 Calvert Street Station at North Calvert and Bath/East Franklin Streets, in downtown Baltimore, built 1849-1850, razed 1949; designed by James Crawford Neilson | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Baltimore |
| Reporting mark | NCRY |
| Locale | Pennsylvania and Maryland |
| Dates of operation | 1858–1976 |
| Predecessor | Baltimore and Susquehanna Railroad, York and Maryland Line Rail Road, Susquehanna Railroad |
| Successor | Conrail |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Length | 380 miles (610 km) (including leased lines)[1] |
Northern Central Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Northern Central Railway (NCRY) was a Class I Railroad in the United States connecting Baltimore, Maryland, with Sunbury, Pennsylvania, along the Susquehanna River. Completed in 1858, the line came under the control of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) in 1861, when the PRR acquired a controlling interest in the Northern Central's stock to compete with the rival Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O).
For eleven decades, the Northern Central operated as a subsidiary of the Pennsylvania Railroad until much of its Maryland trackage was washed out by Hurricane Agnes in 1972, after which the Penn Central declined to repair destroyed sections and the remainder fell into disuse. It is now a fallen flag railway, having come under the control of Conrail and then the Norfolk Southern Railway.
The northern part in Pennsylvania is now the York County Heritage Rail Trail which connects to a similar hike/bike trail in Northern Maryland down to Baltimore, named the Torrey C. Brown Rail Trail. Trackage from Camden Station in Baltimore to Timonium, Maryland, remains in service as part of the Baltimore Light RailLink line, while much of the line in Pennsylvania is operated by the Norfolk Southern for freight service. The Northern Central Railway of York, a heritage railway, operates on former Northern Central track between New Freedom and Hanover Junction, Pennsylvania.
Early history
The Baltimore and Susquehanna Railroad Company was chartered by an act of the General Assembly of Maryland on February 13, 1828,[2] as the second designated rail system in the state, with authority to construct a railroad from Baltimore northeast to the Susquehanna River. To reach the Susquehanna at any commercially useful point, the new railway would have to cross the state line into York County, Pennsylvania. George Winchester, president of the new railroad company, and its board of directors sought approval of their charter from the Pennsylvania General Assembly; however, legislators—especially those from Philadelphia—did not look favorably on the prospect of the trade of its southern counties being tapped for the benefit of Baltimore, instead of Philadelphia. In spite of the fact that Pennsylvania would have gained access to the Chesapeake Bay, its legislature would not grant a charter for a connecting railroad.[3]

Nevertheless, construction of the Baltimore & Susquehanna Railroad began in 1829, following the Jones Falls valley, and in 1831 reached what today is Lake Roland. The railroad company celebrated the first trains carrying passengers, pulled by horses between Belvedere Station in Baltimore and the future Lake Roland area, on July 4, 1831. The following year, they built a relay station at that point, where fatigued horses could be exchanged for fresh ones; appropriately, they named the station “Relay” (this was sometimes confused with the Baltimore and Ohio’s station of the same name, around which the town of Relay, Maryland developed).[4] Construction of the railroad continued north, reaching Timonium in 1832, the village of Texas in 1834, and York Road at Cockeysville by 1835.[5]
At that time, the B&S obtained an amendment to its charter from the Maryland legislature which allowed it to be extended northwest to Westminster in Carroll County. The line would continue towards the headwaters of the Monocacy River and reach Gettysburg, Pennsylvania.
New construction began at Hollins, Maryland, and ran west through the Green Spring Valley north of Baltimore. The line reached Reisterstown Road at Owings Mills on June 13, 1832. Despite fierce opposition from Philadelphia business and political interests, the Pennsylvania legislature chartered the York and Maryland Line Rail Road on March 14, 1832, authorizing it to connect the Baltimore & Susquehanna.
The Adams County Railroad was chartered on April 6, 1832, in Pennsylvania, to run from Gettysburg to the Maryland state line, but was never constructed, nor was the line to Westminster (later known as the Green Spring Branch) extended further northwest. A further amendment to the York & Maryland Line's charter in 1837, allowed it the unlimited use of the Wrightsville, York and Gettysburg Railroad, which it had aided financially.
The Baltimore & Susquehanna and York & Maryland Line completed the line from Baltimore to York by 1838. This line included the use of the Howard Tunnel near Seven Valleys, Pennsylvania, the earliest railroad tunnel in the U.S. still in use today.

In 1832, the railroad purchased its first locomotive, the Herald,[6]: 168 and built Bolton Station in Baltimore.[7]: 88
In April 1840, the Wrightsville, York & Gettysburg R.R. had been completed between York and Wrightsville, Pennsylvania. There a connection was made to the Columbia-Wrightsville Bridge, allowing trains to cross the river and reach the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad and later, the Pennsylvania Railroad.
The York and Cumberland Railroad Company was chartered on April 21, 1846, to connect the York & Maryland Line with the Cumberland Valley Railroad somewhere north of Mechanicsburg. It was opened on February 10, 1851, running north from York to the Susquehanna and then following the river to Lemoyne. It was briefly operated by the Cumberland Valley, but the Baltimore & Susquehanna took over operations on June 7. Work also began on the Hanover Branch Railroad, a line connecting Hanover with the York & Maryland Line at Hanover Junction.
The Baltimore & Susquehanna system built and opened the Calvert Street Station, an Italianate-style structure of stucco-covered brick with two towers that was designed by locally-famous architect James Crawford Neilson, in Baltimore in 1850, while continuing to use Bolton Station for freight.
On April 14, 1851, the Susquehanna Railroad was chartered and authorized to build north from the York & Cumberland or the Pennsylvania Railroad up the Susquehanna through Halifax, Millersburg and Sunbury, where it would fork into two branches reaching Williamsport and Wilkes-Barre. Its charter was amended on April 24, 1852, to allow the York & Cumberland and Wrightsville and York & Gettysburg to subscribe or loan up to $500,000 (equivalent to $17,588,000 in 2022) to the capital-starved company, and to permit the counties and boroughs along the way to contribute funds. The Maryland legislature authorized the City of Baltimore to contribute the same amount on May 14. The Susquehanna RR finally elected officers on June 10, and was soon embroiled in a dispute with the Sunbury and Erie Railroad over right-of-way.
Meanwhile, on May 27, the Baltimore, Carroll and Frederick Railroad (renamed the Western Maryland Railway in 1853) was incorporated to build from the end of the line at Owings Mills towards Hagerstown. On July 4, a serious accident occurred on the Baltimore & Susquehanna when a special picnic excursion collided with a York local, killing thirty-one persons. The Hanover Branch Railroad was opened to Hanover on October 22 and operated by the Baltimore & Susquehanna. On May 10, 1853, the Baltimore & Susquehanna's charter was amended to permit it to build two branches to the Patapsco River, but this was stymied by legal problems and difficulties in tunneling.
On the northward extension, the Susquehanna RR let contracts for the line from Lemoyne to Sunbury in November 1852, and construction began on February 22, 1853. A financial crisis beginning in the fall of 1853 proved a severe embarrassment to the Baltimore & Susquehanna and associated railroads, and on March 10, 1854, the Maryland legislature authorized the Baltimore & Susquehanna, York & Maryland Line, York & Cumberland, and Susquehanna Railroads to merge, writing off its investment in the lines in exchange for a mortgage on the new railroad. Construction halted on the Susquehanna RR. The Pennsylvania legislature authorized the merger on May 3, and articles of consolidation were signed on December 4 (filed December 16, 1854), forming the Northern Central Railway Company.[1]
On April 1, 1855, the Northern Central stopped operating the Hanover Branch RR, which began independent operation. On December 20, 1855, construction resumed on the northward extension, and by December 28, 1856, the line had bridged the Susquehanna at Dauphin and reached Millersburg, connecting with the Dauphin and Susquehanna Railroad and the Lykens Valley Railroad, respectively. These were lateral lines tapping coal mines east of the Susquehanna, and the extension afforded them a direct outlet by rail rather than by canal boat. In 1857, it reached Herndon and the Trevorton Coal and Railroad Company, another mining line. On June 28, 1858, the line was opened to Sunbury, where it connected with the Shamokin Valley and Pottsville Railroad towards Shamokin and the Sunbury and Erie Railroad, and Williamsport.
In 1861, the PRR acquired a controlling interest in the Northern Central's stock to compete with the rival B&O. Thereafter, the Northern Central operated as a subsidiary of the Pennsylvania Railroad until the latter's demise in the late 20th century.[7]: 22
On February 23, 1861, President-elect Lincoln was scheduled to arrive at the Calvert Station as part of the inauguration whistle-stop train ride. Warned of the Baltimore Plot, Lincoln changed plans and arrived earlier at 3:30 a.m. that morning at the President Street Station downtown, thereby avoiding the suspected assassination attempt.[8][9][10][11]
From 1856 to 1858, trains running north towards Sunbury were diverted across the Susquehanna River at Herndon via the Trevorton Coal Railroad bridge. From here, passengers boarded canal boats and continued the journey to Sunbury on the Pennsylvania Canal, until 1858 when the rail line was completed up the east bank of the river to Sunbury.
Consolidation and Civil War


During the Civil War, the Pennsylvania Railroad-controlled Northern Central served as a major transportation route for supplies, food, clothing, and materiel, as well as troops heading to the South from Camp Curtin and other Northern military training stations. During the 1863 Gettysburg Campaign, Confederate Major General Jubal A. Early raided the NCRY in York, burning some rolling stock and a few machine shops in the rail yard. To impair traffic between Baltimore and Harrisburg, his cavalry destroyed a large number of bridges in York County originally constructed by the B&S. They were quickly rebuilt by Herman Haupt and the U.S. Military Railroad in conjunction with the NCRY. Traffic resumed shortly thereafter, and thousands of wounded soldiers from the Battle of Gettysburg, including Union Maj. Gen. Daniel Sickles, were evacuated via the Northern Central to hospitals in Harrisburg, Baltimore, York, and elsewhere.
The Northern Central was attacked again on July 10, 1864, when a 130-man Confederate cavalry detachment attacked the line near Cockeysville, under orders from Gen. Bradley T. Johnson. After cutting telegraph wires along Harford Road, they encamped at Towson overnight. The next day, the Confederate cavalry skirmished with a smaller force of Union cavalry along York Road before heading west to rejoin Gen. Johnson's main force.[12]: 127–129
Abraham Lincoln traveled on the Northern Central on his way to deliver the Gettysburg Address in November 1863, changing trains in Hanover Junction, Pennsylvania. After Lincoln's assassination, his body was transported via the same rails on the funeral train's journey from Washington, D.C., to Springfield, Illinois. The nine-car train departed Washington, D.C., on April 21, 1865, and arrivied at Baltimore's Camden Station at 10 a.m. on the B&O Railroad.[12]: 152 After public viewing of the President's remains, the train departed Baltimore on the Northern Central at 3 p.m. and arrived at Harrisburg at 8:20 p.m., with a brief stop at York.[13][14]
In 1873, the NCRY opened its Charles Street Station, and the Union Railroad of Baltimore opened a new line connecting to the station. This 9.62 mile (15.48 km) railroad gave the NCRY access to the Canton area, where it established a shipping terminal on the Inner Harbor. The line also completed a crucial link in central Baltimore between the NCRY, the PW&B and the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad. In February 1882 the Northern Central acquired the Union Railroad.[15] The Union Railroad link enabled the PRR to operate through trains between Philadelphia, Baltimore and Washington, D.C. Today this PRR system is part of the Northeast Corridor.
In 1898, the NCRY built the Millersburg Passenger Rail Station.[16]
20th century


The Pennsylvania Railroad's Northern Central line was double-tracked and equipped with block signals between Baltimore and Harrisburg by World War I. The line carried heavy passenger and freight traffic until the 1950s. On-line freight included flour, paper, milk, farm products, coal, and less-than-carload shipments between such settlements as White Hall, Parkton, Bentley Springs, Lutherville, and the city of Baltimore.
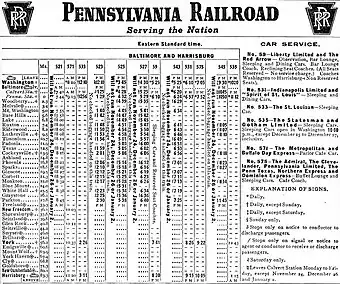
Local commuter service, referred to as the "Parkton local", operated over the 28 miles (45 km) between Calvert Station in Baltimore and Parkton, Maryland. Long distance passenger trains equipped with sleepers and dining cars were also operated by the PRR over the line from Baltimore Penn Station to Buffalo, Toronto, Chicago, and St. Louis, with through-sleeping car service as far as Houston.[17] Much of the PRR through freight service to points west was routed via its electrified Port Road Branch along the Susquehanna River to Enola Yard in Harrisburg, however, instead of the Northern Central line.
With the decline in rail passenger and freight service in the 1950s, accelerated by the completion of Interstate 83, the "Parkton locals" were dropped in 1959 and the line was reduced from double-track to single-track. The Red Arrow The Washington, D.C., section to Detroit ended service in 1960.[18]
Some long-distance trains, such as the General (to Chicago), the Penn Texas (to St. Louis) and the Buffalo Day Express (to Buffalo), continued to operate until the late 1960s. In 1972, when Hurricane Agnes caused bridge damage and washouts along the line, all operations ceased. One of the oldest rail lines in the country at the time, it had run for a total of 134 years.
Penn Central and aftermath
In 1968, the PRR merged with the New York Central railroad, to form the Penn Central (PC). A spur of the Spirit of St. Louis, which later became the National Limited, ran along the Washington, D.C.-Harrisburg corridor until 1979.[19]
After sustaining damage along the main line due to Hurricane Agnes, the Penn Central petitioned the Interstate Commerce Commission to allow it to abandon the railroad south of York. The section of the line between York and New Freedom was acquired by the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation in June 1973.[20]
The Penn Central filed for bankruptcy protection in 1970.[21]: 233–234 It operated under court supervision until 1976, when its lines were transferred to Conrail under the Railroad Revitalization and Regulatory Reform Act.[22]: 4–5
Legacy today
A 13-mile segment of the former Northern Central Railway between Baltimore and Cockeysville continued to be operated by Conrail successor Norfolk Southern until 2005. Rebuilt and electrified in the late 1980s for the now double-tracked Baltimore Light Rail system, NS local freights were permitted to operate over the Light Rail line during late-night hours when no passenger trains were running by agreement with the Maryland Transit Administration.
Rail trails

The Maryland Department of Natural Resources converted the corridor north of Cockeysville into a trail which opened to the public in 1984. Officially known as the Torrey C. Brown Rail Trail, the trail's history is reflected in its more popular name, Northern Central Railroad (NCR) Trail. The trail continues into Pennsylvania, where it becomes the York County Heritage Rail Trail.[23]
In York County, the Bridge 182+42, Bridge 5+92, Bridge 634, South Road Bridge, Howard Tunnel, and New Freedom Railroad Station are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.[24]
Heritage railway
A heritage railway operated on the NCRY line as a dinner train in the mid-1990s to the early 2000s.
In 2013, the Northern Central Railway of York (then known as Steam Into History) began operations between New Freedom and Hanover Junction, operating a replica of a Civil War-era 4-4-0 steam locomotive.[25]
See also
Gallery
 Northern Central Railway 17 York
Northern Central Railway 17 York
References
- 1 2 Henry Varnum Poor (1900). Poor's Manual of the Railroads of the United States. Vol. 33. New York: H.V. & H.W. Poor. p. 703.
- ↑ Gunnarsson, Robert L. (1991). The Story of the Northern Central Railway: From Baltimore to Lake Ontario. Sykesville, MD: Greenberg Pub. Co., p. 13.
- ↑ Gunnarsson, Robert L. (1991). The Story of the Northern Central Railway: From Baltimore to Lake Ontario. Sykesville, MD: Greenberg Pub. Co., p. 13.
- ↑ Gunnarsson, Robert L. (1991). The Story of the Northern Central Railway: From Baltimore to Lake Ontario. Sykesville, MD: Greenberg Pub. Co., p. 15.
- ↑ Gunnarsson, Robert L. (1991). The Story of the Northern Central Railway: From Baltimore to Lake Ontario. Sykesville, MD: Greenberg Pub. Co., p. 19.
- ↑ White Jr., John H. (1980). A history of the American locomotive: its development, 1830-1880. Mineola, NY: Courier Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-23818-0.
- 1 2 Harwood Jr., Herbert H. (1990). Royal Blue Line. Sykesville, MD: Greenberg Publishing. ISBN 0-89778-155-4.
- ↑ Road to Lincoln's end ran through Baltimore, Jonathan M. Pitts, The Baltimore Sun
- ↑ The Thwarted Plot to Kill Lincoln on the Streets of Baltimore, Boundary Stones, WETA's Washington DC History Blog
- ↑ The Unsuccessful Plot to Kill Abraham Lincoln, Daniel Stashower, Smithsonian Magazine
- ↑ The Baltimore Plot, The First Conspiracy to Assassinate Abraham Lincoln, Michael J. Kline, Chapter 16, An Unexpected Arrival, pg. 258-259
- 1 2 Toomey, Daniel Carroll (1983). The Civil War in Maryland. Baltimore, MD: Toomey Press. ISBN 0-9612670-0-3.
- ↑ Goodrich, Thomas (2005). The Darkest Dawn. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University. p. 195. ISBN 0-253-32599-4.
- ↑ Hansen, Peter A. (February 2009). "The funeral train, 1865". Trains. Kalmbach. 69 (2): 34–37. ISSN 0041-0934.
- ↑ Hall, Clayton C., ed. (1912). Baltimore: Its History and Its People. Vol. 1. Lewis Historical Pub. Co. pp. 487–8.
- ↑ "National Historic Landmarks & National Register of Historic Places in Pennsylvania". CRGIS: Cultural Resources Geographic Information System. Archived from the original (Searchable database) on 2012-07-22. Retrieved 2011-11-12. Note: This includes Elizabeth Roman (July 2001). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form: Millersburg Passenger Rail Station" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ More broadly, see also Pennsylvania Railroad timetable, January 18, 1954 http://streamlinermemories.info/PRR/PRR54-1TT.pdf
- ↑ Pennsylvania Railroad timetable, January 18, 1954, Tables 36, 37 especially http://streamlinermemories.info/PRR/PRR54-1TT.pdf
- ↑ Washington-Baltimore-Harrisburg section eliminated in Amtrak's first timetable, May 1, 1971 http://www.timetables.org/browse/?group=19710501&st=0001
- ↑ Northern Central Railcar Association, New Freedom, PA. The northern portion of the old main line, running from York, PA to Sunbury, is still in use today, albeit with some alterations in the vicinity of Harrisburg. "Northern Central History" Accessed 2012-05-26.
- ↑ Stover, John F. (1997). American Railroads (2nd ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-77658-3.
- ↑ United States Railway Association (USRA), Washington, DC. "The Conveyance Process: A Supplement to the Final Report of the United States Railway Association." December 1986.
- ↑ "Blazing a Trail". Chesapeake Life Magazine. Alter Communications. July 2002. Archived from the original on 2007-11-25. Retrieved 2008-01-27.
Passenger service along the NCR had been curtailed in 1959, but freight service continued until 1972, when Hurricane Agnes swept through the area, destroying much of the track, as well as bridges and culverts.
- ↑ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ↑ "Steam Into History Aboard the Northern Central Railway". New Freedom, PA: Steam Into History, Inc. Retrieved 2015-02-09.
External links
- NCRY Annual reports, 1865-1866 (11th-12th), 1869-1910 (15th-56th)
- PRR Corporate History
- PRR Chronology, Chris Baer Archived 2008-12-02 at the Wayback Machine
- Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) No. MD-38, "North Central Railroad, Baltimore Freight House", 7 photos, 3 data pages, 1 photo caption page