaccines for humans.[22] In 2020-2021, amid the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran, Iran developed multiple COVID-19 vaccines[35] with five that have received emergency use authorization (COVIran Barekat,[36] Pasteurcovac,[37] FAKHRAVAC,[38] COVAX-19[39] and Razi Cov Pars[40]).
The new drugs launched in Iran for the treatment of MS include an interferon beta-1b by CinnaGen.[41] Gamma Immunex (recombinant interferon beta 1), Pegaferon (recombinant pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN)) and regenerative human factor VIII are among other recombinant-based medication made in Iran. A generic version of fingolimod by Novartis has been launched as well as a biosimilar version of EMD Serono′s Rebif.
Iranian researchers have developed 41 types of anti-cancer medications, overcoming the need for importing pricey cancer drugs from abroad (2011).[42][43] There are also 24 additional biosimilar drugs which Iran plans to bring into production by end of 2012.
According to the Food and Drug Administration in 2014, trade in counterfeit commercial drugs has become more lucrative than dealing in illegal narcotics. Most of which come from Pakistan. Drugs for sexual enhancement, weight control, aesthetics, height enhancement, hair growth and body building are among the more prevalent fake drugs on the market. [44]
Innovation
In recent years several drugmakers are gradually developing the ability to innovate, away from generic drugs production itself.[27]
Iran has around 8000 species of plant life and researches indicate that more than 2300 species have remedial characteristics or can be used as cosmetic products;[45] only 100-300 of which are being used in pharmaceutical industries at present.[46][47] Iran has 80 percent of the world medicinal herbs. Due to lack of required technology, they are exported raw and in limited quantities to foreign markets.[47]
Pharmaceutical companies

In 2010, 92 companies were active in the pharmaceutical industry of Iran.[29]
The Social Security Investment Co. (SSIC), which is affiliated to the Ministry of Welfare, was reported in 2008 to be Iran's largest holding company, owning and controlling 22 pharmaceutical manufacturing companies and possessing a 40% share of Iran's total pharmaceutical production.[48]
The leading pharmaceuticals company is Darou Pakhsh, which is majority-owned by the Social Security Organization. The company manufactures, distributes, imports and exports finished products and pharmaceutical raw materials. Darou Pakhsh has an annual turnover of US$400m and claims to have the largest research and development operation of any Iranian drug firm. The company formed a plasmapheresis joint venture with a German medical firm, Biotest AG, in early 2004.[4]
The Razi Institute for Serums and Vaccines and the Pasteur Institute of Iran are leading regional facilities in the development and manufacture of vaccines.[49]
The Barkat Pharmaceutical Group is a major pharmaceutical holding that supplied 14% of the pharmaceutical market of Iran in 2016.[50]
Iranian pharmaceutical manufacturers are reported to be disadvantaged by the government's poor intellectual property protection regime and lack of foreign direct investment.[3]
Medical equipment
The Department of Medical Equipments in the Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME) is responsible for supervising imports in this segment, but the import and distribution of such equipment is mostly handled by the private sector. Iran has undergone the primary stages of development in terms of industrialisation and a rather strong indigenous manufacturing capability exists in the country. Therefore, one can expect to find a handful of local producers for basic medical equipment, making it very hard to penetrate into the Iranian market for similar imported ones.
Iran MED and Iran LAB are the main annual exhibitions relating to medical and laboratory equipment in Tehran.[51] In 2009, approximately $3.1 billion worth of drugs and medical products were consumed in Iran. This shows an 80% increase from 3 years ago.[29] Iran's per capita consumption is $21, as opposed to the global average of $94 because Iran subsidizes heavily its medical and pharmaceutical industry.[29] In 2009, Iran exported $74 million worth of "medical products" to countries such as Iraq, Afghanistan and Russia.[29]
U.S. sanctions against Iran do not apply to medical equipment or pharmaceuticals but the purchase of foreign pharmaceutical products and diagnostics have been greatly hampered since the unilateral retraction of the nuclear deal and the reintroduction of strict financial sanctions by the Trump administration, thereby greatly exacerbating health problems in Iran, such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
There are over 100 Iranian companies representing the international suppliers in this market, handling both promotion and the after-sales service of the products. Iran is a mature market when it comes to medical equipment. Most of the major international players in this sector are present in the Iran market.
See also
References
- ↑ Ayse, Valentine; Nash, Jason John; Leland, Rice (January 2013). The Business Year 2013: Iran. London, U.K.: The Business Year. p. 156. ISBN 978-1-908180-11-7. Archived from the original on 2016-12-27. Retrieved 2014-03-16.
- ↑ "Health services and pharmaceuticals to Iran - For Australian exporters - Austrade". Archived from the original on Jan 5, 2009. Retrieved Oct 20, 2022.
- 1 2 3 "Iran Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare Report Q2". Payvand.com. 2009-03-25. Archived from the original on 2011-11-29. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Iran: Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals Forecast". Economist Intelligence Unit. August 18, 2008.
- 1 2 3 "Iran Health Insurance in Brief". Archived from the original on 2016-08-17. Retrieved 2016-07-05.
- ↑ Tober, Diane (2007). "Kidneys and Controversies in the Islamic Republic of Iran: The Case of Organ Sale". Body and Society. 13 (3): 151–170. doi:10.1177/1357034X07082257. S2CID 146238746. Archived from the original on 2015-10-16.
- ↑ Fry-Revere, Sigrid (2014). The Kidney Sellers:A Journey of Discovery in Iran. Carolina Academic Press. Archived from the original on 2013-12-28.
- ↑ Movassagh, Hooman (2016). "Human Organ Donations Under the 'Iranian Model': A Rewarding Scheme for U.S. Regulatory Reform?". Indiana Health Law Review. 13 (1): 82–118. doi:10.18060/3911.0013. SSRN 2767175.
- ↑ WHO, World Health Organization. "The World Health Report 2000" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2006-10-18. Retrieved 2006-10-12.
- 1 2 "U.S. Health-Care System Ranks as One of the Least-Efficient". Bloomberg.com. 29 September 2016. Archived from the original on 13 April 2018. Retrieved 26 April 2018 – via www.bloomberg.com.
- ↑ (PDF) http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/255336/1/9789241565486-eng.pdf?ua=1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-11-26.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ "Iran Daily - Domestic Economy - 07/02/09". Archived from the original on August 4, 2009. Retrieved February 19, 2016.
- ↑ "At a glance: Iran (Islamic Republic of) - The big picture". UNICEF. Archived from the original on 2012-02-05. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "UNICEF Iran (Islamic Republic of) - Media centre - Iran's Excellent Primary Health Care System". www.unicef.org. Archived from the original on 23 November 2017. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- 1 2 3 "The best and worst of worlds: Tehran's public hospital wards". theguardian.com. 28 January 2015. Archived from the original on 29 January 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
- ↑ "Child and Adult Health Care in Iran | Iranian Surgery". iraniansurgery.com. 4 May 2019. Retrieved 2021-12-23.
- ↑
- ↑ "Medical tourism in IRAN - Why Iran?". ir Persiatour. 2019-10-30. Retrieved 2020-04-01.
- ↑ "Fars News Agency :: Ahmadinejad Stresses Iran's Growing Medical Tourism Industry". English.farsnews.ir. 2012-01-17. Archived from the original on 2012-02-13. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "Iran earned $1.5bn from health tourism last year". www.payvand.com. Archived from the original on 21 November 2017. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ↑ "Iran reports earnings of $1.5bn from health tourism in 2012". International Medical Travel Journal. Archived from the original on 2014-07-14. Retrieved 2014-07-08.
- 1 2 3 "Iran able to produce 90% of needed pharma raw materials: VP". 2019-07-22. Archived from the original on 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2019-07-22.
- ↑ "Special Plans Devised to Counter Sanctions on Iran's Biotech Industries: VP - Science news". Archived from the original on 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2019-07-22.
- ↑ Iran-Daily: Biggest Pharmaceutical Plant to Open Soon Archived February 6, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Iran Daily - National - 07/01/07 Archived July 3, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Iran Daily - Domestic Economy - 10/20/08". Archived from the original on September 23, 2009. Retrieved February 19, 2016.
- 1 2 3 Greg Palast. "Pharmaceuticals: Afghan Ufficiale: La NATO Airstrike Uccide 14". OfficialWire. Archived from the original on 2012-02-22. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "BMI Iran Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare Report". companiesandmarkets.com. Archived from the original on 2016-02-19. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Iran Investment Monthly Dec 2010.pdf" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-03-06. Retrieved 2018-08-15.
- ↑ "$500m; Iran's share of biotechnology products market". mehrnews.com. 12 April 2015. Archived from the original on 17 April 2015. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ↑ "Investment data" (PDF). www.turquoisepartners.com. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-07-17. Retrieved 2010-07-06.
- ↑ "No. 3644 | Science | Page 8". Irandaily. Archived from the original on 2012-03-04. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "Iran joins world vaccine producers". Zawya. 2010-05-06. Archived from the original on 2013-02-10. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "Iran to gain self-sufficiency in vaccine production". Payvand.com. Archived from the original on 2012-02-06. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ Mallapaty, Smriti (2021-08-17). "Iran hopes to defeat COVID with home-grown crop of vaccines". Nature. 596 (7873): 475. Bibcode:2021Natur.596..475M. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-02216-z. PMID 34404947. S2CID 237198729.
- ↑ "FarsNews Agency Iran Licenses Emergency Injection of Home-Made Anti-Coronavirus Vaccine". www.farsnews.ir. Retrieved 2021-09-10.
- ↑ "Second Iranian coronavirus vaccine gets emergency use license". Tehran Times. 2021-06-30. Retrieved 2021-09-10.
- ↑ "Iran Authorizes Emergency Use of Third Homegrown Vaccine - Society/Culture news". Tasnim News Agency. Retrieved 2021-09-10.
- ↑ "Iran issues emergency permit for new local Covid-19 vaccine". Mehr News Agency. 6 October 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ↑ "مجوز مصرف اضطراری داوطلبانه واکسن کووپارس صبح امروز صادر شد". ایسنا (in Persian). 2021-10-31. Retrieved 2021-11-27.
- ↑ "No. 3827 | Front page | Page 1". Irandaily. 2010-11-15. Archived from the original on 2012-04-01. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "Iranian researchers produce new medicine for cancer treatment". Payvand.com. Archived from the original on 2011-11-03. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "Iranian scientists produce new drugs". Payvand.com. Archived from the original on 2012-05-17. Retrieved 2013-04-07.
- ↑ "Fake commercial drugs more profitable than narcotics in Iran". www.payvand.com. Archived from the original on 20 July 2014. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ↑ "Iran to export Alzheimer drug to France". mehrnews.com. 14 June 2014. Archived from the original on 1 July 2014. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ↑ "Iran's share of worldwide medicinal plant trade barely 2%". Mehrnews.com. Archived from the original on 2012-02-05. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- 1 2 "No. 3632 | Domestic Economy | Page 4". Irandaily. Archived from the original on 2012-02-19. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "Resources - Pharmaceuticals". Atieh Bahar. 2008-10-20. Archived from the original on 2011-07-07. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ "Iran - Countries - NTI". www.nti.org. Archived from the original on 13 November 2015. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ↑ "Iran's Giant Pharma Holding Listed on TSE". Financial Tribune. 2016-12-05. Retrieved 2021-12-08.
- ↑ "Iran Daily - Science - 06/11/09". Archived from the original on June 14, 2009. Retrieved February 19, 2016.
External links
![]() Media related to Healthcare in Iran at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Healthcare in Iran at Wikimedia Commons