 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 205 seats in the Pratinidhi Sabha 103 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 65.79%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
|
|
General elections were held in Nepal on 3 and 17 May 1999. The Nepali Congress emerged as the largest party, gaining 28 seats, while the Communist Party of Nepal (Unified Marxist-Leninist) (CPN–UML) lost 17.
Background
The previous elections o the Pratinidhi Sabha in 1994 had seen the CPN–UML emerge victorious and the first-ever popularly elected communist government formed. Yet by 1999, infighting, such as the departure of the Bam Dev Gautam and C.P. Mainali led splinter group, had got in the way of policy decisions and put certain people off voting for the party.
Results
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |
| Nepali Congress | 3,214,786 | 37.17 | 111 | |
| Communist Party of Nepal (Unified Marxist–Leninist) | 2,734,568 | 31.61 | 71 | |
| Rastriya Prajatantra Party | 902,328 | 10.43 | 11 | |
| Communist Party of Nepal (Marxist–Leninist) | 567,760 | 6.56 | 0 | |
| Rastriya Prajatantra Party (Chand) | 295,812 | 3.42 | 0 | |
| Nepal Sadbhavana Party | 278,435 | 3.22 | 5 | |
| Rastriya Janamorcha | 121,426 | 1.40 | 5 | |
| Rastriya Janamukti Party | 94,860 | 1.10 | 0 | |
| United People's Front of Nepal | 74,669 | 0.86 | 1 | |
| Nepal Workers Peasants Party | 48,685 | 0.56 | 1 | |
| Nepali Janata Dal | 11,748 | 0.14 | 0 | |
| Janamukti Party Nepal | 9,616 | 0.11 | 0 | |
| Communist Party of Nepal (Marxist) | 8,101 | 0.09 | 0 | |
| Nepal Dalit Shramik Morcha | 6,852 | 0.08 | 0 | |
| Hariyali Nepal Party | 6,420 | 0.07 | 0 | |
| Communist Party of Nepal (United) | 5,111 | 0.06 | 0 | |
| Nepali Janta Party Rastriya Sambriddhibad | 4,927 | 0.06 | 0 | |
| Rastriya Janata Parishad | 3,799 | 0.04 | 0 | |
| Jana Congress | 1,992 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| Shivsena Nepal | 1,756 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| Nepal Socialist Party | 950 | 0.01 | 0 | |
| Bahujan Samaj Party of Nepal | 835 | 0.01 | 0 | |
| Nepal Praja Parishad | 817 | 0.01 | 0 | |
| Samyukta Prajatantra Party Nepal | 297 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Nepal Samyabadi Party (MLM) | 190 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Save the Nation Movement | 170 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Pragati Upayogoto, Nepal | 155 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Nepal Janabhavana Party | 120 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Rastrabadi Janata Party | 105 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Social Democratic Party | 97 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Samajbadi Garib Party | 86 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Nepal Janahit Party | 68 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Nepal Suraksha Party | 56 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Nepal Rastrabadi Dal | 55 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Mechi-Mahakali Jana Samanwaya Dal | 35 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Prajatantric Nepali Janata Party | 18 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Prajatantra Sagarmatha Dal | 11 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Liberal Democratic Party | 10 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Nepal Rastriya Aketa Party | 8 | 0.00 | 0 | |
| Independents | 251,930 | 2.91 | 0 | |
| Total | 8,649,664 | 100.00 | 205 | |
| Valid votes | 8,649,664 | 97.25 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 244,902 | 2.75 | ||
| Total votes | 8,894,566 | 100.00 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 13,518,839 | 65.79 | ||
| Source: Nepal Research | ||||
Distribution of seats
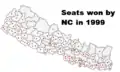 Seats won by Nepali Congress
Seats won by Nepali Congress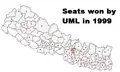 Seats won by CPN(UML)
Seats won by CPN(UML) Seats won by Rashtriya Prajatantra Party
Seats won by Rashtriya Prajatantra Party
Aftermath
Following the elections, the various parties found it difficult to cooperate and finalise a policy of the Maoist rebels, culminating in the 2002 dissolution of the parliament by King Gyanendra.
Following the 2006 Loktantra Andolan, in which all of the parties successful in 1999, except the royalist Rashtriya Prajatantra Party participated in the Seven Party Alliance, the House was reinstated in 2006.
See also
References
- ↑ "Previous Election Facts and Figures". 2008-10-21. Archived from the original on 2008-10-21. Retrieved 2021-01-04.


.png.webp)