
Al-Wayli is a district in the Western Area of Cairo, Egypt.[1] According to the district map (below), and the census,[2] it is subdivided into the qisms (police wards) of al-Wayli and el-Daher, or al-Zahir (Arabic: الظاهر, IPA: [edˈdɑːheɾ, ezˈzˤɑːheɾ]). Some of their better known quarters are Sakakini and Abbassia.
History
The area of al-Zahir was known as the Square of Qaraqush, where it was used as polo grounds by the 12th Century Ayyubid regent Qaraqush, north west of Cairo's walls.[3] After the conquest of Cairo by the Mamluks, the new sultan al-Zahir Baybars built his eponymous mosque over the polo grounds in 1268.[3]
Until the mid 19th Century, the area north of the mosque was the rural fringe of Cairo, consisting of the villages of El-Waylia, El-Demerdash, El-Mohamady and the Kobba palace izba (hamlet).[4]
In 1849, Egypt's ruler, Abbass Pasha I, redeveloped the area into the Abbasia neighbourhood.[4] However, by the late 19th Century the area was sparsely developed, where the contractor and real estate developer Sakakini Pasha bought a parcel of "swampy mosquito infested" land immediately north of al-Zahir mosque, and built a radial grid development in 1897, with his circular palace placed in the middle of the grid.[5] This area is known today as the Sakakini quarter (shiakha) in qism al-Zahir.
Administrative subdivisions and population
Al-Wayli district is divided into the qisms of al-Zahir and al-Wayli according to the Cairo Governorate district map and the census.[2]
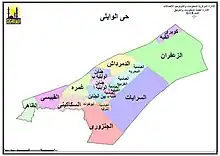
In 2017 qism al-Wayli had 79,292 residents in its 12 shiakhas.[2]
| Shiakha | Code 2017 | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Dimirdâsh, al- | 012401 | 3503 |
| Za`farân, al- | 012402 | 4797 |
| Sarâyât, al- | 012403 | 10513 |
| `Abbâsiyya al-baḥriyya, al- | 012404 | 7424 |
| `Abbâsiyya al-sharqiyya, al- | 012405 | 3512 |
| `Abbâsiyya al-gharbiyya, al- | 012406 | 10170 |
| `Abbâsiyya al-qibliyya A, al- | 012407 | 4857 |
| `Abbâsiyya al-qibliyya B, al- | 012408 | 4228 |
| Bayn al-Janâyin | 012409 | 5758 |
| Janâyyîn al-Wâyliyya A | 012410 | 10911 |
| Janâyyîn al-Wâyliyya B | 012411 | 4732 |
| Kûbrî al-Qubba | 012412 | 8887 |
While qism Al-Zahir had 71,870 residents in its six shiakhas in 2017.[2]
| Shiakha | Code 2017 | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Abû Khûda | 012301 | 4792 |
| Janzûrî, al- | 012302 | 10803 |
| Sakâkînî, al- | 012303 | 16239 |
| Ẓâhir, al- | 012304 | 10234 |
| Qubaysî, al- | 012305 | 13517 |
| Ghamra | 012306 | 16285 |
References
- ↑ "Western Area". www.cairo.gov.eg. Retrieved 2023-02-23.
- 1 2 3 4 Central Agency for Public Mobilisation and Statistics (CAPMAS) (2017). "2017 Census for Population and Housing Conditions". CEDEJ-CAPMAS. Retrieved 2023-02-21.
- 1 2 Taqi al-Din Ahmad al-Maqrizi, "Khitat," trans. Martyn Smith, 2009, 2:299-300.
- 1 2 Hussein, Mummad Fahmy (1965). Potential design for mass transportation in Egypt (PhD Dissertation Thesis). University of Michigan. p. 18.
- ↑ Rafaat, Samir (1997-04-05). "SAKAKINI PALACE: HOW ABOUT THE PALACE THAT TURNS A HUNDRED YEARS OLD THIS YEAR?". www.egy.com. Retrieved 2023-03-22.

