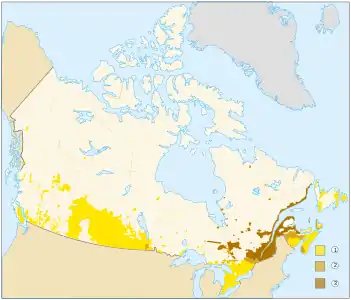
Approximately 98 percent of Canadians can speak either or both English and French:[1]
English – 56.9%
English and French – 16.1%
French – 21.3%
Sparsely populated area ( < 0.4 persons per km2)
English Canada comprises that part of the population within Canada, whether of British origin or otherwise, that speaks English.
The term English Canada is also used for any of the following:
- Describing all the provinces of Canada that have an anglophone majority. This is every province except Quebec. When used in this way, English Canada is often referred to as the "ROC" (rest of Canada). This type of usage excludes French-speaking areas in English-majority provinces like the East and North of New Brunswick, Northern and Eastern Ontario, Saint-Boniface and the few small pockets of French localities in Western Canada. It also excludes areas where a third language is widely spoken, such as German, Russian or First Nations languages.
- When discussing the culture, values and lifestyles of English-speaking Canadians as opposed to those of French-speaking Canadians. This usage is most often employed to compare English- and French-language literature, media, art and institutions.
- When discussing the Two Solitudes, in which English Canada (i.e. the anglophones of Canada) is one of two founding nations of Canada along with French Canada (i.e. the francophones of Canada), and in which these two societies share a country but rarely communicate with each other.[2] The term was often used during the conscription crisis.[3] The population whose native language is neither English nor French are often included into one of the two official languages or are classified as allophones.[4]
- English Canadians, in some contexts, refers to Canadians who have origins in England, in contrast to French Canadians, Scottish Canadians, Irish Canadians, etc.
See also
References
- ↑ "2006 Census: The Evolving Linguistic Portrait, 2006 Census: Highlights". Statistics Canada, Dated 2006. Archived from the original on April 29, 2011. Retrieved October 12, 2010.
- ↑ Forsey, Eugene A. (1962). "Canada: Two Nations or One?". The Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science. 28 (4): 485–501. doi:10.2307/139291. ISSN 0315-4890. JSTOR 139291.
- ↑ "Musée McCord Museum - To Which Voice Will He Listen?". collections.musee-mccord.qc.ca. Retrieved 2019-07-29.
- ↑ "Allophone". parli.ca. Toronto: Campbell Strategies Inc. 8 May 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.