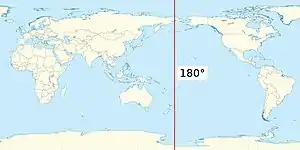

The 180th meridian or antimeridian[1] is the meridian 180° both east and west of the prime meridian in a geographical coordinate system. The longitude at this line can be given as either east or west.
On Earth, the prime and 180th meridians form a great circle that divides the planet into the Western and Eastern Hemispheres. The antimeridian passes mostly through the open waters of the Pacific Ocean but also runs across land in Russia, Fiji, and Antarctica. An important function of this meridian is its use as the basis for the International Date Line, which snakes around national borders to maintain date consistency within the territories of Russia, the United States, Kiribati, Fiji and New Zealand.
Starting at the North Pole of the Earth and heading south to the South Pole, the 180th meridian passes through:
The meridian also passes between (but not particularly close to):
- through the Aleutian Island chain of US territory
- the Gilbert Islands and the Phoenix Islands of Kiribati
- North Island and the Kermadec Islands of New Zealand
- the Bounty Islands and the Chatham Islands, also of New Zealand
The only places where roads cross this meridian are in Fiji and Russia. Fiji has several such roads and some buildings very close to it. Russia has three roads in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug.
Software representation problems
Many geographic software libraries or data formats project the world to a rectangle; very often this rectangle is split exactly at the 180th meridian. This often makes it non-trivial to do simple tasks (like representing an area, or a line) over the 180th meridian. Some examples:
- The GeoJSON specification strongly suggests splitting geometries so that neither of their parts cross the antimeridian.[2]
- In OpenStreetMap, areas (like the boundary of Russia) are split at the 180th meridian.
See also
Notes
- ↑ The word antimeridian can also mean the meridian opposite to any given meridian. E.g. 20° west is the antimeridian of 160° east.
- ↑ Butler, H.; Daly, M.; Doyle, A.; Gillies, S.; Hagen, S.; Schaub, T. (2016). RFC 7946 – The GeoJSON Format. sec. 3.1.9. doi:10.17487/RFC7946. RFC 7946.



.png.webp)