| Model 75 (Stearman Kaydet) | |
|---|---|
_(50906088841).jpg.webp) | |
| Boeing Stearman N7058Q in U.S. Navy markings | |
| Role | Biplane trainer |
| Manufacturer | Stearman Aircraft / Boeing |
| Introduction | 1934 |
| Number built | 8,584 (includes model 70, 75 and 76)[1] |
| Variants | American Airmotive NA-75 |
The Stearman (Boeing) Model 75 is an American biplane formerly used as a military trainer aircraft, of which at least 10,626 were built in the United States during the 1930s and 1940s.[2] Stearman Aircraft became a subsidiary of Boeing in 1934. Widely known as the Stearman, Boeing Stearman, or Kaydet, it served as a primary trainer for the United States Army Air Forces, the United States Navy (as the NS and N2S), and with the Royal Canadian Air Force as the Kaydet throughout World War II. After the conflict was over, thousands of surplus aircraft were sold on the civilian market. In the immediate postwar years, they became popular as crop dusters and sports planes, and for aerobatic and wing walking use in air shows.
Design and development











In late 1933, Stearman engineers Mac Short, Harold W. Zipp, and J. Jack Clark took a 1931 Lloyd Stearman design, and added cantilever landing gear and adjustable elevator trim tabs, to produce the Model 70. Able to withstand +12g and -9g, the aircraft was powered by a 210-hp Lycoming R-680, first flew on 1 January 1934, before flight tests were conducted at Wright Field, Naval Air Station Anacostia, and Pensacola. The Navy then requested a similar model built to Navy specifications, including a 200-hp Wright J-5 engine. The resultant Model 73, was designated NS-1 by the Navy, of which 41 were ordered, including enough spares to build another 20 aircraft.[3]
In the summer of 1934, Stearman engineers refined the Model 73 into the Model X75. The Army Air Corps evaluated the plane that autumn, powered by a 225-hp Wright R-760 or a 225-hp Lycoming R-680. In July 1935, the Army Air Corps ordered 26 with the Lycoming engine, designated the PT-13A, while the navy ordered an additional 20. In August 1936, the Army ordered an additiional 50 PT-13As, followed by another 30 in October, and another 28 in December. Simultaneously, the company received orders for its primary trainer from the Argentinian navy, the Philippine Army Air Corps, and the Brazilian Air Force. In January 1937, the army ordered another 26 PT-13As.[3]
On 6 June 1941, the U.S. government issued Approved Type Certificate No. 743 for the civilian version of the Model 75. Designated the Model A75L3 (PT-13) and Model A75N1 (PT-17), about 60 were sold to civilian flights schools such as Parks College of Engineering, Aviation and Technology, and for export.[3]: 148
On 15 March 1941, the company delivered the 1000th trainer to the Army, and the 1001st trainer to the Navy. Then on 27 August 1941, the company delivered the 2000th trainer to the Army. On 27 July 1944, the company delivered its 10,000th primary trainer.[3]: 145–148, 168
The Kaydet was a conventional biplane of rugged construction, with a large, fixed tailwheel undercarriage, and accommodation for the student and instructor in open cockpits in tandem. The radial engine was usually not cowled, although some Stearman operators choose to cowl the engine, most notably the Red Baron Stearman Squadron.
Operational history
Post-war usage
After World War II, thousands of surplus PT-17s were auctioned off to civilians and former military pilots. Many were modified for crop-dusting use, with a hopper for pesticide or fertilizer fitted in place of the front cockpit. Additional equipment included pumps, spray bars, and nozzles mounted below the lower wings. A popular approved modification to increase the maximum takeoff weight and climb performance involved fitting a larger Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior engine and a constant-speed propeller.
Variants
Data from:United States Navy aircraft since 1911,[4] Boeing aircraft since 1916[5] 8,584 Model 70s, 75s and 76s were built, with additional "spares" bringing the number up to the sometimes quoted 10,346.[1]
USAAC/USAAF designations
The U.S. Army Air Forces Model 75 Kaydet had three different designations, PT-13, PT-17 and PT-18, depending on which type of radial engine was installed.
- PT-13
- Initial production version with Lycoming R-680-B4B engine, 26 built in 1936
- PT-13A Model A75 with R-680-7 engine, 92 delivered from 1937 to 1938.
- PT-13B R-680-11 engine, 255 delivered from 1939 to 1941.
- PT-13C Six PT-13Bs modified for instrument flying.
- PT-13D Model E75 with R-680-17 engine, 793 delivered
- PT-17
- Version with Continental R-670-5 engine, 2,942 delivered.
- PT-17A 136 PT-17s modified with blind-flying instrumentation.
- PT-17B Three PT-17s modified with agricultural spraying equipment for pest control near army bases.
- PT-17C Single PT-17 conversion with standardized Army-Navy equipment.
- PT-18
- Version with Jacobs R-755-7 engine, 150 built. Further production was cancelled as the engines were needed for other types of trainers.
- PT-18A Six PT-18s modified with blind-flying instrumentation.
- PT-27
- USAAF paperwork designation given to 300 D75N1/PT-17 aircraft supplied under Lend-Lease to the Royal Canadian Air Force.
US Navy designations
- NS
- Up to 61 Model 73B1 delivered, powered by 220 hp (160 kW) Wright J-5/R-790 Whirlwind radials[6]
- N2S
- Known colloquially as the "Yellow Peril" from its overall yellow paint scheme.
- N2S-1 Model A75N1 with Continental R-670-14 engine, 250 delivered.
- N2S-2 Model B75 with Lycoming R-680-8 engine, 125 delivered in 1941.
- N2S-3 Model B75N1 with Continental R-670-4 engine, 1,875 delivered.
- N2S-4 Model A75N1 with Continental R-670-4 and -5 engines, 457 delivered of 579 ordered, including 99 PT-17s diverted from U.S. Army orders.
- N2S-5 Model E75 with Lycoming R-680-17 engine, 1,450 delivered.
Company designations
- Stearman 70
- Company designation for prototype, powered by 215 hp (160 kW) Lycoming radial engine, designated XPT-943 for evaluation[7]
- Model 73
- Initial production version, 61 built for U.S. Navy as NS plus export variants[6]
- Model 73L3
- Version for the Philippines, powered by 200 hp (150 kW) R-680-4 or R-680C1 engines, seven built[8]
- Model A73B1
- Seven aircraft for Cuban Air Force powered by 235 hp (175 kW) Wright R-790 Whirlwind, delivered 1939–1940[8]
- Model A73L3
- Improved version for the Philippines, three built[9]
- Stearman 75
- (or X75) Evaluated by the U.S. Army as a primary trainer, the X75L3 became the PT-13 prototype. Variants of the 75 formed the PT-17 family.
- Stearman 76
- Export trainer and armed version of the 75 with a gun ring and one or two fixed forward firing machine guns.
- A76B4
- 5 built for Venezuela.
- A76C3
- 15 built for Brazil.
- B76C3
- 15 built with cameras for Brazil.
- 76D1
- 16 built for Argentina and three for Philippines as BT-1.
- S76D1
- seaplane version of 76D1 for Argentina
- 76D3
- 24 built for Philippine Constabulary as BT-1 armed advanced trainer, and 24 built for Cuba.
Other designations
- Stearman XPT-943
- Designation assigned to the X70 evaluated at Wright Field
- Stearman Kaydet
- Name used for aircraft in Royal Canadian Air Force service
- American Airmotive NA-75
- Single-seat agricultural conversion of Model 75, fitted with new, high-lift wings[10]
Operators
- Argentine Air Force
- Argentine Navy received 16 Model 76D1s 1936 to 1937[11] and 60 N2S Kaydet post-war; all were retired by the early 1960s[12]
 Brazil
Brazil- Brazilian Air Force Model A75L3 and 76.[14]
.svg.png.webp) Canada
Canada- Royal Canadian Air Force received 301 PT-27s under Lend Lease.[15]
 Republic of China
Republic of China- Republic of China Air Force received 150 PT-17s under Lend-Lease,[16] and 104 refurbished aircraft post war in Taiwan. The ROCAF used them until 1958.[17]
 Colombia
Colombia- Colombian Air Force[13]
 Cuba
Cuba
 Iran
Iran- Imperial Iranian Air Force[18]
 Israel
Israel- Israeli Air Force purchased 20 PT-17s.[19]
 Mexico
Mexico- Mexican Air Force[18]
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua- Nicaraguan Air Force
 Paraguay
Paraguay- Paraguayan Air Force[13]
 Peru
Peru- Peruvian Air Force
.svg.png.webp) Philippines
Philippines- Philippine Army Air Corps[14]
- Philippine Air Force[18]
 United States
United States- United States Army Air Corps/United States Army Air Forces[14]
- United States Marine Corps
- United States Navy[14]
 Venezuela
Venezuela- Venezuelan Air Force[14]
.svg.png.webp) Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia- Yugoslav Air Force
Surviving aircraft
A considerable number of Stearmans remain in flying condition throughout the world, as the type remains a popular sport plane and warbird.
Argentina

- 308 – N2S-5 airworthy at the Argentine Naval Aviation Museum in Bahía Blanca, Buenos Aires.[12]
Australia
Austria
Brazil
- K-132 – A75L3 on display at the Museu Aeroespacial in Rio de Janeiro[23]
- K-210 – A76C3 on display at the Museu Aeroespacial in Rio de Janeiro[24]
- 38010 – N2S-3 on display at the TAM Museum in São Carlos, São Paulo[25]
Canada
- 41-8621 – PT-17 airworthy at the Canadian Warplane Heritage Museum in Hamilton, Ontario.[26]
- 42-17456 – PT-13D owned by Daniel Jones of Lacombe, Alberta.[27][28]
- 5284 – N2S-3 under restoration to airworthy with Daniel Jones of Lacombe, Alberta[29][30]
- 5293 – N2S-3 owned by J. Kurtin of Collingwood, Ontario[31][32]
- 30083 – N2S-4 on display at the Reynolds-Alberta Museum in Wetaskiwin, Alberta[33][34]
- 61105 – N2S-5 with Bruce Bond of Sarnia, Ontario[35][36]
- 75-3498 – PT-17 airworthy owned by Great River Aviation Ltd. of Whitehorse, Yukon o/a Klondike Airways.[37][38]
Colombia
- FAC-62 – PT-17 airworthy
- FAC-1995 – PT-17 airworthy
Iceland
- T5-1556 – PT-17 is airworthy with Erling Pétur Erlingsson in Hafnarfjörður, Capital Region. It is the oldest airplane in Iceland. It was brought to the country in 1941 by the aircraft carrier USS Wasp and damaged in an accident in 1943.[39][40][41]
Indonesia
- PT-13D is on display at Dirgantara Mandala Museum in Yogyakarta. The aircraft is painted in Taloa Academy of Aeronautics livery.[42][43]
Israel
- 2752 – PT-17 is airworthy at the Israeli Air Force Museum in Hatzerim.[44]
Mexico
- EPS-6084 – PT-17 on static display at the Museo Militar de Aviación in Santa Lucía, Zumpango.[45]
Netherlands
- 75-7027 – PT-13B is airworthy, registered as PH-TOX, owned by Joe Brewer and based at Oostwold Airport.[46]
- 75-7213 – N2S-3 is airworthy, registered as N9912H, owned by the Nordsiek family and based at Breda International Airport.[47]
- 75-5864 – PT-13D Kaydet is airworthy, registered as N1944S based at Texel International Airport[48]
New Zealand
- 75-647 – PT-17 airworthy with R. J. S. Jenkins in Ardmore, Auckland.[49]
- 75-2055 – PT-17 airworthy with R. B. Mackley in Milford.[50]
- 75-2100 – PT-17 airworthy with Classic Aircraft Sales Limited in Blenheim.[51]
- 75-2724 – PT-17 airworthy with B. L. Govenlock in Hastings.[52]
- 75-3132 – PT-17 airworthy with the Antonievich Family Trust in Pukekohe.[53]
- 75-3655 – PT-17 airworthy with M. P. Cantlon in Mount Maunganui.[54]
- 75-4245 – PT-17 airworthy with the Strome Farm Trust in Drury.[55]
- 75-5064 – PT-13D airworthy with the Stearman Syndicate in Drury.[56]
- 75-5907 – PT-13D airworthy with Stearman 03 Limited in Mount Maunganui.[57]
- 75-8025A – N2S-3 airworthy with M. J. Dean in Mount Maunganui.[58]
Peru
- PT-17 is on display at the Instituto de Estudios Históricos Aeroespaciales del Perú, Miraflores, Lima.
Spain
- PT-13 on display at the Fundación Infante de Orleans in Cuatro Vientos, Madrid.[59]
- PT-17 on display at the Fundación Infante de Orleans in Cuatro Vientos, Madrid.[60]
Switzerland
- 75-5436 – PT-13D is airworthy, registered as HB-RBG, and based at the Fliegermuseum Altenrhein.[61] Built in 1943 and restored to airworthiness in 1989 after sustaining considerable damage during an emergency landing in the grounds of the Stadler Rail factory in Altenrhein due to engine failure.[62]
Taiwan
- PT-17 is on static display at the Aviation Education Exhibition Hall in Gangshan District, Kaohsiung City.[63]
United States
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)

- Model 70 is airworthy at the Western Antique Aeroplane & Automobile Museum in Hood River, Oregon. It is the original prototype of the Model 75.[64]
- 37-0099 – PT-13A is on static display at the Museum of Flight in Seattle, Washington.[65][66]
- 41-7960 – PT-17 is airworthy at Mississippi State University in Starkville, Mississippi. It is used as a research aircraft and glider tow-plane.[67][68]
- 41-8786 – PT-17 is in storage at the New England Air Museum in Windsor Locks, Connecticut.[69]
- 41-8882 – PT-17 on static display at the Pima Air and Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona.[70]
- 41-25254 – PT-17 is airworthy at the Military Aviation Museum in Pungo, Virginia.[71][72][73]
- 41-25284 – PT-17 is on static display at the Hill Aerospace Museum in Roy, Utah.[74]
- 41-25588 – PT-17 is airworthy at the Charles M. Schulz–Sonoma County Airport in Santa Rosa, California.[75]
- 41-25623 – PT-17 is on display at Patriots Point in Charleston, South Carolina.
- 42-15687 – PT-27 is on display at the Vintage Flying Museum in Fort Worth, Texas.[76]
- 42-16365 – PT-17 is on static display at the Museum of Aviation in Warner Robins, Georgia.[77][74]
- 42-16388 – PT-17D is on static display at the March Field Air Museum near Riverside, California.[78]
- 42-16691 – PT-17 is on static display at the Castle Air Museum in Atwater, California.[74]
- 42-17591 – PT-13D is on static display at the Planes of Fame Air Museum in Chino, California.[79][80][81]
- 42-17724 – PT-13D is on static display at the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, DC. It was used in 1944 to train members of the Tuskegee Airmen.[82][83][84]
- 42-17763 – PT-13D is on static display at the Planes of Fame Air Museum in Valle, Arizona.[79][80][85]
- 42-17800 – PT-13D is on static display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio. This aircraft is the 63rd to last aircraft built and was donated to the museum in 1959 by the Boeing Aircraft Company, which purchased the Stearman Company in 1934.[86][87][88]
- 3514 – N2S-3 is airworthy with Neil Alan Raaz in Colleyville, Texas.[89][90]
- 3558 – N2S-2 is under restoration to airworthy condition at the Planes of Fame Air Museum in Chino, California.[79][80][91]
- 5369 – N2S-3 is on static display at the National Naval Aviation Museum in Pensacola, Florida. It was flown by George H. W. Bush during his initial training as a naval pilot.[92]
- 7591 – N2S-3 is airworthy at the Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum in Titusville, Florida.[93][94]
- 7718 – N2S-3 is airworthy at the Lone Star Flight Museum in Houston, Texas.[95][96]
- 15923 – N2S is on static display at the Carolinas Aviation Museum in Charlotte, North Carolina.[97]
- 29981 – N2S-4 is on display at the Air Zoo in Kalamazoo, Michigan.[98][99]
- 38278 – N2S-3 is airworthy at the Tri-State Warbird Museum in Batavia, Ohio.[100][101]
- 38490 – N2S-5 is airworthy at the Lone Star Flight Museum in Houston, Texas.[95][102]
- 43197 – N2S-5 is under restoration to airworthy condition with the Commemorative Air Force Utah Wing in Heber City, Utah.[103][104]
- 61064 – N2S-5 on static display at the Udvar-Hazy Center of the National Air and Space Museum in Chantilly, Virginia.[105][106]
- 92468 – N2S-3 is on static display at the Pacific Aviation Museum Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Hawaii. It was flown by George H. W. Bush during his initial training as a naval pilot.[107][108]
- 75-133 – PT-17 is airworthy at the Simsbury Airport in Simsbury, Connecticut.
- 75-3845 – PT-27 is under restoration to airworthy condition at the Texas Air Museum in Slaton, Texas.[109]
- 75-7540 - B75N1 is airworthy and resides at the Commemorative Air Force Airbase Arizona, Mesa, Arizona.
- 75-8498 – N2S-5 is airworthy at the CAF Big Easy Wing in New Orleans, LA. [110]
- A75N1 – PT-17 is on display at the College Park Aviation Museum in College Park, Maryland. It was flown by Gus McLeod for the first open-cockpit flight over the North Pole.[111]
- N2S-3 is on display at the Western Antique Aeroplane and Automobile Museum in Hood River, Oregon.[112]
Specifications (PT-17)
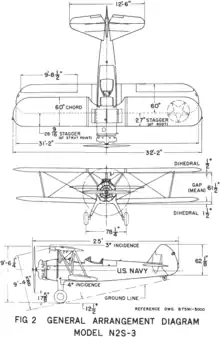
Data from United States Military Aircraft since 1909[113]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 24 ft 9 in (7.54 m)
- Wingspan: 32 ft 2 in (9.80 m)
- Height: 9 ft 8 in (2.95 m)
- Wing area: 298 sq ft (27.7 m2)
- Empty weight: 1,931 lb (876 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 2,635 lb (1,195 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 46 US gal (38 imp gal; 170 L)
- Powerplant: 1 × Continental R-670-5 7-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 220 hp (160 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed-pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 124 mph (200 km/h, 108 kn)
- Cruise speed: 96 mph (154 km/h, 83 kn)
- Service ceiling: 13,200 ft (4,000 m)
- Time to altitude: 10,000 ft (3,000 m) in 17 minutes 18 seconds
- Wing loading: 9.9 lb/sq ft (48 kg/m2)
In popular culture
An iconic movie image is a Stearman cropduster chasing Cary Grant across a field in North by Northwest (the airplane that chased Grant was actually a Naval Aircraft Factory N3N Canary; the plane that hits the truck is a Stearman). A heavily modified PT-17 variant was used as the Tornado in the Sonic The Hedgehog 2 Film.
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Arado Ar 66
- Bücker Bü 131
- De Havilland Tiger Moth
- Fleet Finch
- Focke-Wulf Fw 44
- Gotha Go 145
- Naval Aircraft Factory N3N
- Repülőgépgyár Levente II
- Polikarpov Po-2
- PWS-26
- Stampe-Vertongen SV.4
References
Notes
- 1 2 Bowers, 1989, p.255
- ↑ National Museum of the United States Air Force gives the figure 10,346 but this includes the equivalent airframes in manufactured spare parts.
- 1 2 3 4 Phillips, Edward (2006). Stearman Aircraft: A Detailed History. North Branch, MN: specialtypress. pp. 118–126. ISBN 9781580070874.
- ↑ Bowers, Peter M.; Swanborough, Gordon (1990). United States Navy aircraft since 1911. Annapolis, Md.: Naval Institute Press. pp. 494–495. ISBN 0870217925.
- ↑ Bowers, Peter M. (1989). Boeing aircraft since 1916 (3rd ed.). Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. pp. 251–269. ISBN 978-0870210372.
- 1 2 Bowers 1989, pp. 252–253.
- ↑ Bowers 1989, pp. 251–252.
- 1 2 Bowers 1989, p. 253.
- ↑ Bowers 1989, p. 254.
- ↑ Taylor 1965, p. 178.
- ↑ Bowers 1989, p. 268.
- 1 2 Núñez Padín, Jorge (2000). "BOEING STEARMAN N2S KAYDET". Fuerzas Navales (in Spanish). Jorge N. Padín. Archived from the original on 2014-05-17. Retrieved 2014-05-16.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Andrade 1979, p. 159
- 1 2 3 4 5 Andrade 1979, p. 158
- ↑ Bowers 1989, p. 265.
- ↑ Bowers 1989, p. 262.
- ↑ Bowers 1989, pp. 260–261.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Boeing-Stearman Kadyet". Military Factory. 2013-06-20. Retrieved 2014-05-17.
- ↑ Nordeen 1991, p. 27.
- ↑ "Civil Aircraft Register entry VH-EYC". Civil Aviation Safety Authority. Retrieved 27 March 2021.
- ↑ "Civil Aircraft Register entry VH-USE". Civil Aviation Safety Authority. Retrieved 27 March 2021.
- ↑ "PT-17 Stearman The Flying Bulls". The Flying Bulls. Retrieved 27 March 2021.
- ↑ "BOEING STEARMAN A75L3 – Kaydet". Museu Aeroespacial. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "BOEING STEARMAN A76C3". Museu Aeroespacial. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-3 Kaydet, s/n 0131 ARA, c/n 75-7631, c/r LV-FGD". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Boeing PT-17 Stearman". Canadian Warplane Heritage Museum. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Canadian Civil Aircraft Register: Aircraft Details [C-GVTI]". Transport Canada. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-13D Kaydet, s/n 42-17456 USAAF, c/n 75-5619, c/r C-GVTI". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Canadian Civil Aircraft Register: Aircraft Details [C-GZAL]". Transport Canada. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-3 Kaydet, s/n 05284 USN, c/n 75-6458, c/r C-GZAL". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Canadian Civil Aircraft Register: Aircraft Details [C-FOXU]". Transport Canada. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-13B Kaydet, s/n 5293 USN, c/n 75-6467, c/r C-FOXU". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Aviation". Reynolds Museum. Government of Alberta. Retrieved 1 December 2019.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-4 Kaydet, s/n 30083 USN, c/n 75-3522, c/r CF-UWK". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Canadian Civil Aircraft Register: Aircraft Details [C-GSDK]". Transport Canada. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-5 Kaydet, s/n 61105 USN, c/n 75-5227, c/r C-GSDK". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Canadian Civil Aircraft Register: Aircraft Details [C-GQUA]". Transport Canada. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ↑ "Klondike Airways Vintage Biplane Tours – The Stearman". Klondike Airways. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ↑ "Aircraft Registry Lookup [TF-KAU]". Icelandic Transport Authority. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ Magnússon, Guðmundur (25 April 2019). "The oldest airplane in Iceland". mbl.is (in Icelandic). Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ Marteinsson, Ólafur; Marteinsson, Þorsteinn (23 April 2020). "Stearman, Reykjavík Airfield. March 20, 1943". World War II Crash Sites in Iceland. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Museum TNI AU Dirgantara Mandala Yogyakarta Indonesia". aviationmuseum.eu. Retrieved 10 January 2021.
- ↑ "MAAM – The Widow's Web – Recovery". maam.org. Retrieved 10 January 2021.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-5 Kaydet, s/n 2752 IDF, c/n 75-5096, c/r 4X-AIK". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "EPS-6084 | Boeing PT-17 Kaydet | Mexico – Air Force | Santiago_MN". JetPhotos. Retrieved 2022-06-08.
- ↑ "Boeing Stearman – Oostwold Airport" (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 2021-09-14. Retrieved 2021-10-20.
- ↑ Vlaanderen, Annelies (2020-05-17). "Historisch vliegtuigje van Seppe naar Schiphol 100 jaar na eerste commerciële vlucht KLM". BN DeStem. Retrieved 2023-10-28.
- ↑ "Aerial Visuals – Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-13D Kaydet, s/n 42-17701 USAAF, c/n 75-5864, c/r N1944S". www.aerialvisuals.ca. Retrieved 2023-09-08.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-647". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-2055". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-2100". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-2724". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-3132". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-3655". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-4245". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-5064". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-5907". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman A75N1 75-8025A". Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing Stearman Kaydet – IDA". Infante de Orleans. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Boeing – Stearman Kaydet". Infante de Orleans. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Swiss Aircraft Register entry HB-RBG". Federal Office for Civil Aviation of Switzerland. Retrieved 27 March 2021.
- ↑ "Boeing PT13D Stearman "HB-RBG" Geschichte". Fliegermuseum Altenrhein. Retrieved 27 March 2021.
- ↑ "PT-17教練機". Aviation Education Exhibit Hall. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Stearman Model 70". Western Antique Aeroplane & Automobile Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Stearman PT-13A Kaydet (A75)". The Museum of Flight. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-13A Kaydet, s/n 37-0099 USAAF, c/n 75-0055, c/r N8FL". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "HISTORY: Boeing PT-17 Stearman". Mississippi State University. Archived from the original on 2013-03-27. Retrieved 2021-10-20.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-17 Kaydet, s/n 41-7960 USAAF, c/n 75-1519, c/r N53129". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Stearman PT-17 (Model 75) 'Kaydet'". New England Air Museum. Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "BOEING A75N1 (PT-17) STEARMAN KADET". Pima Air & Space Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "OUR WORLD WAR TWO AIRCRAFT". Military Aviation Museum. 13 April 2018. Archived from the original on 13 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-17 Kaydet, s/n 41-25254 USAAF, c/n 75-2743, c/r N41EE". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ↑ "FAA Registry [N41EE]". Federal Aviation Administration. U.S. Department of Transportation. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- 1 2 3 "LOANED AIRCRAFT BY LOC" (PDF). National Museum of the United States Air Force. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ Hug, Robin (21 March 2012). "New aviation company flying old planes". Windsor Times. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Boeing PT-17 Kaydet". Vintage Flying Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "PT-17 "Kaydet"". Museum of Aviation Foundation. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "PT-13D Stearman". March Field Air Museum. Archived from the original on 22 September 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 "Kaydet". Planes of Fame Air Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 "Flying & Static Aircraft". Planes of Fame Air Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-13D Kaydet, s/n 42-17591 USAAF, c/n 75-5754, c/r N5186N". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Training aircraft used by Tuskegee Institute". National Museum of African American History & Culture. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-13D Kaydet, s/n 42-17724 USAAF, c/n 75-5887, c/r N36360". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ Edwards, Owen (November 2011). "The Tuskegee Airmen Plane's Last Flight". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on April 19, 2013. Retrieved January 30, 2012.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing PT-13D Kaydet, s/n 42-17763 USAAF, c/n 75-5926, c/r N5279N". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Stearman PT-13D Kaydet". National Museum of the United States Air Force. 21 April 2015. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "AIRCRAFT, DRONES AND MISSILES AT THE NATIONAL MUSEUM OF THE U.S. AIR FORCE" (PDF). National Museum of the United States Air Force. June 2016. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "IMAGE GALLERY". National Museum of the United States Air Force. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "FAA Registry [N75804]". Federal Aviation Administration. U.S. Department of Transportation. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-3 Kaydet, s/n 3514 USN, c/n 75-1291, c/r N75804". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-2 Kaydet, s/n 3558 USN, c/n 75-1335, c/r N61445". Aerial Visuals.
- ↑ "N2S Kaydet". National Naval Aviation Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "VAC COLLECTION". Valiant Air Command, Inc. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-3 Kaydet, s/n 7591 USN, c/n 75-7195, c/r N5118N". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- 1 2 "Boeing PT-17 Stearman". Lone Star Flight Museum. Archived from the original on 21 November 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-3 Kaydet, s/n 07718 USN, c/n 75-7322, c/r N84LK". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "BOEING/STEARMAN PT-17 KAYDET". Carolinas Aviation Museum. 12 February 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "WWII: 1930s-1945". Air Zoo. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-4 Kaydet, s/n 29981 USN, c/n 75-3412, c/r N2PP {2}". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Restored Aircraft". Tri-State Warbird Museum. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman Kaydet, s/n 38278 USN, c/n 75-7899, c/r N224DF". AerialVisuals.ca. www.AerialVisuals.ca. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-5 Kaydet, s/n 38490 USN, c/n 75-8111, c/r N75272". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Boeing Stearman N2S / PT-13 / PT-17". Commemorative Air Force Utah Wing. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Challenge Coin Stearman 75-8291". Commemorative Air Force Utah Wing. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "Boeing-Stearman N2S-5 Kaydet". National Air and Space Museum. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier – Stearman-Boeing N2S-5 Kaydet, s/n 61064 USN, c/n 75-5186". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ↑ "Boeing N2S-3 Stearman (Trainer)". Pearl Harbor Aviation Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ "2012 Annual Report" (PDF). PacificAviationMuseum.org. Pacific Aviation Museum. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ↑ "Facebook". Facebook. Retrieved 2023-04-16.
- ↑ "The Stearman". Commemorative Air Force-Big Easy Wing. Retrieved 13 March 2023.
- ↑ "1941 Boeing A75N1/PT-17 "Stearman"". College Park Aviation Museum (M-NCPPC). Retrieved 2023-08-30.
- ↑ "Stearman N2S-3". Western Antique Aeroplane & Automobile Museum. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ↑ Swanborough and Bowers 1963, p. 443.
.
Bibliography
- Andrade, John. U.S. Military Aircraft Designations and Serials since 1909, Midland Counties Publications, 1979, ISBN 0 904597 22 9
- Avis, Jim and Bowman, Martin. Stearman: A Pictorial History. Motorbooks, 1997. ISBN 0-7603-0479-3.
- Bowers, Peter M. Boeing Aircraft since 1916. London:Putnam, 1989. ISBN 0-85177-804-6.
- Nordeen, Lon. Fighters Over Israel. London: Guild Publishing, 1991.
- Phillips, Edward H. Stearman Aircraft: A Detailed History . Specialty Press, 2006. ISBN 1-58007-087-6.
- Sapienza, Antonio Luis (May 2001). "L'aviation militare paraguayenne durant la seconde guerre mondiale" [Paraguayan Military Aviation During the Second World War]. Avions: Toute l'Aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (98): 30–33. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Swanborough, F.G. and Peter M. Bowers. United States Military Aircraft since 1909. London: Putnam, 1963.
- Taylor, John W. R. Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1965–66. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Company, 1965.
- United States Air Force Museum. Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio: Air Force Museum Foundation. 1975.
Videography
- Stearman, Lloyd. Stearmans, You Gotta Love Them. Lap Records, 2005. (NTSC Format)
External links
| External videos | |
|---|---|