| Albanian revolt of 1432–1436 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Ottoman Wars in Europe | |||||||
 A map of the military activities during the Albanian Revolt of 1432–6 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Albanian rebels |
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Gjergj Arianiti Andrea Thopia Depë Zenebishi † Nicholas Dukagjini |
Sinan Pasha Turahan Bey Ali Bey Ishak Bey | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| unknown | unknown | ||||||
The Albanian revolt of 1432–1436 was a series of conflicts between Albanian rebels and the Ottoman Empire during the early period of Ottoman rule in the region. Prompted by the replacement of large parts of the local nobility with Ottoman landowners, centralized governance, and the Ottoman taxation system, the population and the nobles, led principally by Gjergj Arianiti, revolted against the Ottomans.
During the early phases of the revolt, many land (timar) holders were killed or expelled. As it spread, the nobles, whose holdings had been annexed by the Ottomans returned to join the revolt and attempts to form alliances with the Holy Roman Empire were initiated. While the leaders of the revolt were successful in defeating successive Ottoman campaigns, they failed to capture many important towns of the sanjak of Albania. Protracted sieges like that of Gjirokastër, capital of the sanjak, gave the Ottoman army time to assemble large forces from other parts of the empire and to subdue the main revolt by the end of 1436. Ottoman forces conducted a number of massacres in the aftermath of the revolt.
After the revolt had largely been suppressed, those who accepted Ottoman suzerainty were initially allowed to retain their holdings and partial autonomy. Many timars were also granted to local Albanians holding high posts of the administration, especially during the rule of Yakup Bey Muzaka and Skanderbeg. Throughout the pacification process, various primarily rural areas were still in revolt and new rebellions erupted, like that of Theodor Corona Musachi in 1437. As the empire further extended its area of rule in the Balkans, centralization attempts and the replacement of local timar holders with Ottoman landowners resumed. These policies would lead in part to the formation of the League of Lezhë under Skanderbeg in 1444, and a new era in the Ottoman–Albanian wars.
Background
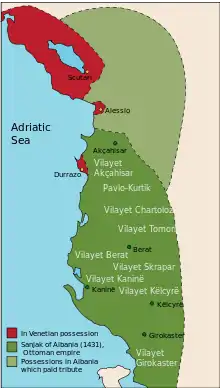
Gradually in the late 14th and early 15th century the Ottoman Empire defeated local Albanian principalities, forming the sanjak of Albania as an administrative division of the empire. As part of the Timar system the local feudal lords were largely replaced with Ottomans from Anatolia.[1] The cadastral survey (defter) of 1431–1432 indicates that about 75% to 80% of the timars were granted to Ottoman Muslim spahis (feudal cavalry), while the remainder and especially remote areas, which were not under full Ottoman control, were granted to Albanian spahis, both Christian and Muslim. The replacement of the existing nobility with the timar system led to conflicts, as a result of which many rural areas were not under complete Ottoman rule.[1]
Under the previous taxation code, farmers were required to pay a tenth of their seasonal agricultural output, 1 ducat and 4 groshe (two-ninths of a ducat) to their lords.[2] The Ottoman system aimed towards revenue increase to support military expenses, thus new taxes were imposed and existing ones were altered. In addition to 1/10 of agrarian production Muslim convert families were required to pay 22 akçe (~0.6 ducats) to the timar holders, while non-Muslim families had to pay 25 akçe (~0.7 ducats).[2][3] Both groups were subject to additional taxes including the avarız, an annual cash tax that affected households registered to the cadasters. Non-Muslims were also required to pay 45 akçe (~1.3 ducats) as part of the jizya and had to supply regularly the Ottoman state with young recruits in accordance with the devşirme, which required the enlistment of young males in the Ottoman army and their conversion to Islam.[2][3]
Consequently, the changes in property rights, relations between feudal lords and peasants, the taxation system and the enactment of devşirme resulted in further resistance. As changes affecting both nobles and peasants were principally implemented through registration in the cadastral survey, many families tried to avoid becoming registered in the 1431–2 survey and took refugee in mountainous areas, while the nobility prepared for armed conflict.[4]
Revolt

The revolt began in 1432 when Andrea Thopia defeated a small Ottoman force in central Albania.[1] His victory encouraged the other leaders and the revolt spread throughout Albania. Later that year the Ottomans lost control of the central seaport of Vlorë.[5] Gjergj Arianiti, who was living at the Ottoman court as a hostage, was called by rebels to lead the revolt in his family's domains. In response, he fled from Edirne and returned to Albania.[6] In the winter of 1432, Sultan Murat II gathered around 10,000 troops under Ali Bey, who marched along the Via Egnatia and reached the central valley of Shkumbin, where he was ambushed and defeated by forces under Gjergj Arianiti.[7] His victory prompted the Albanians in the area of Gjirokastër to call upon Depë Zenebishi, who had settled in his estates in Corfu after the Ottoman conquest of the Principality of Gjirokastër, to lead the rebels in the south.[8] After spreading the revolt in nearby areas including Këlcyrë, Zagorie and Pogon his forces besieged the southern city of Gjirokastër, capital of the sanjak of Albania.[9] At nearby Këlcyrë the rebels captured the castle, but the concurrent siege of Gjirokastër was prolonged and Turahan Bey attacked and defeated the troops that surrounded the city in early 1433.[7][10] Zenebishi himself was captured and executed.[11]
In the summer of 1433 an army led by Sinan Pasha, beylerbey of Rumelia, pillaged the areas of Kanina and Yannina and moved northwards, where they subdued the rebels in the domains of Gjon Kastrioti, who was reduced again to vassal status, while his son Skanderbeg, who was also called to join the revolt, remained in Ottoman service in Anatolia.[1][12] In August 1433, the senate of Venice convened to evaluate the situation and deemed that the revolt posed a threat to the Venetian territories in the region too. However, by the end of October they re-evaluated the crisis and rejected the deployment of a war galley to the Venetian colonies.[12] In northern Albania Nicholas Dukagjini captured territories of the pre-Ottoman Principality of Dukagjini and besieged and captured Dagnum. Dukagjini then tried to ally himself with Venice by offering to accept Venetian suzerainty and granting them control of Dagnum. However, Venice refused any kind of involvement in his plan and the revolt in general. Dukagjini was not aware that Hasan Bey, the Ottoman governor of Dagnum, had requested Venetian assistance after his defeat. As Venice did not want to provoke Ottoman hostility, the captain of Shkodër (Scutari) was ordered to assist Hasan Bey in recapturing Dagnum. Arms were subsequently sent to the garrison of Lezhë (Alessio) and by 1435 the fort had been returned to Ottoman control.[1][6] In central Albania, Andrea Thopia unsuccessfully besieged the castle of Krujë, while in the region of Vlorë the siege of the fort of Kaninë began. Vlorë was lost to the rebels as early as May 1432, but must have been recovered by May 1434 as contemporary Venetian documents mention an Ottoman official (subaşi) stationed there at that time.[13]
Another Ottoman army was assembled in Manastir in the summer of 1434.[11] Again under the command of Sinan Pasha, this Ottoman expedition was defeated by Gjergj Arianiti in south-central Albania in August 1434. After his defeat, all beys of the territories bordering Albania were ordered to gather their forces and attack the rebels. In December 1434 Ishak Bey, sanjakbey of Üsküb marched into south-central Albania but was defeated by Gjergj Arianiti. Contemporary sources from the senate of Ragusa mention that many Ottoman soldiers were captured, while Ishak Bey escaped with a small group.[11] In April 1435, Arianiti defeated another Ottoman campaign and hostilities virtually ceased until the beginning of 1436, as Murat II's military efforts were focused against Ibrahim of Karaman in Anatolia.[11][14] At the end of 1435 reports of the Ragusan senate assessed the situation as calm and noted that the belligerents had retreated to their respective territories.[14]
During the revolt many attempts were made to form an anti-Ottoman coalition including the Holy Roman Empire. Pope Eugene IV requested troops to be sent to assist the revolt and tried to gather funds.[15] In 1435, Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund of Luxemburg sent Fruzhin, a Bulgarian nobleman, and in early 1436 Daud, a pretender to the Ottoman throne, to negotiate the possibility of a coalition with the rebels.[16] However, by mid-1436 a large force under Turahan Bey had been assembled. Despite the military victories the rebel leaders acted autonomously without a central leadership, the lack of which contributed greatly to their final defeat.[16] Turahan's forces eventually subdued the revolt and marched through Albania, committing widespread massacres of civilians.[1]
Aftermath

In order to stabilize Ottoman authority, Murat II appointed native Albanians like Yakup Bey Muzaka and Skanderbeg to high positions within the sanjak of Albania. The nobles who accepted Ottoman overlordship were granted their pre-Ottoman holdings and border estates as well as a degree of autonomy, while others were exiled or continued warring. In 1436–37, rebels were active in the regions of Gjirokastër and Vlorë and Theodor Corona Musachi led a revolt in the region of Berat.[16][17] As many rebels used Venetian territories like Shkodër and Parga as bases to launch raids into Ottoman territory, representatives of Mehmed II asked the Venetians to outlaw their activity in October 1436.[16]
As Ottoman rule in the Balkans expanded, Albanian timar holders and officials were once again replaced with Anatolian ones.[18] The status quo ante bellum policies of the Ottomans gradually led to the formation of the League of Lezhë under Skanderbeg in 1444 and the beginning of a new era in the Ottoman-Albanian wars.[19]
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Fine 1994, p. 535
- 1 2 3 Islami et al. 2002, p. 331
- 1 2 Pamuk 2000, p. 46
- ↑ Islami et al. 2002, p. 333
- ↑ İnalcık 1954, p. 12
- 1 2 Buda 2002, p. 246
- 1 2 Islami et al. 2002, p. 336
- ↑ Imber 1990, p. 114
- ↑ Pulaha 1967, p. 39
- ↑ Imber 2006, p. 27
- 1 2 3 4 Islami et al. 2002, p. 337
- 1 2 Imber 1990, p. 115
- ↑ Shuteriqi 2012, pp. 129–130
- 1 2 Biçoku 1970, pp. 142
- ↑ Buda 2002, p. 247
- 1 2 3 4 Islami et al. 2002, p. 338
- ↑ Frashëri 1964, p. 65
- ↑ Islami et al. 2002, p. 339
- ↑ Islami et al. 2002, p. 340
References
- Biçoku, Kasem (1970). "Mbi disa çështje lidhur me jetën dhe veprimtarinë e Gjergj Kastriotit-Skënderbeut para vitit 1443". Studime Historike (in Albanian). University of Tirana. 7.
- Buda, Aleks (2002). Shkrime historike (in Albanian). Toena. ISBN 978-99927-1-651-9.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (15 June 1994). The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-08260-5. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- Frashëri, Kristo (1964). The history of Albania: a brief survey.
- Imber, Colin (1990). The Ottoman Empire, 1300–1481. Isis Press. ISBN 978-975-428-015-9.
- Imber, Colin (2006). The Crusade of Varna, 1443–45. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-0144-9. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- İnalcık, Halil (1954). Hicr ̂ı835 tarihli sûret-i defter-i sancak-i Arvanid (in Turkish). Türk Tarih Kurumu Yayınlarından.
- Islami, Selim; Anamali, Skënder; Korkuti, Muzafer; Prendi, Frano; Shukriu, Edi (2002). Kristaq Prifti, Muzafer Korkuti (ed.). Historia e popullit shqiptar (in Albanian). Botimet Toena. ISBN 9789992716229.
- Pamuk, Şevket (9 March 2000). A Monetary History of the Ottoman Empire. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-44197-1. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- Pulaha, Sami (1967). "Sur les causes des insurrections des annees '30 du XVe siecle en Albanie". Studia Albanica (in French). 4.
- Shuteriqi, Dhimitër (2012). Zana Prela (ed.). Aranitët: Historia-Gjenealogjia-Zotërimet (in Albanian). Toena. ISBN 978-99943-1-729-5.