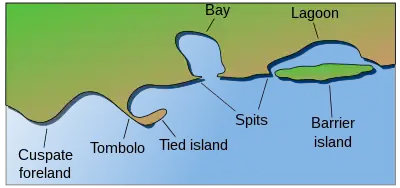
Coastal engineering is a branch of civil engineering concerned with the specific demands posed by constructing at or near the coast, as well as the development of the coast itself.
The hydrodynamic impact of especially waves, tides, storm surges and tsunamis and (often) the harsh environment of salt seawater are typical challenges for the coastal engineer – as are the morphodynamic changes of the coastal topography, caused both by the autonomous development of the system and human-made changes. The areas of interest in coastal engineering include the coasts of the oceans, seas, marginal seas, estuaries and big lakes.
Besides the design, building and maintenance of coastal structures, coastal engineers are often interdisciplinary involved in integrated coastal zone management, also because of their specific knowledge of the hydro- and morphodynamics of the coastal system. This may include providing input and technology for e.g. environmental impact assessment, port development, strategies for coastal defense, land reclamation, offshore wind farms and other energy-production facilities, etc.
Specific challenges

The coastal environment produces challenges specific for this branch of engineering: waves, storm surges, tides, tsunamis, sea level changes, sea water and the marine ecosystem.
Most often, in coastal engineering projects there is a need for metocean conditions: local wind and wave climate, as well as statistics for and information on other hydrodynamic quantities of interest. Also, bathymetry and morphological changes are of direct interest. In case of studies of sediment transport and morphological changes, relevant properties of the sea bed sediments, water and ecosystem properties are needed.
Long and short waves
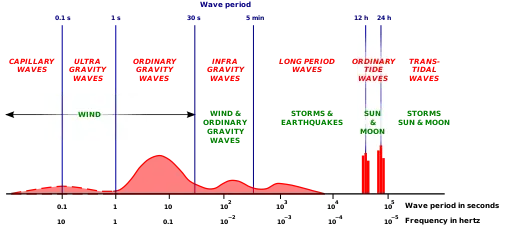
The occurrence of wave phenomena – like sea waves, swell, tides and tsunamis – require engineering knowledge of their physics, as well as models: both numerical models and physical models. The practices in present-day coastal engineering are more-and-more based on models verified and validated by experimental data.
Apart from the wave transformations themselves, for the waves coming from deep water into the shallow coastal waters and surf zone, the effects of the waves are important. These effects include:
- the wave loading on coastal structures like breakwaters, groynes, jetties, sea walls and dikes
- wave-induced currents, like the longshore current in the surf zone, rip currents and Stokes drift, affecting sediment transport and morphodynamics
- wave agitation in harbors, which may result in harbor downtime
- wave overtopping over seawalls and dikes, which may e.g. threaten the stability of a dike
Underwater construction
Coastal engineering takes place at or near the interface between land and water. Consequently a significant part of coastal engineering involves underwater construction, particularly for foundations. Breakwaters, sea walls, harbour structures like jetties, wharves and docks, bridges, tunnels, outfalls and causeways usually involve underwater work.
Sustainability and soft engineering
In recent decades, coastal engineers have favored non-structural solutions, which avoid adverse impacts that are typically cause by structures, such as sea walls, bulkheads, jetties, etc. These solutions include beach nourishment, marsh restoration/creation, and habitat restoration. More recently, beneficial use of dredge material, which utilizes material dredged for navigation maintenance to nourish beaches and restore wetlands. Beneficial use is also employed to increase the elevation of marsh platforms in an attempt to adapt to sea level rise.
Regional sediment management has also become a focus strategy for coastal practitioners. This essentially uses nearshore sediment sources and knowledge of coastal morphology to identify which accretional features can be harvested to bolster erosional areas, understanding the harvested material will continue to accumulate. A common regional sediment management option is to dredge ebb and flood shoals to nourish beaches.
Both beneficial use and regional sediment management recognizes the scarcity of material resources offshore and upland.
See also
- Beach erosion and accretion – Area of loose particles at the edge of the sea or other body of water
- Beach evolution – Changes to a shoreline by accretion and erosion
- Beach evolution#Modern beach recession – Changes to a shoreline by accretion and erosion
- Beach nourishment – Sediment replacement process
- Raised beach – Emergent coastal landform
- Beach evolution – Changes to a shoreline by accretion and erosion
- Integrated coastal zone management – Environmental management system
- Coastal management – Preventing flooding and erosion of shorelines, to prevent coastal erosion and creation of beach
- Coastal and oceanic landforms – Feature of the solid surface of a planetary body
- Coastal development hazards – Type of anthropogenic effect on the environment
- Coastal erosion – Displacement of land along the coastline
- Coastal geography – Study of the region between the ocean and the land
- Coastal engineering
- Hard engineering – Construction of hydraulic structures to reduce coastal erosion
- Soft engineering – Shoreline management based on sustainability principles
- Coastal morphodynamics – Interaction of shoreline seafloor topography and fluid hydrodynamic processes
- Coastal and Estuarine Research Federation – U.S. nonprofit organization (CERF)
- Human impacts on coasts – Area where land meets the sea or ocean
- Sea level rise – Rise in sea levels due to climate change
- Natural hazard – Major adverse event resulting from natural processes of the Earth
- Erosion – Natural processes that remove soil and rock
- Bioerosion – Erosion of hard substrates by living organisms
- Blowhole – Hole at the top of a sea-cave which allows waves to force water or spray out of the hole
- Natural arch – Arch-shaped natural rock formation
- Wave-cut platform – Narrow flat area created by erosion
- Hydrodynamic scour – Removal of sediment near an obstruction by swiftly moving water
- Bridge scour – Removal of sediment from around bridge abutments or piers by the movement of water
- Tidal scour – Sea-floor erosion caused by strong tidal currents
- Seabed gouging by ice – Outcome of the interaction between drifting ice and the seabed
- Longshore drift – Sediment moved by the longshore current
- Deposition (sediment) – Geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or landmass
- Coastal sediment supply – Transport of sediment to the beach environment
- Sand dune stabilization – Coastal management practice
- Submersion – Aspect of coastal erosion
Notes
- ↑ Munk, W.H. (1950), "Origin and generation of waves", Proceedings 1st International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Long Beach, California: ASCE, pp. 1–4
References
- Dean, R.G.; Dalrymple, R.A. (2004), Coastal Processes with Engineering Applications, Cambridge University Press, Bibcode:2004cpea.book.....D, ISBN 9780521602754
- Hughes, S.A. (1993), Physical Models and Laboratory Techniques in Coastal Engineering, Advanced series on ocean engineering, World Scientific, ISBN 9789810215415
- Kamphuis, J.W. (2010), Introduction to Coastal Engineering and Management, Advanced series on ocean engineering, World Scientific, ISBN 9789812834843
- Kraus, N.C. (1996), History and Heritage of Coastal Engineering, American Society of Civil Engineers, ISBN 9780784474143
- Sorensen, R. (2013), Basic Coastal Engineering, Springer, ISBN 9781475726657
External links
- The Coastal Engineering Page, University of Delaware, archived from the original on 2017-10-30, retrieved 2018-09-13
- Coastal Engineering Proceedings, Texas Digital Library, retrieved 2015-06-05 – Proceedings of the International Conference on Coastal Engineering (ICCE), held since 1950 (biannually since 1960).