| Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary | |
|---|---|
IUCN category V (protected landscape/seascape) | |
 | |
  | |
| Coordinates | 34°N 120°W / 34°N 120°W |
| Area | 1,470 sq mi (3,800 km2) |
| Established | 1980 |
| Governing body | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| www | |


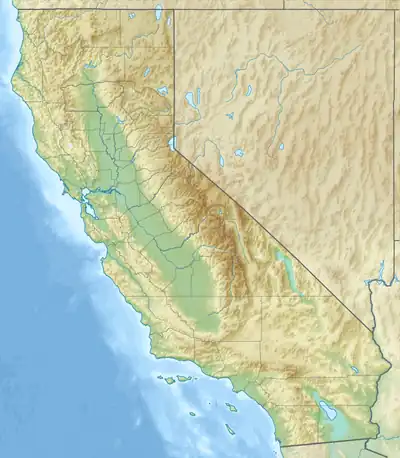
The Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary[1] is a sanctuary off the coast of Santa Barbara and Ventura counties in Southern California 350 miles south of San Francisco and 95 miles north of Los Angeles. It was designated in 1980 by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
The sanctuary encompasses approximately 1,470 square miles of ocean waters around Anacapa, Santa Cruz, Santa Rosa, San Miguel and Santa Barbara Islands, extending from the mean high tide of these islands to six nautical miles offshore, and surrounding Channel Islands National Park. It is part of the National Marine Sanctuary program under the administration of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).[2]
Its remote, isolated position at the confluence of two major ocean currents supports remarkable biodiversity and productivity. It's a special place for endangered species, sensitive habitats, historic shipwrecks, other maritime heritage artifacts, and living Chumash culture. Many valuable commercial and recreational activities thrive in the sanctuary, such as fishing, shipping, and tourism.
The sanctuary was federally designated because of its national significance as an area of exceptional natural beauty and resources, and due to heightened concerns following the 1969 oil spill in the Santa Barbara Channel. Protection of sanctuary resources is supported through research, education, conservation, and stewardship programs. The primary goal of the sanctuary is the protection of natural and cultural resources contained within its boundaries. The sanctuary is managed to promote ecosystem conservation, protect cultural resources, and support compatible human uses.
Education


The Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary (CINMS) is dedicated to education and outreach aiming to promote understanding, support, and participation in the protection and conservation of marine resources.[3]
Visitors Centers, Education Partners and Related Organizations
The sanctuary's visitor center works to interpret the living and maritime heritage resources that are a part of this iconic place.[4]
Outreach Products
The sanctuary distributes brochures and other resources such as posters, maps and coloring books for the public mostly informing about the biodiversity in the sanctuary as well as how to preserve it.[5]
Students at Sea
Program addressed to High Schools and college students. The objective is to explore different career pathways and learn how science is used to address different resource protection issues that threaten the health of our ocean.[6]
Teachers at See
Program addressed to elementary through high school teachers. They are involved in some hands-on activities such as conducting plankton tows, viewing plankton under a video microscope, piloting remotely operated vehicles, sampling water quality parameters such as pH and salinity and learning about current sanctuary research. The aim of the program is for these teachers to have the tools and resources to then pass them on to their students.[7]
Research

The sanctuary has partnerships with National Marine Fisheries Service, the National Park Service, and the Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada, as well as regional and international academic institutions such as the University of California, Santa Barbara, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Simon Fraser University, and the University of Auckland, New Zealand. These partnerships are facilitated by staff research expertise as well as operational support provided by the NOAA research vessels Shearwater and Shark Cat.
The sanctuary is currently engaging in the following research:
Marine Protected Area monitoring
Within the sanctuary, there is a network of 13 state and federal marine reserves and conservation areas that provide additional protections to the ecosystem. The marine reserves network was established to protect whole ecosystems and restore ecosystem health. One possible effect of marine reserves is that they may provide "spillover benefits" to areas outside the reserves. Sanctuary staff are currently conducting research on the effectiveness of marine reserves for community dynamics.[9] In one project, performed in collaboration with the Channel Islands National Park and colleagues at Simon Fraser University in Burnaby B.C., staff are evaluating the food web interactions expressed in the long-term, Kelp Forest Monitoring data set that the Channel Islands National Park has been collecting since 1984. That project has revealed that trophic relationships within MPAs are more robust, while outside MPAs these relationships are less so and the food web shows lower resilience and stability. In other work, with colleagues at the University of Auckland, they are examining potential competition between predators protected within MPAs (large fish and lobsters) and fishers who are targeting the prey of those predators (sea urchins). In addition, the sanctuary's ongoing maintenance of a network of oceanographic sensors provides a data stream that can contribute to our understanding of larval transport and adult animal movement across MPA boundaries.
Climate variability

Sanctuary staff are currently looking at how short-term changes in climate can affect local conditions across large areas. Their work on the role of variability in jet stream trajectory and strength in determining seasonal variability in central Siberia allows a new and significantly more accurate ability to forecast the arrival of harsh winters several months in advance. This work has contributed to a better, more mechanistic understanding of the connectedness of climate processes across the Northern Hemisphere, from Siberia all the way to the US West Coast. More recently, they are looking at how these same processes manifest in long term data on winds along the Central and Southern California coast to see how climate variability signals can affect local winds in the Santa Barbara Channel area. Variation in wind strength has ecological effects by driving upwelling and also has a practical implication for local mariners: if climate change causes more windy days, there are fewer days for boating and fishing in the sanctuary. Additionally, the sanctuary's ongoing maintenance of a network of moorings provides a continuous data series of oceanographic conditions in nearshore waters that is informing climate variability studies.
Sanctuary Aerial Monitoring and Spatial Analysis Program
The Sanctuary Aerial Monitoring and Spatial Analysis Program (SAMSAP) is an ongoing long-term aerial monitoring program that collects data on vessel and visitor use patterns and cetacean populations within the sanctuary. SAMSAP has been active since 1997 and has been instrumental in providing vital data for management, research, and emergency response needs.
Whale research
After populations of large whales were decimated by whaling in the last two centuries, several species are rebounding. Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary is a seasonal home to several species of those large whales. From early spring to late fall, the sanctuary sees increasing numbers of humpback, blue, and fin whales- with seasonally migrating gray whales transiting the sanctuary on their trips between the North Pacific and the lagoons of Baja California. At times, large whales aggregate in tremendous numbers, with as many as 186 unique photo identifications occurring in a single day. Understanding the causes of this aggregation, such as bloom dynamics of the krill the whales feed on, can provide valuable forecasting information to predict where whales are likely to be in the near term.[10] This information in turn could aid in reducing whale-ship interactions. Ongoing work has focused on behavioral responses of large whales to close encounters with large vessels transiting the Santa Barbara Channel. This work is being extended to focus on two problems: how variability in krill depth is key to whale decision making, and how the whales are selecting specific sized prey within pools of mixed-age krill. To get after these questions, sanctuary staff and contractors are combining an ongoing program of tagging large whales with time-depth-location recording tags with systematic mapping of krill fields around the sanctuary. The sanctuary is assisting the work of partners from Cascadia Research Collective and Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
Shipping
The Port of Los Angeles and Long Beach is the largest commercial harbor on the west coast with over 6,500 vessels stopping each year. Much of that traffic passes the Santa Barbara Channel and the Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary on its way to ports around the Pacific Rim. These vessels are large, with some being over 1,000 feet long, and fast; they can travel at speeds over 20 knots. They also emit significant exhaust into the area and are the principal source of underwater noise in the sanctuary. To keep track of how these ships may affect the sanctuary staff have been building on a long-term program to monitor broad band acoustics in and around the sanctuary.[11] As a first step they are developing data management solutions with partners at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis for two new data streams: broadband acoustic data and Automatic Identification System (AIS) data on ship travel. Although both sources of data were originally developed for other objectives—oceanographic research and safety at sea—these data streams provide valuable information for evaluation of spatial use patterns. For example, recent work evaluating California State air quality rulings on vessel fuel use demonstrated a major change in traffic patterns and emerging conflicts in use of the ocean by shipping and National Defense interests. Evaluating these data in the context of shifts of vessel traffic has also revealed quantitative relationships between economic indicators (numbers of ships and amount of cargo) and noise levels in the sanctuary.
Deep water communities
The sanctuary contains a significant amount of deep-water habitat: about 91.5% of the sanctuary is deeper than 100 ft. From depths of 100 ft to over 5,000 ft, deep water habitat experiences cold water, almost no light, and low oxygen, yet a variety of specially adapted animals such as corals, sponges, crabs, shrimp, fish, anemones, cucumbers, sea stars, and worms reside here. In 2010, a NOAA expedition surveyed an underwater feature in the Footprint Marine Reserve to learn more about the abundance and distribution of coral and sponge habitat and to study the chemistry of the water in which these animals live.
Recreational activities
_CINMS.jpg.webp)
The sanctuary is also a site for recreational activities, such as scuba diving, snorkeling, kayaking, boating, viewing wildlife, and fishing.[12]
In an effort to balance recreation and conservation, the California Fish and Game Commission established a network of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) within the nearshore waters of the sanctuary in 2002. The NOAA expanded the MPA network into the sanctuary's deeper waters in 2006 and 2007. The entire MPA network consists of 11 marine reserves: Richardson Rock, Judith Rock, Harris Point, South Point, Carrington Point, Skunk Point, Gull Island, Painted Cave, Scorpion, Footprint, and Anacapa Island.[13] All take and harvest from these marine reserves is prohibited. There are two marine conservation areas that allow limited take of lobster and pelagic fish. This MPA network encompasses 241 square nautical miles (318 square miles).
More than 150 historic ships and aircraft have been reported lost within the waters of the sanctuary, although just 25 have been discovered to date.
Maritime Heritage
Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary is responsible for the protection and preservation of submerged remains of the past that occupy the bottomlands of the sanctuary. Cultural and historic submerged sites include archaeological remains of shipwrecks and prehistoric land sites. Sanctuary stewardship responsibilities include a mandate to inventory sites, encourage research, provide public education and oversee responsible visitor use.
Chumash

The Northern Channel Islands have been home to the Chumash people for millennia, with the earliest known human remains dating back more than 13,000 years ago. The Chumash community continues to celebrate their maritime heritage through local cultural events such as an annual crossing of the Santa Barbara Channel on traditional plank canoes known as tomols.[14]
Protected species

%252C_CINMS.jpg.webp)
The species listed below, found within the Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary, are recognized as endangered, threatened, or species of concern under the Endangered Species Act and/or the California Endangered Species Act.[15]
Endangered species found within the sanctuary
The species listed below are categorized by Federal and California state government as endangered:
Threatened species found within the sanctuary
The species listed below are categorized by Federal and California state government as threatened:
Species of concern found within the sanctuary
The species listed below are categorized by Federal and California state government as species of concern
Delisted species found within the sanctuary
The species listed below are categorized by Federal and California state government as delisted
Sanctuary Advisory Council
The Sanctuary Advisory Council was established in December 1998 to assure continued public participation in management of the sanctuary. It provides a public forum for consultation and community deliberation on resource management issues affecting the waters surrounding the Channel Islands. It is composed of 21 members and 21 alternate seats that include local stakeholder groups and governmental agencies.
Threats to the sanctuary
Protecting the resources of Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary is a collaborative effort involving local, state and federal agencies as well as numerous non-governmental organizations. The sanctuary focuses on education, permitting, regulations, emergency response preparedness, enforcement, and consultation with other agencies to help protect the sanctuary's resources.
Current threats in the sanctuary include ship strikes on endangered whales, ocean acidification, invasive species, damage to eelgrass beds, marine debris, poaching, and water pollution.[17]
See also
References
- ↑ "Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ "NOAA Office of National Marine Sanctuaries". sanctuaries.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ "Learn | Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-07.
- ↑ "Visitor Centers and Exhibits | Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-07.
- ↑ "Outreach | Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-07.
- ↑ "Students at Sea | Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-07.
- ↑ "Teachers at Sea | Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-07.
- ↑ Floating Forests Revealed, NASA Earth Observatory, January 6, 2015
- ↑ Hamilton, SL; Caselle, JE; Malone, DP; Carr, MH (2010). "Incorporating biogeography into evaluations of the Channel Islands marine reserve network". PNAS. 107 (43): 18272–18277. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908091107. PMC 2973008. PMID 20176956.
- ↑ "Blue whale habitat and prey in the California Channel Islands". Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography. 45.
- ↑ Administration, US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric. "NOAA's Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2016-11-05.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Things To Do | Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-07.
- ↑ US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. "NOAA's Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary". channelislands.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2019-04-11.
- ↑ Rick, Torben C.; Erlandson, Jon M.; Vellanoweth, René L.; Braje, Todd J. (2005). "From Pleistocene Mariners to Complex Hunter-Gatherers: The Archaeology of the California Channel Islands". Journal of World Prehistory. 19 (3): 169–228. doi:10.1007/s10963-006-9004-x. S2CID 162492009.
- ↑ California, State of. "Threatened and Endangered Species - California Department of Fish and Wildlife". www.dfg.ca.gov. Retrieved 2016-11-05.
- ↑ "Island Fox - Channel Islands National Park (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved 2016-11-05.
- ↑ Keller, BD; Gleason, DF; McLeod, E; et al. (December 2009). "Climate Change, Coral Reef Ecosystems, and Management Options for Marine Protected Areas". Environmental Management. 44 (6): 1069–88. doi:10.1007/s00267-009-9346-0. PMC 2791481. PMID 19636605.
External links
- Official Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary Website
- http://mcbi.marine-conservation.org/what/what_pdfs/Channel_Islands.pdf
- http://www.eoearth.org/article/Channel_Islands_National_Marine_Sanctuary
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120109063517/http://www.edcnet.org/learn/current_cases/marine_conservation/sbchannel_issues/index.html
- http://channelislands.noaa.gov
- http://sanctuaries.noaa.gov/report2011/pdf/cinms.pdf