| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
165 seats in the National Council of Austria 83 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Austria |
|---|
 |
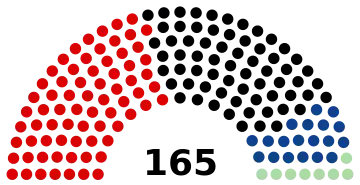
Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 9 November 1930.[1] The Social Democratic Workers' Party emerged as the largest faction in the National Council, with 72 of the 165 seats, but the Christian Social Party (with 66 seats) formed a new coalition government with Otto Ender as Chancellor. Voter turnout was 90%.[2]
This was the last parliamentary election to take place in the period of the First Austrian Republic. A series of socialist-fascist clashes in 1934 was followed by the authoritarian Federal State of Austria and eventual Anschluss in 1938 with Nazi Germany.
Results
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Social Democratic Workers' Party | 1,517,146 | 41.14 | 72 | +1 | |
| Christian Social Party | 1,314,956 | 35.65 | 66 | – | |
| National Economy Bloc (GDVP–LB) | 428,255 | 11.61 | 19 | – | |
| Homeland Bloc | 227,401 | 6.17 | 8 | New | |
| German National Socialist Workers' Party | 111,627 | 3.03 | 0 | 0 | |
| Landbund for Austria | 43,689 | 1.18 | 0 | – | |
| Communist Party of Austria | 20,951 | 0.57 | 0 | 0 | |
| Austrian People's Party | 14,980 | 0.41 | 0 | New | |
| Democratic Centre Party | 6,719 | 0.18 | 0 | New | |
| Jewish List | 2,133 | 0.06 | 0 | New | |
| Kaiser Loyalty People's Party | 157 | 0.00 | 0 | New | |
| National Democratic Association | 54 | 0.00 | 0 | New | |
| Total | 3,688,068 | 100.00 | 165 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 3,688,068 | 99.24 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 28,098 | 0.76 | |||
| Total votes | 3,716,166 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 4,121,282 | 90.17 | |||
| Source: Nohlen & Stöver | |||||
Results by province
| Province | Votes | SDAPÖ | CS | GDVP–LB | HB | DNSAP | LB | KPÖ | ÖVP | DCP | JL | KLPP | NDA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |||||
| Vienna | 1,192,672 | 58.98 | 23.72 | 10.43 | 2.21 | 2.31 | 0 | 0.89 | 0.71 | 0.56 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0 | |||
| Lower Austria | 818,302 | 35.63 | 44.13 | 8.58 | 6.62 | 4.2 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Upper Austria | 479,285 | 28.37 | 45.42 | 7.29 | 8.29 | 2.41 | 7.71 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Salzburg | 123,152 | 29.96 | 41.52 | 12.69 | 5.73 | 3.69 | 5.49 | 0.61 | 0.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Tyrol | 176,843 | 21.99 | 54.97 | 12.34 | 9.28 | 1.24 | 0 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Voralberg | 77,516 | 20.92 | 56.79 | 20.94 | 0 | 1.14 | 0 | 0.22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Styria | 510,164 | 34.38 | 32.52 | 16.51 | 12.48 | 3.42 | 0 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Carinthia | 175,640 | 38.73 | 22.54 | 22.38 | 8.47 | 6.90 | 0 | 0.66 | 0.32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Burgenland | 134,494 | 37.75 | 41.23 | 16.01 | 3.80 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 3,688,068 | 41.14 | 35.65 | 11.61 | 6.17 | 3.03 | 1.18 | 0.57 | 0.41 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| Source: Statistische Nachrichten : Sonderheft. Die Nationalratswahlen vom 9. November 1930, 12.[3] | ||||||||||||||||
References
- ↑ Nohlen, Dieter; Stöver, Philip (31 May 2010). Elections in Europe: A data handbook. Nomos Verlagsgesellschaft. p. 196. ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7.
- ↑ Nohlen & Stöver, p213
- ↑ "Sonderheft der Statistischen Nachrichten 9 November 1930" (PDF). Bundesministerium für Inneres. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 July 2022.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
_1919_WIZ_C._Pietzner.png.webp)




